Block 3 - CNS Flashcards
___ aggregates are seen in Alzheimer’s, Pick disease, and progressive supranuclear palsy
Microtubule associated protein
Soluble in monomeric form
Insoluble fibrillary aggregates escape degradation and form neurofibrillary tangles
In some patients, the enzyme that cleaves the protein can be altered ( familial AD and PD)
tau
___ aggregates seen in Parkinson’s, dementia with lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy
synuclein
____ aggregates seen in Alzheimer’s and cerebral amyloid angiopathy
beta-amyloid
___ protein aggregates seen in CJD, vCJD, FFI, and animal diseases
prion
Type of degeneration seen in alzheimer’s
diffuse cortical
type of degeneration seen in diffuse lewy body disease
diffuse cortical
degeneration seen in frontotemperol dementias
diffuse cortical
type of degeneration seen in parkinson disease
midbrain/brainstem
type of degeneration seen in progressive supranuclear palsy
midbrain/brainstem
type of degeneration seen in huntington disease
caudate nucleus
type of degeneration seen in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
motor neurons
chromosome associated with beta-amyloid precursor protein in Alzheimer’s disease
21
(alzheimer’s increased in Down syndrome)
gene associated with presenilin 1, associated with Alzheimer’s
14q24.3
gene associated with presenilin 2, associated with Alzheimer’s
1q31-q42
gene associated with tau, associated with Alzheimer’s
17q21.1
____ plaques as seen in alzheimer’s

amyloid
____ ____ of Tau protein as seen in alzheimer’s disease

neurofibrillary tangles
Superficial cortical dark spots denote ____ deposition in Alzheimer’s

hemosiderin
Parkinson’s disease involves the deposition of ____ inclusions (Lewy bodies) with progressive loss of neurons, visible grossly in the substantia nigra.

synuclein
Parkinson’s disease involves the deposition of synuclein inclusions, called ______ _____, with progressive loss of neurons, visible grossly in the substantia nigra.

Lewy bodies
Parkinson’s disease involves the deposition of synuclein inclusions (Lewy bodies) with progressive loss of neurons, visible grossly in the ____ ____.
substantia nigra
Huntington chorea involves chromosome ___, which codifies Huntingtin, containing a polyglutamine sequence due to CAG repeats. Repeats increase with each subsequent generation, increasing the severity of the disease.
4p
Huntington chorea involves chromosome 4p, which codifies Huntingtin, containing a polyglutamine sequence due to CAG repeats. Repeats increase with each subsequent generation, increasing the severity of the disease. This phenomenon is called ___.
anticipation
Huntington’s disease shows ___ nucleus atrophy and neuronal loss. Causes significant dilation of the lateral ventricles.

caudate
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis involves the loss of ____ neurons
motor (upper and lower)
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis involves the loss of motor neurons, which appears as degeneration of the ____ tracts.

corticospinal
Anencephaly is one of the more common neural tube defects due to closure failure of the ___ ___, resulting of the cerebrum and calvarium.
frontal neuropore
Anencephaly is associated with ___ deficiency
folic acid
____ is closure failure of the frontal to caudal neuropores, exposing the spinal cord and adjacent nerve roots.
Craniorachischisis
Failure of closure of part of the spinal cord. Spinal cord/roots can protrude from the defect.
meningomyelocele
Meningomyelocele is associated with ___ deficiency.
folic acid
Meninges and/or brain herniate through a mesodermal defect. Usually occipital, secondly frontoethmoidal.
encephalocele
fluid accumulation in the central canal of spinal cord.
hydromyelia
downward herniation of cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum. Asymptomatic or neck pain, lower CN palsies, sleep apnea, and sudden death. Cerebellar atxia and long tract signs. Syringomyelia is common.
chiari malformation type 1
downward herniation of tonsils and brainstem. Highly associated with lumbosacral myelomeningocele and hydrocephalus.
chiari malformation type 2
failure to divide the brain into hemispheres. Associated with mutations: SHH, SIC2, SIX3, TGIF1
holoprocencephaly
holoprocencephaly is associated with abnormalities of which chromosome?
trisomy 13
agenesis of the ___ ___ is total or partial disruption of cerebral interhemispheric axonal migration across the midline during development. Asymptomatic or seizures and cognitive impairment.

corpus callosum
Agenesis of the corpus callosum shows remnants of ____ matter bundles called bundles of Probst.
white
Common incidental finding on imaging or autopsy that involves the failure of the two halves of the septum pellusidum go fuse at the midline. Typically asymptomatic.
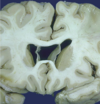
cavum septum pellusidum
cerebral cortical defects are due to impairment of ____ migration and cortical differentiation.
neuroblast
____ is the absence of normal convolutions on the brain, “smooth brain.” Seen in neuronal migration disorders.
lissencephaly
autosomal dominant syndrome of defective neuronal migration that results in lissencephaly
miller-dieker syndrome
chromosomal abnormality for miller-dieker syndrome
17p13.3
x linked syndrome associated with defective neuronal migration, resulting in lissencephaly
filamin A and doublecortin (DCX)
autosomal recessive syndrome associated with defective neuronal migration, resulting in lissencephaly
Walker-warburg syndrome
2 genes associated with Walker-warburg syndrome
POMT1 and POMT2
group of conditions of various etiologies that show nodules of abnormally placed gray matter. Arrest of neurons during migration, which stay around ventricles and white matter. Asymptomatic or seizures.

heterotopias
disruption of normal gyration (too many, too small). Diffuse, focal, bilateral, or unilateral. Seizures and severe psychomotor retardation. Results from fetal infection, prenatal hypoxia, metabolic disease, or genetics.

polymicrogyria
The least severe degree of CNS destruction from stroke during gestation. any fluid-filled cavity in the fetal or neonatal brain. A thin membrane may separate the cavity from the lateral ventricle or the subarachnoid space.
porencephaly
Moderately severe degree of CNS destruction from stroke during gestation. ongenital clefts in the cerebral mantle.

schizencephaly
the most severe degree of CNS degradation from stroke during gestation. erebral hemispheres are replaced by a thin-walled, fluid-filled cyst. The aqueduct is usually atretic, and increased fluid pressure causes the cyst (and the head) to enlarge.

hydranencephaly
Mycobacterial infection commonly seen in the brains of AIDS patients.

TB
Fungal infection that begins as a pulmonary infection and spreads hematogenous to the brain in immunosuppressed patients. Angioinvasion leads to infarcts. Fibrin and hyphae are seen in the artery wall.

Aspergillosis
Infection that spreads hematogenously from the lung in immunosuppressed patients. Abscesses, thick & slimy meninges, and parenchymal cysts. Yeast with thick capsules invade macrophages.

cryptococcosis
RNA virus that replicates in the muscle and migrates to the CNS via centripetal axonal transport –> salivary and lacrimal glands. Neurons with cytoplasmic Negri bodies.

Rabies
Herpes virus causes necrosis of the ____ lobes, called necrotizing panencephalitis. Causes severe memory disturbances and other deficits

temporal
Diffuse white matter damage caused by JC virus. Shows small, round, confluent white matter lesions (demyelination).

Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
JC virus goes latent in which two organs?
kidneys and tonsils (B cells)
Infection in immunosuppressed patients, especially pregnant women transplacentally to fetus, that encysts and remains dormant in the CNS. Reactivation due to immunosuppression. Shows multifocal areas of necrosis and inflammation, bradyzoite cysts and tachyzoites.

toxoplasmosis
Cystic infection that reactivates in immunosuppressed patients.

Toxoplasmosis
Most common CNS parasitic infection and a leading cause of epilepsy. Tapeworms develop cysts in any organ. Inflammation follows the parasite’s death and eventual calcification

Neurocysticercosis
___ hematoma occurs between the dura and the skull.
Associated with skull fracture.
Progressive mass effect, so patient may have a lucid intervan with subsequent mental decline.
Biconcave (lens) shaped and does not cross suture lines.

Epidural (extradural)
____ hematoma occurs between the dura and the brain.
Associated with trauma and injury to bridging veins, which may be more common in elderly patients due to fragility of the veins. Increased risk with anticoagulation and alcoholism.
Progress quickly.
May become chronic
Banana shaped and may cross suture lines.

___ hemorrhage between the arachnoid membrane and CNS parenchyma.
Commonly caused by ruptured aneurysms, AVM, or cortical contusion.
“Worse headache of my life.”
High fatality due to hemorrhage and vasospasm.
Blood can be seen in the CSF on LP or anywhere that CSF is present.

Subarachnoid
Aneurysms are commonly seen at the ____ of an artery
bifurcation
_____ hemorrhage is located within the cortex.
Related to HTN (basal ganglia or thalamus), metastases, or vascular lesions
Hemorrhage after CNS infarct.
Presents as sudden headache, loss of function, weakness, and hemiplegia
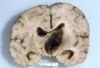
Parenchymal
Traumatic brain injury can lead to progressive brain atrophy and cortical ___ deposition in deep sulci
Tau
Cerebral contusions usually occur in the ___ gyri and ___ lobe.
Can cause diffuse axonal and vascular rinjury.

supraorbital
temporal
Cerebral contusions can present with ____ lesions, where the brain hits the skull on the opposite side from the trauma.
countercoup
diffuse axonal and vascular injury, typically caused by a ____ contusion.
cerebral
____ herniation involved the movement of part of the temporal lobe under the free edge of the tentorium, compressing the midbrain and the oculomotor nerve (ipsilateral palsy). This is usually caused by a rapidly expanding middle cranial fossa epidural, subdural, or infratemporal lobe hematoma.
uncal
In ____ herniation, the part of both the cerebral hemispheres are squeezed through a notch in the tentorium cerebelli.
Diencephalic/central
_____ herniation is the most common form of intracranial herniation and occurs when brain tissue is displaced under the falx cerebri. The cingulate gyrus is herniated under the falx, and if progression occurs, other areas of the frontal lobe are involved.
subfalcine
____ ____ can be drilled in the skull to relieve intracranial pressure
Burr holes
A ____ herniation is characterized by the descent of the cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum, which compresses the medulla against the clivus/odontoid process. It is described as “coning” as the brain tissue is squeezed down through the foramen like being squeezed into a cone.
tonsillar
____ ___ phenomenon occurs with uncal herniation, which causes contralateral pupillary dilation and ipsilateral oculomotor nerve weakness.
Kernohan’s notch
Secondary ___ hemorrhages in the brainstem occur after uncal herniation, due to overstretching of the vessels.

Duret
Brief episodes of CNS symptoms lasting <1 hr, due to ischemia and thromboembolism.
TIA (transient ischemic attack)
Abrupt onset of CNA symptoms lasting >24 hours, due to tissue infarct and necrosis from thromboembolism.
Stroke
____ injury occurs when an infarcted area of the cortex bleeds after treatment to reestablish blood flow.
Reperfusion
Dural based tumors in adults. Slow growing with good prognosis. Women > men.Increased in neurofibromatosis and post-radiation. May grow through bone without being histologically malignant.
Well-circumscribed. Uniform tumor cells grow in whorls with no evidence of malignancy.

Meningioma
Ill-defined, infiltrating tumor. Occur anywhere in the CNS but more commonly supratentorial. Cause seizures, headaches, and focal signs. The tendency to become malignant.
MRI shows ill-defined hyperdensity (hypercellular) with higher water content than normal white matter.

astrocytoma
Most frequent glial tumor in adults. >supratentorial. Highly malignant.
Present as seizures, headaches, focal deficits.
Hypercellular, especially at rim.
Cells have marked atypia and mitosis.

Glioblastoma
benign tumor in adults. More common in peripheral nerves, but within the CNS, more common in vestibular branch of CN 8 (cerebellopontine angle).
sporadic = solitary
Neurofibromatosis 2 = bilateral
Well circumscribed

schwannoma
Well-circumscribed tumor, typically intraventricular or in the spinal cord, centrally placed. Any age. Causes hydrocephalus, increased ICP, and atxia.

ependymoma
_____ frequently form perivascular “pseudo rosettes.” Centered by blood vessels and tumor cells arrange around them.

ependymoma
Most frequent glial tumor in children. Occur mostly in the cerebellum, but also in the optic nerve, thalamus, hypothalamus, and supratentorially. Well circumscribed, solid and cystic. Present with increased ICP and cerebellar signs (ataxia).
Spindle cells with dense, fibrillary cytoplasm. Low cellularity and characteristic Rosenthal fibers.

pilocytic astrocytoma
Common malignant tumor in children, <15yo. Typically in the posterior fossa, vermis. Present with ataxia and signs of increased ICP. Tendency to disseminate along the subarachnoid space (drop metastases).
Mt: SHH, WSH
Solid, typically in the midline.
Markedly cellular, frequently with “rosettes.” Some neuroblasts within these tumors form nodules of more differentiated cells, called neurocites.

medulloblastoma
Steroid myopathy involves (proximal/distal) muscle weakness
proximal
Steroid myopathy preferentially affects (type 1/type 2) muscle fibers

type 2
Dermatomyositis preferentially affects the (proximal/distal) muscles
autoimmune, women
Elevated CK
Underlying malignancy
Heliotrope erythema, Gottron sign, mechanics hands
proximal
autoantibodies associated with dermatomyositis
1 = gottron papules and heliotrope rash
2 = arthritis and skin rash, interstitial lung disease
3 = paraneoplastic/juvenile
Anti-Mi2 (against helicase)
Anti-Jo1 (against histidyl t-RNA synthetase)
Anti-P155/P140
Lymphocyte-mediated muscle injury leading to muscle pain and weakness

polymyositis
polymyositis preferentially affects (proximal/distal) muscles, symmetrically
Proximal
Durg-induced myopathy
high CK

Toxic/vacuolar
Inherited myopathy (AD or AR) that can be due to defects in several cellular enzymes
Scattered fibers show more subsarcolemmal mitochondria on NADH staining, indicating increased proliferation
Typical “ragged-red fibers”

Mitochondrial myopathy
X-linked (male) progressive muscle weakness
Floppy baby or asymptomatic at birth
High CK
Duchenne musculodystrophy
Duchene MD favors (proximal/distal) muscles
proximal
Mild dystrophy that also presents with heart disease, typically around 12yo.
Becker Muscular dystrophy
Sarcoglycanopathy favors (proximal/distal) muscles
Intolerance to exercise/cramps
proximal (limb girdle)
Spongiform encephalopathies are a group of progressive, lethal diseases that involve the accumulation of abnormal ___ protein in the CNS and the formation of ___ plaques.
prion
amyloid
Prion PrPc protein is associated with Chromosome ___. Expressed in all cells, particularly neurons. Decrease in size of a-helices, and increase in size of b-sheets causes the protein to become resistant to digestion and liable to form aggregates.
20
Rapidly progressive dementia presentiing in the 7th decade of life. Also shows myoclonus. Progressive and fatal in months.
Increased signal in the basal ganglis and cortex.
Vauolization of the gray matter neutrophil (sponge-like)
Progressive neuronal loss and reactive gliosis
PrP deposition as amyloid plaques

sporadic Creutxfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)
sporadic Creutxfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) shows vacuolization of (gray/white) matter
gray
sporadic Creutxfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) involves ___ protein deposition in the form of amyloid plaques
PrP
PrP protein disease that appears in younger patients in the UK. Initially as sensory and psychiatric disturbances and unsteadiness. Slowly progressive dementia to akinetic mutism. Death around 14 months.
Plaques and vacuolization
Spongiform degeneration in the basal ganglia and thalamus
PrPsc also found in follicular dendritic cells of tonsil, LN, spleen, thymus and GALT (all immune tissues)

variant Creutxfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)
Prion protein diseases are transmissible but are not ____.
contagious
•Destruction of myelin in CNS or peripheral nerves, with relative preservation of axons
Multifocal with lesions of different ages
Autoimmune ; women > men
Increased incidence with increased latitude
- Variable presentation with weakness, paresthesia, sensory loss of one or more limbs, optic neuritis, diplopia, incoordination, vertigo
- Others with loss of vision, dysarthria, disturbances of micturition, painful muscle spasms, seizures
- Usually associated with oligoclonal bands of immunoglobulins on electrophoresis of CSF

Multiple sclerosis
Classify the MS:
–multiple acute attacks, each followed by clinical improvement
relapsing remitting
Classify the MS:
–after years of RRMS, the patient enters a stage with no recovery between attacks
secondary progressive
Classify the MS:
progressive disease without episodes of recovery
primary progressive
Classify the MS:
repeated acute attacks superimposed on progressive disease without episodes of recovery
relapsing progresssive


