cell pathology practical Flashcards
(43 cards)
what is the screening test for bowl cancer *
check stool for blood using biochemical or immunological methods
do sigmoidoscopy for bowel polyps because most polyps that become cancer are at the bottom of the colon - remove the polyps so the cancer cant develop, or if already cancer - detect it early
possible reasons for blood in stool
GI bleeding from oesophagus, small/large bowel, stomach because of ulcers/haemorrhoids
inflammatroy bowel disease eg chron’s
what do you do if a screening test is positive *
do full colonoscopy
what are polyps *
a mass growth form a tissue wall
any part of body that is hollow can develop a polyp
adenomas are polyps with dysplasia of the glandular epithelium
what do you do if you find polyp in colonoscopy *
snip it and send it to a histopathologist
what would the report on this polyp be *

high nucleocytoplasmic ratio - polyp is darker than the underlying tissue - shows it is an adenoma (dysplastci tissue)
size of polyp - bigger more likely to be malignant >5cm is high risk
low grade dysplasia - still architecturally correct
is it cancer already
has it invaded
is it completely excised - yes you can see normal mucosa at base
is it a tibular or villus adenoma
consequence of polyp is in the mucosa *
definitely invasive - have to go to surgery
what can be seen from this image - polyp *

it has gone through the muscularis externa - see because muscle either side of it but not below
what is stage *
how far the tumour has spread
either through nodes and vessels, or into the muscle
what lymph system would colon cancer drain into *
mysenteric nodes, then thoracic duct, then superior vena carvae
how would colon cancer spread in the blood 8
too the liver
how would colon cancer spread locally *
through submucosa to muscle to peritoneum
describe the TNM staging for colon cancer *
T1 spread into mucosa
T2 into muscle
T3 through muscle
T4 reach peritoneum

what is the TNM staging for this tumour *

T3 - because no muscle below it - so gone through the muscle
what is Duke’s staining for colon cancer *

through the muscularis externa or not
a is not through muscularis externa
b is
this tumour is b
what is grade *
how well differentiated the tumour is - hwo much do teh cells look like the normal tissue that they have come from
well differentiated means look a lot like original tissue and is good prognostically
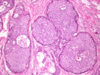
how do adenocarcinoma’s change the structure of the cells *
they form a ball of glandular epithelial cells that secrete mucin
where can you get adenocarcinoma
colon
adrenal cortex
lung
pancreas
fallopian tubes
prostate
breast
bowel
stomach
oesophagus
uterus
what is teh grade of this adenocarcinoma *

well differentiated
what can be seen on this mammogram *

dense pyramidal area
how would a person present with breast cancer *
lump on breast
screening program - mammogram - imaging based system
what would make a lump less likely to be cancer *
if it could be moved - means not attached to muscles/skin (although inflammatory lumps can become attached)
if there are not enlarged lymph nodes
no distant metastises eg liver
what lymph nodes would you feel to see if there was an enlargement *
axillary if cancer was lateral (most breast cancers are)
medial drain into internal mammary chain behind below sternum and ribs - harder to palpate
what would you do if you suspected a lump was cancer *
send for a clinically indicated mammogram
biopsy