Antithrombotic Drugs Flashcards
Which drug is an angiotensin receptor blocker?
losartan
Describe the process of clot formation, including the actions of platelets and clotting factors
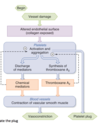
- Clot formation begins with subendothelial matrix exposure due to damaged vessel wall that exposes underlying endothelial proteins that are not normally exposed (ie. collagen and TF)
- Platelet adhesion and activation
- forms a platelet plug
- platelets start to make ADP and TxA2 (thromboxane)
- now a feedforward action starts where more platelets come in and form clot
- Coagulation cascade
- receptors on the cell membrane that grab onto fibrinogen that ultimately form the clot and go from fibrinogen precursor to fibrin that forms the clot
- Thrombin will then take fibrinogen to fibrin which is the active form. It will form the mesh and contain the platelet plug
- T-PA = tissue plasminogen activator. Plasminogen will come in later and break down fibrin to dissolve the clot away

- Binding of platelets to collagen causes activation of what?
Binding of platelets to collagen causes activation:
- Release of chemical mediators: ADP and TXA2
- Change in surface receptor expression: grabs onto fibrinogen
- Become more sticky: sticks to each other and the wall
Activated platelets aggregate: stick to each other; forming a plug

What do ADP and thromboxane A2 cause?
ADP and thromboxane A2 cause further platelet activation and trigger vasoconstriction
What is the function of aspirin and how does it inhibit clot formation?
aspirin inhibits cyclooxygenase which makes TXA2 (thromboxane A2)
Therefore aspirin is an antithrombin drug
Recall: ADP and thromboxane A2 cause further platelet activation and trigger vasoconstriction

How does actin and myosin play a role in clot formation?
Platelets have actin and myosin - contract to close damaged vessels
Once platelets get activated they will pull the actin and myosin to create the plug

Explain coagulation
coagulation
enzymatic steps converge on thrombin, which converts fibrinogen to fibrin (leads to stable clot)
Factor X = prothrombin to Factor Xa = thrombin (active form)
Factor XIII: makes the fibrin mesh = Crosslinked fibrin is broken down by the enzyme plasmin in order to dissolve a stable clot

T/F RBCs are not required to make a clot?
TRUE
Clots in slower moving blood cause them to trap RBC BUT RBC ARE NOT REQUIRED to make a clot!!!!
only platelets are necessary to form a clot
White clot: artery clots
- faster blood flow = platelet-rich
- coronary vessels then an antiplatelet drug is a good choice because they are mainly the activation of platelet clots
Red clot: venous clot
- Sitting for a long time you can get DVT with stasis of blood that involves platelet and clotting factors where there are higher level of clotting factors vs. platelets
- therefore drugs that target the clotting factors are the better drug
What is an embolus vs. embolism
Embolus: a clot moving through to body
Embolism: when the embolus gets lodged in a vessel (ie. lungs)
What are the reasons for taking antithrombin drugs for clot prevention when vascular endothelial cells are disrupted?
- clot prevention when vascular endothelial cells are disrupted
- Atherosclerosis - plaque forming in the arteries that can rupture and cause clot formation
- Stents - the stent in the area causes disruption of the endothelium
- Bypass surgery - working with the BV directly
What are the reasons for taking antithrombin drugs for clot prevention when other risk factors are present
- previous stroke, MI or deep vein thrombosis
- atrial fibrillation (disorganized atrial contraction)
- cardiomyopathy (disease of the heart muscle)
What are antithrombin drug targets for antiplatelet drugs
Antithrombic drug targets
- Antiplatelet drugs: decrease platelt activation/plug formation
- ADP receptor antagonist: clopidogrel (Plavix)
- TXA2 synthesis inhibitor: aspirin
What are antithrombin drug targets for anticoagulants
Antithrombotic drug targets
Anticoagulants: decrease clotting factor activity
- Decrease synthesis of clotting factors: Warfarin (coumadin)
- inhibit factor Xa (thrombin): apixaban
- Inhibit thrombin: dabigatran
- inhibit the action of multiple clotting factors: heparin
inhibit thrombin
dabigatran
inhibit factor Xa
apixaban
inhibit action of multiple clotting factors
heparin
ADP receptor antagonist
clopidogrel (plavix)
antiplatelet drug

decrease synthesis of clotting factors
warfarin (coumadin)
anticoagulant
TXA2 synthesis inhibitor
aspirin
antiplatelet drug

Explain the action of aspirin
what are the adverse effects of aspirin?
inhibits cyclooxygenase - 1 (COX-1), which is required in the pathway to synthesize TXA2 from arachidonic acid
-
COX-I is ubiquitous but low doses (baby aspirin) are more selective for platelets
- due to aspirin has an irreversible quality to it and therefore aspirin is the best antiplatelet medication vs. other anti-inflammatory medications that also target the same receptors but are doing it in a reversible way
- GI symptoms (heartburn, ulcers) are most common adverse effect
- Must weigh risks/benefits with regard to daily prophylactic use (mainly only for those who have already had stroke or heart attack)
Explain the action of Clopidogrel
aka Plavix
-
Irreversibly blocks the P2Y12 (ADP) receptor expression by platelets
-
ADP is a signaling molecule that is produced during platelet activation and therefore it is used for a signaling molecule during platelet aggregation
- the platelets cannot restore the function after the receptor has been inhibited
-
ADP is a signaling molecule that is produced during platelet activation and therefore it is used for a signaling molecule during platelet aggregation
-
Synergistic effects when taken with aspirin
- = EXTREME INHIBITION OF CLOTTING
- Bruising, bleeding most common side effect

Factor IIa = ?
Factor IIa = thrombin (activated form)
vs. Factor II = prothrombin
which is activated by Xa
Explain the Warfarin mechanism
- Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase produces active clotting factors
- Vit. K is a cofactor* that gets *oxidized* in this reaction and *must be reduced in order to be used again
- This step is performed by vitamin K reductase, which is blocked by warfarin

What is prothrombin time?
most related with warfarin
Common lab test to measure ability of blood to clot
-
Tissue factor added to* *patient* *sample,* *timed* *until a clot forms
- often expressed as international normalized ratio (INR), which is a ratio of patient’s clotting time to normal reference value
- INR = 1 = normal
- INR = 2 = longer to clot (2x longer)
- often expressed as international normalized ratio (INR), which is a ratio of patient’s clotting time to normal reference value
-
Higher INR means decreased ability to clot - patients with high likelihood of clotting are purposely kept at elevated INR
- this is how warfarin is titrated for the dose and you want to frequently ccheck the dose



