Block 4 general Flashcards
female genital ducts and glands derive from
UG sinus, paramesonephric ducts
what kind of process is sexual determination of female?
active
what supports persistence and devel of paramesonephric ducts?
estrogens
what does the unfused portion of the paramesonephric duct become?
uterine tubes
what does the fused portions of the paramesonephric duct become?
uterus and superior vagina
what develops from the UG sinus?
inferior vagina bladder, urethra, paraurethral glands, greater vestibular glands
bicornate uterus
incomplete fusion of the paramesonephric ducts
what happens to primitive sex cords in females?
primitive sex cords dissociate in females and second generation of cortical cords develop
where do the gonadal ridges appear?
gonadal (or “genital”) ridges appear on the medial surface of the urogenital ridges
what does the genital system consist of
gonads genital ducts and glands external genitalia
what are the three events initiating puberty
1) proper nutrition 2) gene activation 3) development of limbic system
A 15 year-old male does not demonstrate any signs of puberty. He is short for his age, his testicles show no evidence of enlargement, his testosterone levels are low, and he has a reduced ability to smell.
Kallmann syndrome
- KAL1 gene deficiency
- KAL1 induces migration of nerves from olfactory placode to olfactory bulb
- responsible for differentation and migration of GnRH secreting nerves
- Lack of GnRH results in ↓ LH, FSH, testosterone, sperm count
IGF-3
- allows descent of testes
- under influence of gene HOXA10
precocious puberty
premature development of genital organs and secondary sexual characteristics
- can be due to GnRH secreting tumor (optic glioma or hypothalmic astrocytoma)
chromophils
- acidophils (40%)
- basophils (10%)
- part of pars distalis of the anterior pituitary
- ectoderm origin
- synthesize and secrete a variety of hormones
- each type generally secretes a single hormone
- arranged in cords; envolped by a delicate covering of connective tissue
- large cells, alot of RER, well developed Golgi complex, many secretion granules
- become chromophobes when they dump their hormones
chromophobe
chlorophils that have released their specific hormones and are “degranulated” and thus stain poorly
Identify

Chromophils
- large cells, much RER,well developed Golgi complex, many secretion granules (contain hormone)
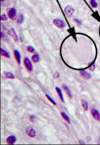
Idenitfy circled structure

Chromophobe
- chromophils that have released their specific hormones and are “degranulated”
- therefore, stain poorly
Steroidogenic TF
promotes gonadotroph lineage
T-box TF (“Tpit”)
promotes the corticotroph lineage
POU1F1
- encodes a POU domain
- this domain is essential for differentiation and expansion of somatotrophs, lactotrophs and thyrotrophs
- transcription factor
- mutations - responsbile for GH, PRL and TSH deficiencies
supraoptic nuclei
ADH
Paraventricular nuclei
oxytocin
hypothalamic nuclei
cell bodies of neurosecretory neurons that releasing or release-inhibiting hormones are synthesized
how do release/release-inhibiting hormones reach their target cells in the pars distalis?
hypophyseal portal system
Hypophyseal Portal System
primary capillary plexus, portal venules and secondary capillary plexus
colloid cysts
found in pars intermedia
- colloid = viscous material within
- cyst = encapsulated structure
Identify

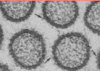
Pars nervosa (of the posterior pituitary)
- dots are nuclei of glial cells
- axons are the stringy lines throughout (where the lines are pointing)
- stores neuroendocrine secretions made by the neurons of the hypothalamus
Identify
Herring bodies
- found in the pars nervosa of the posterior pituitary
- large swellings formed by ends of axons
- stores oxytocin (from paraventricular nuclei) and ADH (from supraoptic nuclei)
Identify

Pars nervosa of the posterior pituitary
- can visualize axons (arrows pointing to them) and lots of secretory vesicles that are storing hormones
- Oxytocin (from paraventricular nuclei of hypothalamus)
- ADH (from supraoptic nuclei of hypothalamus)
- axon terminals end near fenestrated capillary
Diabetes insipidus
excessive thrist and urination due to inadequate secretion or utilization of vasopressin / ADH
- could be caused by damage to hypothalamus, damage to pituitary stalk, brain tumors
- neurogenic
- mutations in neurophysin II
- nephrogenic
- mutation in V2 receptor, aquaporin channel
What do corticotropes express?
express ACTH, contains alpha MSH
therefore, stimulates cortisol synthesis in adrenal gland but IN EXCESS, will stimulate melanin produciton in melanocytes (recall that hyperpigmentation allows differentiation between primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency)
A 15-year-old male presents to his pediatrician with complaints of fatigue, weight loss, and recurrent nausea and vomitting. On physical exam he appears weak and has skin that appears abnormally tan. A basic metabolic panel reveals hyponatremia and hyperkalemia.
Addison disease / Primary adrenal insufficiency
- elevated plasma ACTH
- low cortisol levels in response to ACTH stim test
- decreased aldosterone, therefore
- hyponatremia
- hyperkalemia
- hypoglycemia
- increased BUN & Cr
- metabolic acidosis
- eosinophilia
secondary adrenal insufficency
no hyperpigmentation and overall decreased ACTH
due to: isolated failure of ACTH production
JAK tyrosine kinase
- the type of tyrosine kinases that GH and prolactin receptors associate with
-
activate STAT
- which regulates transcription
STAT
- activated by JAK tyrosine kinase (which is activated by association with GH and prolactin receptors)
- regulates transcription
GH release type
GH is a peptide hormone and therefore release is exocytosis
mucosa
epithelium
lmaina propria
muscularis mucosae
serosa
epithelium and CT
muscularis externa
longitudinal muscle and circular muscle
isthmus of gastric mucosa
parietal cells
neck of gastric mucosa
neck mucous cells
stem cells
parietal cells
base of gastric gland
- peptic cells
- parietal cells
- mucous cells
- neuroendocrine cells
What kind of cells in the stomach make histamine
ECL
What kind of cells make gastrin?
G cells in the pylorus of the stomach
Gastrin
- made by G cells of the pylorus
- peptide
- increases secretion of HCL, pepsionogen
- Increases motility
What are the direct ways of promoting HCl release from the parietal cells?
ACh acts on muscarinic reeptor
Gastrin acts on CCK receptor
Whats an indirect ways of promoting HCl release from the parietal cells?
Acetylcholine and gastrin can work to stimulate the ECL cell, which causes the ECL cell to release histamine
- histamine will then act on H2 receptor to directly stimulate parietal cell to release H
enteroendocrine cells
- “neuroendocrine cells”
- must be stained with certain antibodies
- involved in coordination of GI funciton
- anatomically dispersed throughout GI tract
- Receive and send signals
three phases of bacteria in stomach
1. Active phase -produce ammonia to increase pH through “urase”
2. Stationary phase - attach to a receptor on cell; make proteases, get nutrients from cell, attract leukocytes
3. Colonization phahse - detach from receptor, replicate and then attach to sialic and acid cotaining proteins in mucus blanket
Hormones made in pylorus of the stomach
gastrin
somatostatin
histological features of pyloric stomach
deep pits and short, coiled glands
histological features of the cardiac stomach
equal lengh pits and glands