Biochemistry Chapter 8 Flashcards
back
front
Its fixed
Cell (plasma) membrane ?
Often described as a semipermeable phospholipid bilayer. This phrase alone describes both the function and structure of cell membrane.

Its fixed
Lipid rafts ? glycoprotein coat ? What do cell wall contain ?
A tiny rich cholesterol region on a cell membrane that helps selected molecules enter the cytoplasm. This phospholipid bilayer includes proteins and signaling areas within the rafts. They are also collections of similar lipids with or without associated proteins that serve as attachment points for other biomolecules; these rafts often serve roles in signaling . *
- Carbohydrates associated with membrane-bound proteins create that coat *
- The wall of plants, bacteria, and fungi contain higher levels of proteins
Its fixed
Flippases ?
Specialized enzymes assist in the transition or “flip” between layers
Its fixed
List the following membrane components in order from most plentiful to least plentiful: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids.
- Lipids, including phospholipids, cholesterol, and others are most plentiful:
- then comes proteins, including transmembrane proteins(channels and receptors), membrane-associated proteins, and embedded proteins,
- Then comes carbohydrates, including glycoprotein coat and signaling molecules.
- Finally least plentiful would be nucleic acids which are essentially absent.
Its fixed
What are unsaturated fatty acids and saturated fatty acids? What are the two most important essential fatty aids ?
Unsaturated are regarded as “healthier” fats because they tend to have one or more double bonds and exist in liquid form at room temperature; in the plasma membrane, these characteristics impart fluidity to the membrane. Saturated fatty acids on the other hand are main components of animal fats and tend to exist as solids at room temperature. A-linolenic acid & linoleic acid
Its fixed
What is the importance of cholesterol ?
Not only imparts( transmit) fluidity membranes, but it is also necessary in the synthesis of all steroids, which are derived from cholesterol.
Its fixed
What are membrane receptors ?
Transmembrane proteins which activate or deactivate facilitated diffusion and active transport.
Its fixed
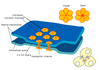
What are Gap junctions ? How are they formed ?
Allowing direct cell to cell communication and are often found in small bunches together. Or known as connexons are formed by the alignment and interaction of pores composed of six molecules of connexin.
Its fixed
What are Tight junctions ? Where are they found and what is their function ?
Prevent solutes from leaking into the space between cells via a paracellular route. * They are founds in epithelial cells and function as a physical link between the cells as they form a single layer of tissue.
Its fixed
What are desmosomes? What do they do ? How are they formed ?
- A site of adhesion between two epithelial cells consisting in each cell a dense attachment with associated intermediate filaments.
- * Bind adjacent cells by anchoring to their cytoskeletons.
- * They are formed by interactions between transmembrane proteins associated wit intermediate filaments indie adjacent cells.
Its fixed
What are Hemidesmosomes ?
Have a similar function to desmosomes, but their main function is to attach epithelial cells to underlying basement membranes( a thin delicate membrane of protein fibers and glycoaminoglycans separating an epithelium from an underlying tissue) {{10 1 0.png}}

Its fixed
How does cholesterol function as both a fluidity- and a stability- imparting molecule for the membrane ?
Cholesterol provides membrane fluidity by interfering with the crystal structure of the cell membrane and occupying space between phospholipid molecules. Cholesterol also provides stability by cross linking adjacent phospholipids through interactions at the polar head group and hydrophobic interactions at the nearby fatty acid trail.
Its fixed
What is the relationship between osmotic pressure and the direction of osmosis through a semipermeable membrane ?
As osmotic pressure increases, more water tend to flow into the compartment to decrease solute concentration. Osmotic pressure is often considered a “sucking” pressure because water will move toward the compartment with the highest osmotic pressure.
Its fixed
What is Osmosis ?
A specific kind of simple diffusion that concerns water; water will move from a region of lower solute concentration to one of higher solute concentration; it will move from a region of higher water concentration (more dilute solution) down its gradient to a region of lower water concentration(more concentrated solution).
Its fixed
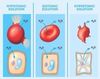
What are the Hypotonic, Isotonic, and Hypertonic solutions?
- * If the concentration of solutes inside the cell is higher than the surrounding solution, and this solution causes the cell to Swell as water rushes in and sometimes to the point of bursting.
- If the solution inside and outside are equimolar; the key point here is that isotonicity does not prevent movement; rather it prevents net movement of particles
- * A solution that is more concentrated than the cell and water will move out of the cell
Its fixed
What is Osmotic Pressure ?
A colligative property; a physical property of solutions that is dependent on the concentration of dissolve particles but not on the chemical identity of the dissolved particles.
Its fixed
Osmotic pressure ?
Van’t Hoff factor is the number of particles obtained from the molecules when in solution. {{16 1 0.png}}
Its fixed
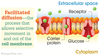
What is facilitated diffusion ? Carrier protein? Occluded state ?
A simple diffusion for molecules that are impermeable to the membrane(large, polar, or charged); the energy barrier is to high for these molecules to cross freely.
* Only open to one side of the cell membrane at any given point, This model is similar to a revolving door because the substrate binds to the transport protein(walks in), remains in the transporter during a conformational change (spins), and then finally dissociate from the substrate-binding site of the transporter(walks out) In which the carrier is not open to either side of the phospholipid bilayer. In addition to carriers, channels are also viable transporters for facilitated diffusion.
Its fixed
What is Active Transport ?
Results in the net movement of a solute against its concentration gradient, just like rolling a ball uphill. It always requires energy but the source of its energy varies.
Its fixed
What is Primary Active Transport ? Secondary active transport ?
Uses ATP or another energy molecule to directly transport molecules across a membrane. Also known as coupled transport also uses energy to transport molecules across the membrane; however in contrast to primary active transport, there is no direct coupling to ATP hydrolysis.

Its fixed
What is symport ? Antisymport?
When both particles flow the same direction across the membrane. * When the particles flow in opposite directions * Active transport is important in many tissues, for instance primary active transport maintains the membrane potential of the neurons in the nervous system.
Its fixed
Endocytosis ? Exocytosis ?
Occurs when the cell membrane invaginates and engulfs material to bring it into the cell. * Occurs when the secretory vesicle fuse with the membrane, releasing material from inside the cell to the extracellular environment
Its fixed
Pinocytosis ? Phagocytosis ?
The Endocytosis of fluids and dissolved particles * The ingestion of large solids such as bacteria
Its fixed
Nernst equation ?
Used to determine the membrane potential from the intra- and extracellular concentrations of the various ions. {{23 1 0.png}}R is the ideal gas constant, T is the temperature in Kelvins, z is the charge of the ion, and F is the Faraday constant (96,485 C/mole e-)
Its fixed
What are the two membranes of mitochondria ? What do they do ? Mitochondrial matrix ?
- Inner & Outer mitochondrial membranes The outer one is highly permeable due to many large pores that allow for the passage of ions and small proteins. It completely surrounds the inner mitochondrial membrane, with the presence of a small intermembrane space in between two layers.
- The inner has a much more restricted permeability compared to the outer mitochondrial membrane. Enclosed by the inner membrane where the citric acid cycle produces high-energy electron carriers used in the electron transport chain. The inner membrane contains a very high level of cardiolipin and does not contain cholesterol.


