Case 4 - Bowel Cancer Flashcards
What enteroendocrine cells?
- function
- location
- Main sensory cells 1% of mucosal cells
- open at the lumen, contianing microvilli to increase surface area
- they contain hormones/neurotransmitters ready to be released

What are the effects of stimulating the enterochromaffin cells?
- Stimulated by mechanical or chemical stimulus
- It contains the enzymes to form serotonin
- Serotonin is released and it acts on vagal afferents to the brain
- Enterocytes have reuptake channels which can be blocked by SSIRs, leading to side effects such as diarrhoea
How is motility coordinated?
- Luminal stimulus causes 5HT release, leading to inteneurons working together to cause contraction and relaxation in the gut wall
- Contraction narrows the gut wall, behind the bolus, relaxation occurs in front of bolus of smooth muscle
- Luminal causes releases stimulates primary afferent neurones which interconnect with inter neurones and efferent neurones which release Ach and SP for contraction
What are the neurotransmitters of extrnsic nerves of the PNS?
- Acetlycholine
- Substance P
- GRP
- NO
- VIP
What are viral oncogenes?
- e.g. SV40
- Viral genes that when introduced into the cells have a dominat transformative effect
- Viruses infect cells and cause cancer via vira oncogenes which have analagoue human variants and viral vectors
What is p53?
- Describe its function
- A transcription factor
- It is kept at low levels in the cell.
- When there is damage in the celll cycle or a mistake is made in the cell cycle, signalling pathways converge on p53 and stop it from being degraded
- P53 activates pathways to either destroy the cell or to arrest cell cycle and repair the damage
- it is activated by stabilisation kinases and ubiquitin ligases
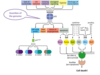
What is MYH - associated polyposis
- What causes it?
- Recessive form of polyposis caused by mutations in both alleles of the MUTYH gene
- The protein product of MUTYH is glycosylase involved in excision repair of damaged DNA
- Affected patients typiclaly develop 10 - 100 polyps in their 40s are at high risk of developing CRCs
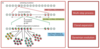
Explain the process of multistep tumourigenesis.
- Caused by mutations in genes
- Initial mutation in one cell
- this mutated cell divides and goes under clonal expansion resulting in many cells with that mutation
- a daughter cell of the original mutated cell gains another mutation there is an increased mutation rate
- Leads to multiple independent mutations in the daughter cells
- Genome of cancer cells have many mutations, it takes x12 mutaton from normal cell to cancer cell and all mutations must be present in the one cell
What CDK - Cyclin complex drives the cell into mitosis?
- Cyclin B and CDK1
Describe the mechanism that leads to adenomatous polyposis
- Germline mutations in the APC TSG
- Followed by a second hit mutation or deletion of the second allele
- Manifestation of CRC
pRb can act as a TSG decribe the way in which mutation in pRb will lead to tumour formation.
- In the normal physiological function pRb holds E2F down and inhibits its release into the cell
- E2F is only released when pRb is phosphorylated by the CDK4 and CD1 complex
- A mutaiton in the pRb gene means the other copy will still be able to give rise to a normal and controlled E2F
- However is both copies are mutated then E2F is no longer held down/inhibited within the cell
- E2F will then constantly enter the nucleus at any time even in the absence of stimuli and activate the cell cycle.

Explain how serotonin causes vomitting
- what stimutates this mechanism
- Toxins released by bacteria target rapidly dividing clells and stimulate the release of 5HT which travels via vagal vagal efferent going up to the vomitting center in the medulla
- This induces vomiting
- This mechanism is stimulated by
- 5HT3 antagonists
- antiemetics
Cancer staging: N - describes whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes
- N2
- Cancer cells in 4 or more neaby lymph nodes
Cancer staging
- T4
- a
- b
- The tumour has grown through the outer layer of the bowel wall serosa and through the peritoneum
- T4a - Other organs and other parts of the bowel
- T4b - tumour has caused a hole in the bowel (perforation) and cancer cells have spread outside the bowel
Descibe the mechanism of action of CCK
- CCK acts as a classic hormone, it is released into the bloodstream from I cells of the duodenum and stomach
- It travels to the gall bladder and causes the contraction of the gall bladder muscle releasing the bile
- CCK acts locally to stimulate vagal afferent nerves which travel to the dorsal vagal complex , which then releases Ach via vagal efferent that synaspse with the ENS to release Ach on the gall bladder for more contraction
- The dorsal vagal complex also releases vagal efferents towards the sphincter of Oddi and releases Ach on the ENS which releases NO/VIP to relax the smooth muscles and allow release of bile into duodenum

Describe the mechanism of action leading to mutation of APC and its effects!
- chromosome 5 band 21
- Gene codes for large proteins that bind to beta cetenin
- In sporadic disease it is mutate
- First allel undergoes mutation that results in truncuation
- second allele leads to a loss of heterozygosity
- Needs to lose both copies as it is a TSG
Explain how P53 leads to cell cycle arrest
- When there is damage to the cell, such as:
- lack of nucleotides
- UV radition
- ionising radiation
- oncogene signalling
- hypoxia
- blockage of transcription
- pathways converge to stop degradation of p53 which will activate the pathway to arrest cell cycle
- this yields p21 a CKI which will inhibit all the CK - CDK complexes resulting in cell cycle arrest

What CDK binds to Cyclin D1 and what is the function of the complex?
- CDK4/6 binds to cyclin D
- Drives the cell through G1
Where does CRC spread to?
- Local lymph nodes via enteric venous drainage to the liver
- haematogenously to the lungs
- less commonly to bone and brain
What are cellular oncogenes?
- Cancer DNA transfered into normal cells causes transformation, in a dominant manner
- a single activation mutation is sufficient - Beta catenin and KRAS
Decribe the Wnt pathway and how it leads to CRC.
- Wnt is a ligand that binds to receptors
- In the absence of Wnt Beta catenin is degraded and therefore it enters the cells and drives proliferation
- in the crypts of the colo adjacent to the sem cells are stem cell niche which secrete wnt to encourage the stem cells to proliferate
- The daughter stem cells proliferate and migrate up in the crypt towards the lumen, the further away it migrates the greater the distance to cell secreting wnt and therefore naturally stop proliferating and differentiate
- however, if there is a mutation the signalling pathway remains active within the cell
- the cells continue to proliferate, they no longer differentiate or migrate forming a lesion
Describe the oncogenic activity of RAS
- An oncogenic mutation locks RAS in the active form
- RAS acts as a switch its a GTPase,
- When RAS is bound to GDP it is inactive
- GDP changes to GTP triggering RAS
- Leading to triggering of signalling pathways
- RAS as a GTPases hyrolyeses GTP to GDP the inacive form, turning itself off
- When RAS is mutated it is locked into the active form where it can never be switched off
- There are constant signals being sent
Describe the EGF pathway
- EGF acts as a ligand, binds to the receptor
- Through RAS it triggers an intracellular transduction cascade
- Activates transcription factors in the nucleus
- Changes the function of transcription factors
- Changes gene expression of the cell
- Changes cell function
Cancer staging: N - describes whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes
- N1
- N1 - means there are cancer cells in up to three nearby lymph nodes
Cancer staging: N - describes whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes
- N0
- No lymph nodes contain cancer
Describe the mechanism that leads to cyclin E being produced and driving cell cycle?
- Wnt or GF bind to their receptors
- This affects the production of Beta catenin (Wnt) and RAS (GF)
- These affect transcription factors leading to increased production of Cylin D1 which then binds to CDK 4/6
- CDK 4/6 - CD1 complex phosphorylates pRb which releases a transcription factor E2F
- E2F enters the nucleus and binds to the promoter causing an upregulation of Cyclin E which binds to CDK2 and drives cell into S phase
- through a positive feedback loop pRb is phosphorylated by cyclin E leading to more cyclin E
*

What are the neurotransmitters of excitatory ENS nerves?
- Acetlycholine
- Substance P
- Gatrin releasing peptide
How do opioids affect motility?
- Opioids mainly work on inhibitory neurones which cause relaxation, therefore rudeces propulsion
- Food isnt pushed down
- Failure for sphincters to relax = slow down motility = increasing transit time
What are the effects on the GI from eating too much?
- Enzyme transporters have maximum capacity rate
- Overload means food is not digested quickly
- Therefore, gastric emptying is slowed down
- Allows maximum digestion and therefore absoption
What are the side effects of opiates?
- Vomiting in 30% of patients
- Dysphoria
- constipation - needs to be managed in palliative care
What are the effects of using an opioid receptor antagonist
Humans treated with naloxone:
- decreased motility
- decreased intestinal secretions
What are mismatch repair genes?
- How do they lead to cancer
Mismatch repair genes e.g. MHS2 repair DNA when it is replicated wrongly or there is a mutation in one of the genes
MHL1 a mismatch repair gene is silenced by methylation
- When the mismatch repair gene is silenced or mutation this elevates mutation rates
- Cells are more likely to have mutations that will cause cancer
- TGF beta binds to TGF betareceptor and stops cell from dividing/proliferating
- TSG - both copies must be destoryed
Cancer staging
- Tis
- Cancer it is in its earliest stage - it is growing into the mucosa but no further
Cancer staging:
- T2
- Tumour has grown into muscle layer of the bowel but no further
What are the neurotransmitters of Inhibitory ENS nerves?
- NO (nitric oxide)
- Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)
What binds and inactivates the cyclin complexes?
- Cyclin Kinase Inhibitor e.g. P21
How do the following bind to receptors:
- Growth factors
- Hormone factors
- Growth factors:
- bind to receptors on the cell surface and trigger a signalling cascade
- Hormone factors
- go through the cell membrane and bind to receptors within the cell
Mutation of which receptors lead to IBS?
- 5HT4
- 5HT3
What are the neurotransmitters of the extrinsic nerves of the SNS?
- what does it elicit
- Post ganglionic fibres release noradrenaline which decreses moltility and decreases blood flow
- Noradrenaline is only useful in fight or flight response to dampen down GI
Descibe the mechanism of action of opiods
- Receptor activation = G protein leading to drirect interactions with channel proteins
- it activates potassium channels - decreasing synaptic transmittion
- it inhibits calcium channels - decreasing synaptic transmission
- Main mechanism for analagesia and for decreasing in motility is increased tranit time
Regarding TSG, what are the differences between:
- Familial
- sporadic
TSGs require two random mutations in the same cell
- Familial - one of the genes is already mutated and inherited as a mutated copy, therefore only one extra random hit is required
- Sporadic - two mutations have to occur in the same cell to cause effects
Cancer staging
- T1
- Tumour is in the submucosa
What do mechanoreceptors sense?
- distention
What CDK binds to Cyclin A and what is the function of the complex?
- CDK2 binds to cyclin A
- drives the cell in s phase (to G2 phase)
- CDK 1 binds to Cyclin A to drive the cell into G2
*
What CDK binds to cyclin E and what is the function of the complex?
- CDK2 binds to Cyclin E
- Drives cell cycle into S phase
Cancer staging: M - describes whther the cancer has spread to another part of the body such as liver/lungs
- M0
- M1
M0 - cancer hasnt spread to distant organs
M1 - means the cancer has spread to distant orans such as the liver or lungs
Why is iron absorption regulated?
Iron absorption is regulated as too much iron can be toxic
What are the hallmarks of cancer?
- Self - sufficiency in growth signals - does not need growth signals, can grow and proliferate in the absence of growth signals
- insensitivity to anti-growth signals - continue proliferation
- avoid immune destruction
- tumour promotic inflamamtion
- tissue invasion and metastasis
- limitless replicative potential
- sustained angiogenesis
- genomic instability
- deregulated metabolism
- evading apoptosis (immortal)
What do chemoreceptors sense?
Acidity and digesitve products
What hormones are released by the enteroendocrine cells?
- GIP - gastric inhibitory peptide/glucose independent peptide
- Incretins control endocrine pancreatic functio
- Molin - acts in the absence of food, forces contents of the gut propulsion to remove the remaining contents in the gut, force remainig contents from SI to colon and to prevent bacteria travelling from colon to SI before they become sinister
Cancer staging:
- T3
The tumour has grown into the outer lining of the bowel wall serosa
What do osmoreceptors sense?
- osmolality


