Benign Non-Odontogenic Lesions Flashcards
Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma clinical features
3-4th decade 5:1 female predilection Common in mandible
Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma radio appearance
Well-demarcated lesion Radiolucent to mixed appearance
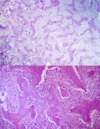
Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma histo appearance
Potato-like mass that usually comes out in one chunk Lots of connective tissue and bone/cementum interspersed. NO inflammation seen
Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma treatment
Enucleation This is a TRUE neoplasm.
Fibrous Dysplasia Types of Lesion
Polyostotic Monostotic
Fibrous Dysplasia clinical features
MAXILLA more common Bones have fracture risk because they are weaker. Can have a hockey stick discrepancy. One leg longer than the other Will see SWELLING over time. Can see expansion.
Fibrous Dysplasia radio appearance
Ground glass appearance with ill-defined borders Narrowing PDL space and the lamina dura hard to make out
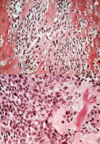
Fibrous Dysplasia histo appearance
Irregular shaped woven bone (Chinese characters) Bone has NO OSTEOBLAST around it. Distinctive feature. Bone arises in slide via metaplasia from fibroblasts Woven bone becomes more lamellar over time
Fibrous Dysplasia treatment
Resection, but not in children. Lesion will regress over time maybe to 70% of size. Remove at skeletal maturity. Radiation is CONTRAINDICATED. It may actually cause malignant transformation to osteosarcoma.
Fibrous Dysplasia age
Stage of fetal development determines if polyostotic or monostotic (MOST cases are monostotic) 1-2nd decade (YOUNGER) population
Fibrous Dysplasia types of polyostotic involvement
Jaffe Type
- Cafe au lait spots on the trunk and thigh
- Multiple bone involvements
McCune-Albright Type
- Cafe au lait spots
- Endocrine hyperfunction
- Precocious puberty
Types of cemento-osseous dysplasias
Periapical
Focal
Florid
Clinical features of periapical osseous dysplasias
14:1 Black female predilection
30-50 years old
Clinical features of focal osseous dysplasias
80% in Caucasian females
4-5th decade
Clinical features of florid osseous dysplasias
Black females
Location of periapical osseous dysplasias
Mandibular anterior
Multiple lesions
Location of focal osseous dysplasias
Posterior mandible ONE lesion
Location of florid osseous dysplasias
More than one quadrant
Radiograph of periapical osseous dysplasias
Start as RL then add more osteoid and become RO
Radiograph of focal osseous dysplasias
RL to RO. RL rim remains over time
Radiograph of florid osseous dysplasias
Multiple “cotton-wool” radiopacities
Treatment of periapical osseous dysplasias
NONE needed. No biopsy
Treatment of focal osseous dysplasias
Biopsy to rule out cemento-ossifying fibroma
Treatment of florid osseous dysplasias
MAINTAIN DENTITION. Normal alveolar bone will resorb, but dysplastic bone will not and osteomylitis could occur.