B bone tumor 2 Flashcards
what is it

osteoma
what is a hamartoma
histologically normal tissue in an abnormal location
where do osteomas develope
intramembranous bones
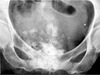
homogenously dense painless mass

osteoma
common locations for osteoma

calvarium
paranasla sinuses- esp ethmoid and frontal
*not common in maxillary
sometimes in mandible (gardener syndrome)
what is garender syndrome and what type of tumor is it assoccated with
aka familial colorectal polyposis
autosomal DOMINANT
presence of multiple polyps in colon and tumors outside the colon
extra colonic tumors: skull, thyroid cancer, epidermoid cysts, fibromas
projects from internal table of the skull

osteoma
usually _________radiodense and featureless
not ____________ unless blocking sinus

homoneously
symptomatic
frontal sinus osteoma
common sites for osteoid osteoma
50% tibia/ femur
10% spine
long bones metaphyseal or diaphyseal
_____% diagnosed before age 25
90
osteoid osteoma predelection
males 2:1
pain worse at night
relieved by asprin
long hx of pain before dx
self resolve over months/years
resection to remove
will reoccur if nidus not removed
osteoid osteoma
possbile locations of osteoid osteoma

subperosteal
intracortical
intramedullary
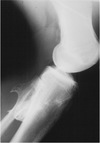
radiolucent nidus <1cm
maybe obscured by reactice sclerosis

osteiod osteoma

osteiod osteoma

osteiod osteoma

osteiod osteoma

osteiod osteoma

osteoid osteoma
one of 3 _____bone tumors that predilicts posterior elements of the spine

primary
osteoid osteoma
histological twin to osteoid osteoma
osteoblastoma
Long hx of pain; typically mos. – yrs.
´Larger, more expansile lesion
´30-50% in posterior arch of spine
´30% in long bones
´Femur and tibia most common
´Diaphyseal/metadiaphyseal location
sx
osteoblastoma
Expansile, geographic lesion
May be big; 2-12 cm dia. Matrix lucent, but may have stippled calcification
Often with sclerotic border and sharp transition zone
Usually lacks reactive dense reactive sclerosis of osteoid osteoma

osteoblastoma

osteoblastoma