Assessment Final UPDATE Flashcards
(107 cards)
Which cranial nerves control the extraocular muscles (EOM)?
- Oculomotor (III),
- Trochlear (IV)
- Abducens (VI),
Documenting Heart Sounds x4
- Frequency/Pitch
- Intensity/Loudness
- Duration
- Timing: systole/diastole
How often should males 15 y/o+ do a testicular self exam?
Once a month
skin normal findings seen mostly in infants? x3
- Cafe Au Lait Spot
- Mongolian Spot
- Lanugo
Where is the most common site for breast tumors
upper outer quadrant
Striae which occur when elastic fibers in the reticular layers of the skin are broken after rapid or prolonged stretching, have a distinct color when of long duration. What is this color?
Silvery White

- Keloid
- hypertrophic scar
- elevetated skin by excess scar tisue
Straightening a limb at a joint
extension
All Patients Take Meds..
- Aortic (2nd Rt, ICS)
- Pulmonary (2nd Left, ICS)
- Tricuspid (Lt lower sternum)
- Mitral (5th ICS midclavical)

What is the best position for inspecting the breasts for retraction?
Sitting with hand pushing onto hips
Turning the forearm so the palm is up
supination
Cranial Nerve Mneumonic Sensory, Motor or Both
- Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Bad Business Marry Money
degeneration of joint cartilage and the underlying bone, most common from middle age onward. It causes pain and stiffness, especially in the hip, knee, and thumb joints.
Osteoarthritis

- Keloid
- hypertrophic scar
- elevetated skin by excess scar tisue

- Polycyclic
- i.e. psoriasis
- anular lesions grow together
A newborn’s nail beds may be blue (cyanotic) for the first few hours of life, then they turn what color?
pink
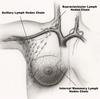
Define a Lymph Node
- Small oval clumps of lymphatic tissue located at intervals along the vessels.
- Filter fluid before returned to bloodstream
- remove harmful organisms.

Compound Nevus
Which of the following options is not a change that comes with menopause?
- The vaginal pH becomes more alkalotic
- The vagina becomes shorter and narrower
- The cervix shrinks
- The ovaries hypertrophy

junctional nevus

- Scale
- compact flakes of skin
Characteristics of Osteoarthritis?
- Joints ache and may be tender but have little or no swelling.
- Symptoms often begin on one side of the body and may spread to the other side.
- Onset develops slow over the years
During assessment of the spine, what do you ask the patient?
- Flex
- Extend
- Abduct
- Rotate
A murmur heard after S1 and before S2 is classified as
systolic (possibly benign)