Arrhythmias & ECGs Flashcards
What is the likely diagnosis if a patient has a history of palpitations, has had one TIA and presents to A&E after a holiday?
A. Fib
What is the likely diagnosis if a patient presents with a history of SOB on exertion, and several episodes of syncope?
Aortic stenosis
What is this ECG showing

Asystole
What is this ECG showing

NSTEMI
What is this ECG showing
STEMI

What is this ECG showing

Ventricular tachycardia
What is this ECG showing

Ventricular fibrillation
(proper fucked bro)
What is this ECG showing

Atrial fibrillation
(no p-waves)
What is this ECG showing
1st degree heart block

What is this ECG showing

2nd degree heart block
What is this ECG showing

3rd degree heart block
What bpm is tachycardic in a healthy 20yo man
100bpm
What are some treatments for arrythmias
Amiodarone
Pacemaker
What is the pathway of heart conduction
SAN
v
AVN
v
Bundle of His
v
Purkinje fibres

What is the term for normal heart rythm
Sinus rythm
What stage of heart conduction is shown on:
a) P-wave
b) QRS complex
c) T-wave
d) PR interval
e) ST segment
f) QT interval
g) U-wave

a) atrial depolarisation
b) ventricular depolarisation
c) ventricular repolarisation
d) AVN delay (end of p-wave -> start of q-wave)
e) time between depolarisatoin and repolarisation
f) time taken for ventricular depolairsation and repolarisation
g) repolarisation of papillary muscles and purkinje fibres
What wave on an ECG is not always present but shows repolarisation of papillary muscles and purkinje fibres
U-waves

On an ECG, how many seconds is their in a small and a large box
Small -> 0.04s
Large -> 0.2
How do you work out the rate in an ECG
300/(number of big sqaures between QRS complexes)
(obvs you know that one big sqaure is 0.2s)
A broad QRS complex is a sign of what ECG abnormality
Ventricular tachycardia
What do you look for in interpreting an ECG

ARI BAR
Any electrical activity
Rate
Irregualr or regular rythm
Broad QRS complexes
Absent P-waves
Relationship beteen P-waves and QRS complexes
Before interpreting an ECG, what should you always observe first
The bloody patient
Absent p-waves are a sign of what
Ventricualr tachycardia
A. fib
What phenomeon is characterised by a gradually increasing PR interval
Weckenbach phenoneon
(AKA 2nd degree heart block)

When p-waves and QRS complexes don’t match up, what is the likley ECG abnormality
3rd degree heart block
When analyzing a rhythm strip, it qualifies as being regular when
A. the QT intervals are the same
B. the PR interval measures the same
C. the QRS complexes measures the same
D. the R - R intervals measure the same
D
Which of the following steps is not one of the five-steps of rhythm analysis?
A. PR interval measurement
B. Rhythm regularity
C. QT Interval
D. QRS complex measurement
C
Which of the following is considered normal range of the QRS complex?
A. 0.12 - 0.20 minutes
B. 0.06 - 0.10 minutes
C. 0.12 - 0.20 seconds
D. 0.06 - 0.10 seconds
D
Which of the following is considered normal range of the PR interval?
A. 0.12 - 0.20 minutes
B. 0.06 - 0.10 minutes
C. 0.12 - 0.20 seconds
D. 0.06 - 0.10 seconds
C
Which feature is most closely associated with ventricular arrhythmias?
A. Narrow QRS complex
B. PR interval measuring greater than 0.20 seconds
C. Absence of P waves and wide & bizarre QRS complexes
C
Which rhythm presents with regularly occurring P waves and a total absence of QRS complexes?
A. Ventricular Fibrillation
B. Ventricular Tachycardia
C. Ventricular Asystole
D. Asystole
C

Select the heart rate most closely associated with this tracing.
A. 200
B. 166
C. 100
D. 87

B
(its ventricular tachycardia)
mon the glasgow
celtic
What is the PR interval measurement in this tracing?
A. 0.12 sec
B. 0.42 sec
C. No PR interval to measure
D. 0.68 sec
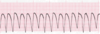
C
What would be the most proper description of the pattern of the activity in this tracing?
A. Regularly Irregular
B. Constant
C. Absent
D. Irregular

D


