Boards Flashcards
Hereditary angioedema is the result of:
C1-INH esterase deficiency
Chipmunk facies
Beta thalassemia
Name the procedure for removing thyroglossal duct cyst
sistrunk procedure
DX?
Syndromic association?

Hollman miller sign: Anterior bowing of the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus that occurs as a result of nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
Can be associated with Gardner’s syndrome
Conditions that cause elevated vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) (3)
*note ALL neuroectodermally derived 1. Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy 2. Olfactory neuroblastoma 3. Pheochromocytoma
Burton line
Bluish pigmentation of the marginal gingiva that results from lead poisoning
3 Fun facts about chordomas
- most often seen involving the clivus
- contains physaliferous cells
- stains positive with brachyury
Dermatofibroma staining vs dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
DF: CD34- F13A+ DFSP: CD34+ F13A -
Intestinal type sinonasal adenocarcinoma is associated with what professions

leather and woodworking
What are 4 risk factors of sinonasal adenocarcinoma (not intestinal type)
- Southeast Asia
- EBV infection
- high salt fish diet (chinese male population greatly affected)
- vitamin C deficiency
Warthin-Finkeldey giant cells are seen in what 5 conditions?
- measles
- lymphoma
- Kimura disease
- AIDs associated lymphoproliferative disorders
- Lupus erythematosus
DX?
Name the two cell types indicated by the arrows
What is the causitive organism?

Rhinoscleroma caused by : Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis (gram negative bacteria)
Mikulicz cells(foamy histiocyte), Russell bodies (eosinophilic inclusions in plasma cells)

Depicted entity:
- Chronic and localized infection of the mucus membranes
- Lesions present clinically as polypoid, soft masses (sometimes pedunculated) of the nose, throat, ear, and even the genitalia in both sexes.
What is the infectous organism?

Rhinosporiodosis- caused by Rhinosporidium seeberi (seems to be a fungus when you google it) -clinical presentation is an enlarged nostril/end of the nose

Ascher syndrome features (3)
- Double lip 2. Goiter 3. upper eyelid edema (blepharochalasia)
Paramedian lip pit associated syndromes (3)
- Van der woude syndrome 2. Kabuki syndrome 3. Popliteal pterygium syndrome
Premature exfoliation of the mandibular incisors may be seen in
hypophosphatasia
Beaten metal/copper skull is seen in which 3 conditions?
-Crouzan Syndrome (beaten-metal) -Apert syndrome (beaten metal) -Hypophosphatasia (beaten-copper)
“Teeth floating in air” + skin plantar/palmar hyperkeratosis

Papilon-Lefevre syndrome
Name that condition: Vertical bone trabeculae, Missing premolar, Retained primary molar
-List 2 other clinical findings
Segmental odontomaxillary dysplasia
Gingival overgrowth in the area of missing teeth
Becker nevus: hyperpigmentation with hypertrichosis
Ghost teeth on radiology enameloid conglomerates on histo
regional odontodysplasia
Black coated tongue cause
Bismuth staining
Skull radiology: best diagnosis for punched out radiolucent lesions in a child vs an older adult
child: LCH adult: multiple myeloma
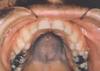
Hydroxychloroquine pigmentation (antimalarial medication also given to lupus patients)
Lateral Calcifications seen on PAN DDX (5)
- tonsilith
- sialolith
- phlebolith
- dystrophic acne
- calcified lymph node




















































































