Breast Cancer Flashcards
(17 cards)
Breast Caner genetics
12% are due to identifiable inheritable genes 80-90% BRCA
BRCA 1 vs 2
1: increased risk uterine cancer 2: not as much uterine cancer, more male breast cancer
CHEK2
5% breast familial cancers Tumor suppressor genes = more incidence of other cancers (prostate, thyroid, kidney, colon)
Cowden
Rare mutation in PTEN gene
Peutz-Jeghers
Mutation in STK11/LKB1 Rare
Metatastic tumor Breast Cancer
Lymphoma most common Usually gets there late so bad prognostic sign
p

Ductal carcinoma In situ More likely to form masses/calcifications Cribiform pattern High grade very likely to progress Other patterns: solid, papillary, …
Paget’s Disease
Ductal carcinoma in situ involving the nipple (rash like) If associated with mass very likely that it is carcinoma
p

Lobular Carcinoma In-situ Loss of e-cadherin (cell-cell adhesion molecule) - can use to differentiate Usually found incidentally Increased risk for carcinoma in either breast
p

Invasive ductal carcinoma Most breast cancers in this category Tubes lined only by one layer of cells (only epithelial) Cells a little larger and pleomorphic
p

Invasive lobular carcinoma Loss of e-cadherin = grow in single file linear pattern or in targetoid pattern
p

Tubular Carcinoma Well differentiated = well form tubular but invades the fat in the periphery Angulated glands Always small, Her2 negative, great prognosis
p

Mucinous Carcinoma Often well-circumscribed 7th decade Good prog More in BRCA1 not HER2 Small Islands of tumor floating in mucin
p

Medullary Carcinoma Well-circumscribed Triple neg tumor but a little better than IDC More in BRCA1 Indistinct cell borders, lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate
p
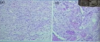
Metaplastic Carcinoma Nonglandular, restricted to squamous (d), spindle cell (a), or pseudosarcomas Triple negative Grow faster
p

Angiosarcoma Lumen with blood in it Breast common location Often radiation or chronic edema associated
p

Phyllodes tumor Biphasic (stroma & epithelium) Leaflike Many mitosis, more stroma, infiltrative borders


