Biochemistry - MCAT Flashcards
Pinocytosis can also be called what due to the fact that it ingests dissolved electrolytes and solvents?
cell drinking
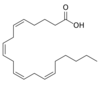
Can urea diffuse across the membrane?
yes
Can an ion moving through an ion channel down its concentration gradient also be moving against an osmotic gradient?
yes
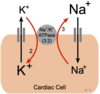
How many potassium (K) are pumped inside and sodium (Na) are pumped outside of the cell with NaK ATPase?
2, 3
Does phagocytosis take up solids or liquids?
solids
During the citric acid cycle, what form of energy is phosphorylated/is the energy product?
GTP
What molecules are oxidized in the electron transport chain?
NADH, FADH2
How many NET ATP are produced in glycolysis?
2
How many ATP are produced per NADH oxidized?
2.5
How many ATP are produced per FADH2 oxidized?
1.5
Does higher salt content in your sweat mean higher or lower salt content in your blood?
lower
If a molecule is reduced will it have more or fewer bonds to oxygen?
fewer
If a molecule likes to be reduced, will it have a higher or lower reduction potential?
higher
As you go across the ETC, each complex has a higher or lower reduction potential than the last?
higher
What glucose transporter is in nearly *all* tissues and increases when blood glucose is low? hint: “baseline”
GLUT1
What glucose transporter is on gluconeogenic cells, is bidirectional, and senses glucose on the pancreas?
GLUT2
What glucose transporter has a high glucose affinity even during low conc.? note: in brain and placenta
GLUT3
What glucose transporter is expressed at high glu conc because it stores glucose?
GLUT4
Where does glycolysis take place in the cell?
cytosol
Where does the citric acid cycle take place in eukaryotes?
mitochondrial matrix
Draw the graphs for competitive inhibitors
Vmax doesn’t change Km increases (binding affinity decreases bc more than one molecule is competing for binding site)

Draw the graphs for *noncompetitive* inhibitors
Binds allosterically and decreases the enzyme activity (Vmax) but binding affinity stays the same (no change to Km)

Draw the graphs for *uncompetitive* inhibitors
Binds allosterically and won’t let enzyme release the substrate (increases binding affinity/decreases Km), Vmax decreases bc less enzyme is left to work

What is the brain division for the forebrain called?
prosencephalon (personality and behavior)
What is the developing brain division for the area that carries the thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal gland, and posterior pituitary called?
diencephalon
What is the developing brain division for the area that carries the cerebrum, cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and basal ganglia called?
telencephalon
The limbic system controls what? hint: 3 m’s
motion, motivation, memory
What are the functions of the frontal lobe?
higher-level cognition, executive functions
What are the functions of the temporal lobe?
sound and language processing memory consolidation
What are the functions of the occipital lobe?
primary visual cortex
What are the functions of the parietal lobe?
sensory processing (such as touch via the postcentral gyrus)
What is the function of the cerebrum?
coordination of motor control (contains basal ganglis, hippocampus, and pons)
What is the function of the medulla oblongata?
controls autonomic functions (breathing, HR, etc)
What are the functions of the pons?
sleep, respiration, swallowing, taste, bladder control, balance
What is the name for the developing division of the midbrain and what are its functions?
mesencephalon motor control, sleeping, homeostatic regulation + superior colliculus (visual reflex) +inferior colliculus (auditory reflex)
What is the developing brain division for the hindbrain?
rhombencephalon
What are the components of the brainstem?
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
What are the functions of the somatic nervous system?
voluntary movement, innervation of muscles
How long are sympathetic nerves (preganglionic axons) and where do they release neurotransmitter?
Short, onto ganglions near the spinal cord typically
What is the pre-ganglionic neurotransmitter for both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
ACh
What is the post-ganglionic neurotransmitter for the PSNS?
ACh
What neurotransmitter’s loss is associated with loss of fine motor control?
Dopamine
What is the most prominent excitatory neurotransmitter?
glutamate
What is the most prominent inhibitory neurotransmitter?
GABA
What sensation does the medial geniculate body of the thalamus process?
Auditory along with the inferior colliculus
What areas of the brain help with voluntary motor control?
Precentral gyrus, cerebellum, basal ganglis (substantia nigria with Dopamine)
What cells provide nutrients, protection, and insulation for neurons?
glial cells
What type of glial cell coats the blood brain barrier?
Astrocytes (transport nutrients in and out)
What glial cells protect the central and peripheral nervous system respectively?
Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells (form myelation)
What acts as macrophages in the CNS?
microglia
What cells secrete CSF?
ependymal
How long are pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibers respectively?
long, short
Draw an action potential on a depolarization graph with sodium and potassium channels
ok - add a pic if you can get this to work
What sensation does the *lateral* geniculate body of the thalamus process?
vision along with the superior colliculus
What are the structures of the limbic system?
the amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, and cingulate gyrus
Do endo and exo-cytosis require ATP?
yes!
What is the electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane?
negative because cytoplasm is negative in relation to the extracellular fluid
What direction do potassium leak channels and Na/K ATPase channels move potassium respectively?
out of cell, into cell
Na/K ATPase moves how many molecules of Na and K and in what direction?
3 Na out / 2 K in
Do axons with large or small diameters transmit signals faster?
large (greater conductance)