Biological Basis of Behavior Flashcards
(51 cards)
Describe the synapse between a motor neuron & a muscular junction
- Synapse btw moror neuron & muscular junction
- AP propogates wave of depolarization (opens Nav)
- Cav that causes flux of Ca at the presynaptic terminal - leads to fusion of vesicles that contain neurotransmitters (ACh)
- ACh diffuses into the synapse - binds to nicotinic AChR (Na channels)
- causes depolarization - AP on muscle membrane
- propogates to sarcoplasmic T-tubules which creates calclium flux -> muscle contraction

Nicotinic ACh receptors are what type of receptor?
Describe their composition & binding sites.
ligand-gated ion channel
5 subunits in a donut shape looking into plane of membrane w/ ion channel in middle ; 2 agonist binidng sites on alpha subunits -> conformational change
leads to Na influx and depolarization

Muscarinic ACh receptors are what type of receptor?
G protein coupled recptors
What are the 5 subunits of the nicotinic AChR?
a2Byd
alpha(2), beta, gamma, delta
What is the function of agrin?
triggers the clustering of acetylcholine receptors (AChR)

How does agrin trigger the clustering of AChR?
binds to receptor & co-receptor -> activates muscle specific tyrosine (MuSK) -> phosphorylates other kinasea & leads to clustering
What two proteins are required for clustering?
Agrin
Rapsyn
What is the goal of ACHR regulation with regards to location?
upregulate AChR syntheis at NMJ
down regulated AChR synthesis distant from NMJ
How is synthesis of AChR downregulated?
Where would you want this to occur?
Electrical activity
down regulated AChR synthesis distant from NMJ
Describe the pathophysiology of MG & how this might relate to AChR expression at the NMJ
- Presentation
- muscle weakness that worsens after periods of activity & improves after periods of rest
- d/t autoAb for AChR -> decreased signaling & degradation of NMJ
Symptomatic Acute treatment for MG?
pyridostigmine
Chronic treatment MG?
immunosupression / thymmectomy
Pyridostigmine
MOA
AE
Pyridostigmine
- MOA
- ACh esterase inhibitor
- does not cross BBB
- AE
- sweating
- diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, increased salivation
What word describes:
physiological responses that occur more or less unconsciously when the brain detects situations
emotions
What word describes:
the conscious experience resulting from the emotions
feelings
What word describes:
some stimuli evoke emotions automatically
emotional competence
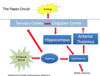
Describe the pathway of emotional stimuli
- Emotional stimuli -> thalamus -> hypothalamus & sensory cortex

What is the role of the hypothalamus in the emotional response?
Descending & ascending connections?
- evaluates the emotional quality &
- descending connections give rise to emotional response
- asecnding connections to hippocampus & anterior thalamus give rise to feelings
How is synthesis of AChR up regulated?
Neuregulin activation of ErbB tyrosine kinase - HER2 receptor
Induces AChR synthesis
What is the function of the Cingulate Cortex?
How does it communicate wihth the hypothalamus?
creating feelings
hypothalamus -> anterior thalamus -> cingulate cortex
cingulate cortex -> hippocampus -> hypothalamus
What are the roles of the limbic system?
- emotional behavior
- memory
- integration of homeostatic responses
- preservation of the species
- securign food
- fight or flight response
- sexual behavior
- motivation
What is the major function of the hippocampal formation?
learning & memory formation
What is the major function of the cingulate gyrus?
emotional behavior & pain
What is the major function of the amygdala?
v. important site for emotion & fear


