Block 1 Flashcards
(533 cards)
pharmacology definition
biomedical science concerned w/study of drugs and their effects on life processes
goal of pharmacology
understand mechanisms by which drugs interact w/biologic systems to enable rational use of effective agents in diagnosis & treatment of disease
2 subdivisions of pharmacology
- pharmacokinetics
- pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics definition
study of actions of body on drug (ADME)
Pharmacodynamics definition
Study of actions of drug on body
4 domains of pharmacokinetics
ADME:
- Absorption
- Distribution
- Metabolism (biotransformation)
- Excretion
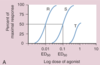
dose-response relationship
relationship btwn concentration of drug in tissue and magnitude of tissue’s response to drug
Most drugs produce their effects by
bind to protein receptors in target tissues → activate signal transduction cascade
Toxicology definition
study of poisons and organ toxicity; focuses on harmful effects of drugs & mechanisms by which these agents produce pathologic changes, disease, and death
Pharmacotherapeutics definition
medical science concerned with the use of drugs in the treatment of disease
clinical trials
Human studies used to determine efficacy & safety of drug therapy in human subjects
Pharmacy definition
science & profession concerned w/preparation, storage, dispensation, proper use of drug products
Pharmacognosy definition
study of drugs isolated from natural sources, including plants, microbes, animal tissues, and minerals
Medicinal chemistry definition
branch of organic chemistry that specializes in design & chemical synthesis of drugs
Pharmaceutical chemistry / pharmaceutics definition
concerned w/formulation & chemical properties of pharmaceutical products, such as tablets, liquid solutions and suspensions, and aerosols
drug definition
natural product, chemical substance, or pharmaceutical preparation intended for administration to human or animal to diagnose or treat a disease
types of drugs produced by body
hormones, neurotransmitters, or peptides
xenobiotic
synthetic or natural drug produced outside the body
poison
a drug that can kill
toxin
a drug that can kill and is produced by a living organism
alkaloid definition
contain nitrogen groups and produce an alkaline reaction in aqueous solution
alkaloid examples
morphine, cocaine, atropine, quinine
Antibiotics
drugs targeted to bacteria; isolated from numerous microorganisms, including Penicillium and Streptomyces species
structure-activity relationship
relationship btwn drug molecule, its target receptor, and resulting pharmacologic activity