Cell Organelles Flashcards
State the function of the Nucleolus

The location of ribosome/RNA sythesis
State the function of the Nuclear Pores

Part of Nucleus. It allows substances/proteins and mRNA to get into the nucleus
State the function of the Nuclear Envelope

Part of Nucleus. Acts as a membrane/skin for the nucleus
What is Chromatin?
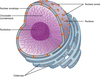
Part of Nucleus. Coils of DNA that codes for cells/proteins
State the function of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Name it’s two main features and their function.

Found very close/attached to to the nucleus. Ribosomes attached to rER make it rough. The ribosomes build up amino acid chains, then get folded into a 3D shape in the rER to be pinched off in vesicles.
Cisternae- interconnected fluid filled sacs formed from double membranes
Lumen- where proteins are collected and transformed to glycoproteins to be taken off in vesicles

What are ribosomes and what are its two main structural features and their functions?
Protein builders found in the cytoplasm or attached to rER. Made of 2 parts:
Small Subunit - reads the RNA Large
Subunit - joins amino acids to make polypeptide chains
State the function of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum

Found in the cytoplasm. An extensive network of membranes with a tube like structure, where lipids and steroids are synthesised.

State the function of the Golgi Body/Complex

Stacks of flattened membrane bound sacs formed by the fusion of vesicles taken from the rER. It is involved in protein trafficking- where material from vesicles are modified and packed into more vesicles where they then bud off.
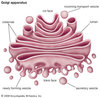
What is a Vesicle?
A small membrane bound sac that stores and transports substances throughout the cell.
State the function of Lysosomes

Found in eukaryotic cells.They’re specialised transport vesicles that harbour enzymes that have the ability to digest food or even the cell when it dies. The proteins/enzymes that do this are made in the rER, taken to the Golgi Complex, and transformed, then the lysosome pinches off with it.

State the function of Centrioles
Made of microtubules. A pair present just outside the nucleus at right angles. Helps in cell division (mitosis & meiosis)- they form spindle during cell division to seperate chromosomes in the nucleus at each pole.

State the function of the Cilia & Flagella

Allow things to move over/around the cell or the cell itself to move.

State the functiom of the Cell Membrane
(see Plasma Membrane deck for more information)
The semi-permeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm controls whart passes through it, protects and it and maintains the internal environment.
Phospholipids- make basic membrane structure
Proteins- found in holes to help substances move
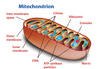
State the function of the Mitochondrian
Name its 5 main features and their functions

Found in cytoplasm in most cells in a great abundance- especially in muscle cells.They take in nutrients, break them down, and create energy/ energy molecules for the cell. They also contain free floating DNA, granules -maybe to control ion concentrations- and ribosomes. Reactions for cellular (anaerobic) respiration occur here.
Outer Membrane- Skin to contain it
Inner Membrane- folds to form cristae
Cristae- increase surface area and rate of reaction
Matrix- Fluid which everything floats in
Main Function: to produce ATP currency/release energy from aerobic respiration
State the function of the Vacuole/Vacuoles

Vacuoles are essentially larger Vesicles, and they are formed by the joining together of many Vesicles.
In an Animal Cell, there are one or more small vacuoles that store water, ions and waste.
In a Plant Cell, there is one large vacuole that accounts for 90% of the cell volume, that stores water and maintains the turgidity -rigidity through water- of the cell.



