BIOCHEMISTRY Flashcards
Biochemistry is the branch of chemistry which studies
the structure, organization and interaction of the substances within living matter; the chemical processes and compounds occurring in or produced by living organisms; Biochemistry can be called the study of the chemistry of living processes. Other names for biochemistry include biological or physiological chemistry.
This unit is technically an aldehyde or ketones derivative of a polyhydroxy alcohol. It results from the oxidation of a polyhydroxy alcohol, in which their ex exists, carbon. And a 2 to 1 ratio with hydrogen and oxygen…
wha are carbohydrates?
2 MAJOR DIVISIONS OF CARBOHYDRATES
ALDOSE SUGARS KETOSE SUGAR
Carbohydrates are found in nature
True. Green plants contain CHLOROPHYLL, a photopigment that captures light energy for use in the process of PHOTOSYNTHESIS, the process by which green plants synthesize carbohydrates from CO2 and H2O. Any animal or fungi not containing chlorophyll cannot synthesize carbohydrates. This is why we have to eat our carbohydrates.
PHOTOSYNTHESIS (also called the plant phase)
6CO2 + 6H2O — Sunlight & Chlorophyll —> C6H12O6 + 6O2 Photosynthesis is carried out by plants as they take in CO2 from the air and H2O from the soil. The chlorophyll in the green leaves along with sunlight act as catalysts to make the simple sugar glucose (a carbohydrate), which is food for the plant, as well as oxygen, which is returned to the air. This process takes places in green plants in the presence of light. The chlorophyll in the plants is what gives them their green appearance therefore green plants are the key place where carbohydrates are made.
OXIDATION (animal phase).
This reaction is also known as Aerobic Cellular Respiration, and takes place in almost all types of cells to produce the energy they need to function. C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy Sugar is ingested and absorbed in the tissues from air expired through the lungs returned to the soil and air 4 Calories obtained for use
3 Main Classes of Carbohydrates
- MONOSACCHARIDES 2. DISACCHARIDES 3. POLYSACCHARIDES
MONOSACCHARIDES
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates which contain only one (1) saccharide (sugar) unit and cannot be hydrolyzed into smaller groups
HEXOSES
6 carbon monosaccharides. They all have the formula - C6H12O6 – and are all isomers of one another.
PENTOSES
5 carbon monosaccharides or sugar molecules.
GLUCOSE
found free in nature; it occurs in the juices of fruits and the sap of trees, but it is mainly known as blood sugar. In the structural formula, is the aldehyde group (CHO); therefore glucose is an aldose sugar.
GALACTOSE
An aldose sugar It is found to be a constituent of brain and nerve tissue. Galactose is not found free in nature; it is formed by the hydrolysis of lactose or milk sugar. The difference between glucose and galactose structurally is the fourth carbon. Note the position of the (OH) group.
ALDOSE SUGARS
carbohydrates that are derivatives of aldehydes (CHO). They contain the aldehyde group in addition to the polyhydroxy alcohol. An aldose is a sugar in which the functional groups are hydroxyl (-OH) groups and an aldehyde group (CHO).
KETOSE SUGARS
carbohydrates that are derived from ketones (C=O). They contain the ketone group in addition to the polyhydroxy alcohol. A ketose is a sugar whose functional groups are hydroxyl (-OH) groups and a ketone (carbonyl) group (C=O).
GLYCOGEN
Carbohydrates are polymerized as glycogen and stored in the muscles and in the liver. This is how animals / humans store sugar for later use, so glycogen is said to be stored energy or a reserve food supply in animals. Glycogen are large molecules, there can be as many as 5000 monosaccharides linked together in a molecule of glycogen starch.
FRUCTOSE
Fructose is a ketose sugar; notice the ketone group (C=O)Fructose is found free in nature in the sap of many plants, honey and in most fruits, thus the name fruit sugar Both glucose and fructose have the same chemical formula, making them isomers. However, the body has to first convert fructose into glucose as cells only run on glucose.
DISACCHARIDES
Disaccharides are those carbohydrates which contain two (2) saccharide groups disaccharides derived from two hexose monosaccharides have the formula C12H22O11. 2 C6H12O6 → C12H22O11 + H2O
LACTOSE
Lactose, also known as milk sugar is formed from the dehydration between a molecule of galactose and a molecule of glucose. Lactose may be hydrolyzed, (split apart by water), to yield galactose and glucose. Therefore lactose is made up of 1 molecule of galactose and 1 molecule of glucose. Lactose is the only sugar that cannot be fermented
SUCROSE
Sucrose is table sugar or cane sugar. It is made up of 1 molecule of fructose and 1 molecule of glucose. When hydrolyzed you get fructose and glucose.
MALTOSE
Maltose, also known as malt sugar is formed from the dehydration between two molecules of glucose. Since it is made up of two glucose molecules, when hydrolyzed you get glucose and glucose.
POLYSACCHARIDES
Polysaccharides are composed of many molecules of monosaccharides, or many saccharide groups, therefore they are called multiple sugars, complex sugars or complex carbohydrates. The prefix “poly- means many. The polysaccharides include the starches, cellulose, glycogen and agar.
STARCH
Starch is a polysaccharide used by plants to store energy. It is a polymer of glucose which can be so big they contain hundreds of glucose molecules
CELLULOSE
Cellulose is the most abundant compound in the biosphere. It is the major component of cell walls and the wood structures of plants. It is what gives plants their rigidity and ability to grow upright. The human digestive tract is unable to digest cellulose, so cellulose serves only as a bulking agent (fiber) and prevents constipation.
AGAR
Agar is cell culture media. It is what the cells live off of when they are “in culture”. When you have a throat culture done, the swab is agar. The cells collected on that swab feed off of the sugar & reproduce enough to be seen under a microscope. Germs love sugar, which is one of the reasons diabetics have such problems with recurrent infections. Agar is made up of galactose molecules, therefore it is said to be a polymer of galactose.
OXIDATION
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy oxidation of carbohydrates, also known as animal phase or the animal metabolism of carbohydrates which ultimately yields carbon dioxide and water, is the body’s chief source of energy
CALORIE
the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of H2O 1° Celsius while at 15° Celsius.
HYDROLYSIS
C12H22O11 + H2O → 2C6H12O6 The final hydrolysis products of carbohydrates are monosaccharides . We know hydrolysis as the splitting of a compound through the reaction of water. However it is important to know that water alone will not hydrolyze most sugars, each reaction will require the addition of the appropriate enzyme as well. For example the enzyme that breaks down starch is amylase
Amylase
the enzyme that breaks down starch. water alone will not hydrolyze most sugars, each reaction will require the addition of the appropriate enzyme as well
FERMENTATION
Fermentation is the chemical decomposition with the evolution of gas. The fermentation of carbohydrates is the anaerobic decomposition by microorganisms which releases the gas carbon dioxide. Fermentation is a process of making energy in a cell with no oxygen present.
Common fermentation reaction
C6H12O6 —yeast enzymes—> 2C2H5OH + CO2 glucose ethyl alcohol + carbon dioxide
Fermentation occurs in two areas of the body
- Stomach 2. Intestines
Stomach - Fermentation
Fermentation occurs in the stomach when not enough hydrochloric acid (HCl) is secreted. The HCl destroys the bacteria that give off the enzymes needed to ferment carbohydrates.
Intestines - Fermentation
Fermentation occurs in the colon when there are excess carbohydrates in the diet.
Normal Flora
Microorganisms that live in the digestive tract, called normal flora, are involved in the digestion process. They contain enzymes that act in the breakdown of carbohydrates, turning the polysaccharides they ferment into fatty acids. Fatty acids provide a major source of energy and nutrients. Since human cells lack these enzymes, without these bacteria we would be unable to break down and use some of the carbohydrates we eat.
LIPIDS
Lipids are fats and fat related substances which are formed by the interaction of an alcohol and fatty acid(s) and are named after the fatty acid in their molecule. organic salts are esters, technically lipids are types of esters. Since they are formed from an alcohol and acid. OH + COOH → COO + H2O (fatty acid) (lipid) Almost all lipids are esters that yield fatty acids on hydrolysis. COO + H2O → COOH + OH (lipid) (fatty acid)
3 types of Lipids
- Simple, 2. Compound 3. Miscellaneous or Derived Lipids
SIMPLE LIPIDS
Simple lipids are esters of fatty acids and various alcohols, which upon hydrolysis produce fatty acids and an alcohol. fatty acids are monocarboxylic organic acids that are straight chain compounds which may be saturated or unsaturated.
2 TYPES OF SIMPLE LIPIDS
A. Fats and Oils B. Waxes
Fats and Oils
Fats are the ultimate type of energy storage molecule due to the fact that the body is able to store fats in unlimited quantities and because of their high caloric value. Fats yield nine calories of energy per gram as compared to four calories per gram of carbohydrates. 1. Fats and oils are found in both animals and plants 2. Fats provide heat and protection. 3. Fats are vitamin carriers because certain vitamins are only soluble in fat 4. Fats and oils are esters of glycerol (a trihydroxy alcohol containing 3-OH groups) and fatty acids. They are sometimes referred to as glycerides
Two major categories of Fatty Acids
- Simple glycerides are those in which all of the fatty acids are the same. 2. Mixed glycerides contain more than one type of fatty acid.
3 Categories of Glycerides
- Monoglycerides which contain only one molecule of fatty acid, 2. Diglycerides which contain two molecules of fatty acids, and 3. Triglycerides are those containing three molecules of fatty acids covalently bonded to one molecule of glycerol.
SATURATED FATS
SATURATED FATS have all of the carbon atoms of their fatty acids linked by single valence bonds. Saturated fats are linked to cardiovascular disease.
UNSATURATED FATS
UNSATURATED FATS have one or more of the carbon atoms linked by double valence bonds. Unsaturated fats are more heart-healthy.
POLYUNSATURATED FATS
POLYUNSATURATED FATS are a specific case of unsaturated fats where two or more pairs of carbon atoms are linked by double bonds.
EMULSIFICATION
Emulsification is the act or process of mixing two insoluble (immiscible) liquids. Lipids are insoluble in water and need to be emulsified to become dissolved in water solutions. By using soap we have created an EMULSION of oil and water. An emulsion is a mixture of two insoluble liquids, one being dispersed throughout the other in small droplets.
EMULSIFYING AGENT
A third substance required in order to create the emulsions of oil and water or digestive fats. That third substance is known as an EMULSIFYING AGENT. It is what you add to create an emulsion. Soap is an emulsifying agent, and in our body it is bile that serves as the emulsifier. Emulsification is a physical property because the chemical composition of the fat or oil was not changed, only the size of the particles.

Triglyceride

Galactose: a monosaccharide (also am aldose sugar)
- Formed by hydrolysis of Lactose.
- Difference between glucose & galatose 4th Carbon

Glucose: Monosaccharide, Aldose sugar.
- Found in Nature in juices and sap
Also known a blood sugar
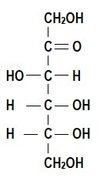
Frutose: A Ketose sugar
- monosaccharide
- sweetestnsugar ever
- found in honey and mosy sweet fruit
glucose and fructose have the same chemical structure

Unsaturated Fatty Acid:
Common in oil

Saturated Fatty Acid:


