Cell Signaling Flashcards
What are the 3 stages of cell signaling?
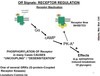
1. Reception
(receptor binds to ligands)
2. Transduction
(receptor protein changes and activates intracellular molecs aka 2nd messengers)
3. Cell Response
(cell responds to signal)

What is another name for G-protein coupled receptors?
7-pass transmembrane receptors

What do the alpha and gamma subunits do for GPCRs?
anchored to cell membrane and keep G-protein next to the receptor
What does a GPCR bind to when it’s inactive?
GDP

What happens to GPCR when its alpha subunit is bound to GTP?
alpha subunit seperates from beta and gamma subunits and alpha subunit is then free to interact with other proteins

Gq
- Bound to adenylate cyclase but inhibits it, causing (-) feedback to Gs
**negative feedback is important with helping to inactivate cells
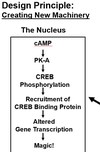
Gi
- stimulates adenylate cyclase
- Activated adenylate cyclase takes ATP and removes 2 phosphate molecs transforming it into cAMP
- regulated subunit then dissociates from catalytic subunit

Gs
Single pass transmembrane proteins (meaning they have 1 transmembrane segment and intracellular end has intrinsic cellular activity)
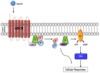
Enzyme coupled receptor
What are the 2 parts of enzyme coupled receptors?
- Receptor
- Enzyme (protein kinase that phosphorylates receptor)
What are the 3 main types of ECRs?
- Tyrosine Kinase associated Receptor
- Receptor Tyrosine Kinase
- Receptor Ser/Thr Kinase
- most common enzyme coupled receptor
- has many subfams
- can’t phosphorylate its own Tyr side chains
receptor tyrosine kinases
- Works similarly to receptor Tyr Kinase
- no intrinsic enzyme activity
- receptor binds to ligand
- Cytoplasmic Tyr Kin
- Phosphorylates target proteins to relay signal
Tyr Kinase associated Receptor
Type ii - Ser/Thr kinase domains receptor phosphorylates and activates type i receptor which recruits and phosphorylates various target proteins to relay signal
Receptor Ser/Thr Kinase

Ion Channel Receptor
Activates a receptor that has access to 2 signal pathways. However, the biased ligand only activates 1 of the pathways
Biased ligands