Atlas A: General Orientation to Human Anatomy Flashcards
What are the systems of protection, support, and movement?
- Integumentary System
- Skeletal System
- Muscular System
What are the systems of internal communication and control?
- Nervous System
- Endocrine System
What are the systems of fluid transport?
- Circulatory System
- Lymphatic System
What are the systems of intake and output?
- Respiratory System
- Urinary System
- Digestive System
What are the systems of reproduction?
- Male Reproductive System
- Female Reproductive System
What are the principal organs of the integumentary system?
- Skin
- Hair
- Nails
- Cutaneous Glands
What are the principal organs of the skeletal system?
- Bones
- Cartilages
- Ligaments
What are the principal organs of the muscular system?
-Skeletal Muscles
What are the principal organs of the lymphatic system?
- Lymph nodes
- Lymphatic vessels
- Thymus
- Spleen
- Tonsils
What are the principal organs of the respiratory system?
- Nose
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Lungs
What are the principal organs of the urinary system?
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra
What are the principal organs of the nervous system?
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Nerves
- Ganglia
What are the principal organs of the endocrine system?
- Pituitary gland
- Pineal gland
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid gland
- Thymus
- Adrenal glands
- Pancreas
- Testes & Ovaries
What are the principal organs of the circulatory system?
- Heart
- Blood vessels
What are the principal organs of the digestive system?
- Teeth
- Tongue
- Salivary glands
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Large & Small intestines
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
What are the principal organs of the male reproductive system?
- Testes
- Epididymides
- Spermatic ducts
- Seminal vesicles
- Prostate
- Bulbourethral glands
- Penis
What are the principal organs of the female reproductive system?
- Ovaries
- Uterine tubes
- Vagina
- Mammary glands
What is included in the axial region?
- Head
- Neck (cervical region)
- Trunk
Where and how is the trunk divided?
The trunk is divided into the thoracic region above the diaphragm and the abdominal region below it.
Desribe the layout of the quadrants and name each of the nine sections.
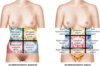
What two lines split the abdominal region vertically and what two lines split the adbominal region horizontally (Superior and Inferior?
Vertical: Midclavicular Line
Horizonal
Superior - Subcostal Line
Inferior - intertubercular line
Where can the abdominal region be split by two perpendicular lines at?
Umbilicus (Navel) divide
What is included in the appendicular region?
Upper & Lower Limbs
What is a part of the upper limb?
- Arm (Brachial region) (shoulder to elbow)
- Forearm (Antebrachial region)
- Wrist (Carpal region)
- Fingers
- Hand
What is a part of the lower limbs?
- Thigh (femoral region)
- Leg (crural region) Knee to ankle
- Ankle (tarsal region)
- Foot
- Toes\
What is a segement of a limb?
It is a region between one joint and the next
What does viscera mean?
The organs contained in the body cavities, such as the brain, heart, lungs, stomach, intestines, & kidneys.
What is the visceral?
(Pertaining to viscera)
The inner or deeper layer of a two-layered memrane such as the pleura, oericardium, or glomerular capsule.


