Biochemistry of Insulin Flashcards
pancreatic islets
also called islet of langerhans
found throughout the pancreas
what do the B, a, gamma and PP cells do in pancreatic islet
B - secrete insulin
a - secrete glucagon
gamma - secrete somatostatin
PP - secrete pancreatic polypeptide
synthesis of insulin
syntehsised in the RER of pancreatic B cell, as a larger single chain preprohormone, called preproinsulin
cleaved to form insulin, which contains two polypeptide chains linked by disulphide bonds
there is a connecting C peptide, which is a byproduct of cleavage and has no known physiological function

use of insulin lispro
ultra fast/short acting
used to allow blood glucose control during meal - injected within 15 min of beginning meal
must be used in combination with longer acting preparations unless used in continuous infusion

what sructural change has occured in inuslin Lispro
lysine and proline amino acids have been switched
insulin glargine
recombinant insulin analogue that has a peakless prolonged action
used to maintain blood glucose over night - single dose before bedtime

how does glucose enter the B cells
through GLUT2 glucose transported by diffusion
describe the secretion of insulin
glucose enters B cell through GLUT2 (diffusion) and is phosphorylated by glucokinase
inc metabolism of glucose leads to an increase in intracellular ATP concentration
ATP inhibits K channel KATP - leads to depolarisation of the cell and opening of voltage gated Ca2+ channels
increase in internal Ca2+ concentation leads to release of insulin

glucokinase activity
glucokinase’s KM for glucose lies in the physiological range of glucose concentration
(in hyperglycaemia glucose conc outwith KM of glucokinase and B cells lose ability to sense changes in glucose)
how many ATP does one molecule of glucose produce
36
carbohydrate metabolism
what can be used as a marker of B cells
insulin - these are the only cells that make and secrete insulin
at what blood glucose level should insulin be made and secreted at
>5mM
describe the pattern of insulin release
biphasic
- 5% insulin granules are immediately available for release - the RRP (readily releasable pool)
- reserve pool must be prepared before it is mobilised and released

what is insulin secretion like in poorly controllled T2DM
weaknes and flattens - down regulation of sensing process due to limited glucokinase acitivty
sulphonylurea drug action
mimic the action of ATP on KATP channel to depolarise the B cell and stimulate Ca channel opening and thus insulin release

KATP channel
consists of 2 proteins: pore subunit (Kir6) and regulatory subunit (SUR1)
both are required to form a functional channel
channel is an octomeric structure
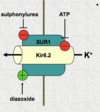
what drug inhibits insulin secretion
diazoxide - stimulates KATP

why are sulphonylurea drugs second line therapy for T2DM
B cells are already under a lot of stress - pharmacologically inducing them to work harder would be counterintuitive
useful in patients who have trouble injecting insulin or when glucose control has been improved and the stress on the B cells lessened
mutations in Kir6
can lead to neonatal diabetes
either due to constitutively activated KATP channels or an increase in KATP numbers = insulin not produced and an increase in blood glucose
in some of these patients the B cells are responsive to SURs
what can some Kir6 or SUR1 mutations lead to
hyperinsulinism
- diazoxide can inhibit insulin secretion
MODY
monogenic - genetic defect in B cell function
familial form early onset type 2 diabetes
what mutations cause MODY
can be caused by AuD mutations in at least 6 different genes on glucokinase or on several transcription factors
what mutation is MODY2 due to
mutations on glucokinase - impaired glucokinase activity, meaning it is less responsive to rising levels of glucose







