Autonomic Pharmacology_1 Flashcards
Afferent and efferent divisions of the peripheral nervous system
Afferent Division
Somatic sensory
visceral sensory
Special sensory
Efferent Division
Somatic motor
Autonomic motor
(sympathetic, parasympathetic, Enteric)
Be familiar with the basic responses of target organs in response to sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation
Parasympathetic: Cranial + sacral
Sympathetic: thoracic + lumbar

Describe the lengths of neurons in the sympathetic vs. parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic = short preganglionic neurons, long postganglionic neurons
Parasympathetic = long preganglionic neurons, short postganglionic neuron

Which neurotransmitter is released at target organs by the parasympathetic nervous system
Acetylcholine
Draw the picture of the neurons with their NT and receptors
Sympathetic -> Adrenergic Muscarinic (sweat glands) tissue receptor
Parasympathetic -> Muscarinic tissue receptor
Somatic -> Nicotinic tissue receptor

What type of receptors are located at target organs of the sympathetic nervous system?
Alpha and beta adrenergic receptors

Explain the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic
- Fight or flight actions: energy mobilization, increased cardiac output and ventilation
- Thoracic and lumbar nerve roots
- Short preganglionic/long postganglionic
- Norepinephrine (NE) and epinephrine (E) are* *main* *neurotransmitters at target organs
- Alpha and beta-adrenergic receptors at target organs
Parasympathetic
- Rest and digest actions: energy storage/conservation, increased digestive secretions
- Cranial nerves and sacral roots
- Long preganglionic/short postganglionic
- Acetylcholine (ACh) is* *main* *neurotransmitter at target organs
- Muscarinic ACh receptors at target organs
Describe the sympathetic nervous system effects on the eyes and heart
EYES
alpha 1 contracts the radial muscle of the iris (widens pupil)
Beta 2 relaxes ciliary muscles (flattens lenses) for far vision
HEART
Beta 1 = SA node = increase heart rate
Beta 1 and 2 = Atria = increase contractility
Beta 1 and 2 = AV node = increases conduction velocity
Beta 1 and 2 = Ventricles = increases contractility
Describe autonomic tone
one division is usually dominant
- Ex: heart beats at ~100 beats/min with no innervation
- parasympathetic division: decreases HR
- Sympathetic division: increases HR
- sympathetic effect (vagal tone) dominates, so resting HR is ~70 BPM
What are blood vessels primary served by?
sympathetic nervous system (alpha adrenergic receptors)
How does an increase in sympathetic activity affect blood vessels?
vasoconstriction
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
terminates signal by breaking down ACh
Muscarinic receptors are activated by
parasympathetic nervous system (ACh)
Explain the function of a synapse
- Neurotransmitter synthesized and packaged in vesicles
- Action potential arrives, carried by voltage-gated Na channels
- Voltage-gated Ca channels open
- Exocytosis of neurotransmitter
- Neurotransmitter binds to receptors; activation of receptors results in ion influx or second messenger formation
- Neurotransmitter is enzymatically degraded or pumped into presynaptic neuron
- Degradation of second messenger

Ways that a drug can increase the activity of a synapse
- Increase neurotransmitter release into the synapse
- Reduce reuptake of the neurotransmitter from the synapse
- reduce degradation of the neurotransmitter in the synapse
- mimic activity of a neurotransmitter at its receptor

Ways that a drug can decrease the activity of a synapse
- block a neurotransmitter’s receptor
- inhibit of synthesis of a neurotransmitter
- prevent the release of a neurotransmitter
- prevent packaging in vesicles

Even numbered muscarinic receptors
Coupled to Gi proteins
Results in decreased cAMP
typically inhibitory affect
Odd numbered muscarinic receptors
paired to Gq receptors, leads to smooth muscle contraction
Describe PSNS neurotransmission
ACh released at target organs to activate muscarinic receptors
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) terminates signal by breaking down ACh

Explain Muscarinic receptors
Muscarine: a mushroom toxin that activates muscarinic receptors, symptoms resemble extreme PSNS activation
- Five M receptor subtypes, M1 - M5
- Even numbered couple to Gi
- Odd numbered couple to Gq
Nicotinic cholinergic receptors
cause depolarization
excitatory

How can muscarinic receptors be indirectly activated?
by inhibiting AChE

Explain the general drug mechanisms with PSNS
- Activate M receptors directly
- Activate M receptors indirectly by inhibiting AChE
- Block M receptors
- Inhibit ACh release
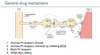
Drugs that enhance parasympathetic nervous system signaling
Parasympathomimetics or cholinomimetics









