Anemias Flashcards
(74 cards)
What is Plummer-Vinson Syndrome?
(1) Iron deficiency anemia with (2) esophageal web and (3) glossitis
Where is iron absorbed?
The duodenum via DMT1 receptors
How does iron get absorbed?
(1) Transported across enterocytes by ferroportin (2) Carried in blood by transferrin (3) Stored in liver and bone marrow macrophages by ferritin







What is an adaptation to slow loss of blood?
Increase in 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate, decreasing Hb affinity for oxygen to allow increased oxygen delivery to tissues
What are four causes of non-megaloblastic macrocytic anemia?
(1) Aplastic anemia
(2) Chronic liver disease
(3) Alcoholism
(4) Reticulocytosis
What are causes of megaloblastic macrocytic anemia?
(1) B12 deficiency
(2) Folate deficiency
(3) Myelodysplasia
(4) Erythroleukemia
(5) Drugs
(6) Orotic aciduria
What is performed in the initial lab assessment?
(1) CBCs
(2) Reticulocyte count
(3) Peripheral blood film exam (to identify abnormalities in number, morphology, or maturity)
What are four causes of iron deficiency anemia?
(1) Inadequate intake
(2) Increased need (pregnancy, infancy, pubertal growth)
(3) Decreased absorption
(4) Blood loss
What is the term for spoon shaped nails from IDA?
Koilonychia
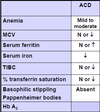
How is IDA diagnosed?
(1) Low serum ferritin
(2) Low serum iron
(3) High TIBC
(4) Low transferrin saturation
What are the three stages of IDA?
(1) Iron deficient state (ID) - low ferritin
(2) Iron deficient erythropoiesis - serum iron, TIBC, %Tf sat, and RDW changing
(3) Iron deficiency anemia - decreased Hb, Hct, MCV, increased retic
How long after oral iron therapy does the reticulocyte count go up?
1 week
What happens in anemia of chronic disease?
Due to inflammatory state, (1) hepcidin goes up, which (2) blocks ferroportin and (3) inhibits erythropoiesis, (4) trapping iron in liver and bone marrow macrophages
What are the four major causes of sideroblastic anemia
(1) Congenital defect
(2) Alcoholism
(3) Lead poisoning
(4) Vitamin B6 deficiency
What step of protoporphyrin synthesis does congenital sideroblastic anemia involve?
Defective aminolevulinic acid synthetase (succinyl CoA to aminolevulinic acid, vit b6 as cofactor)
What does aminolevulinic acid dehydrogenase (ALAD) do?
Converts aminolevulinic acid to porphobilinogen
What attaches protoporphyrin to iron to create heme?
Ferrochelatase
What is the process of protoporphyrin synthesis?
(1) Succinyl CoA to ALA by ALA synthetase with vitamin B6 cofactor (rate limiting, affected in congenital sideroblastic anemia)
(2) ALA to porphobilinogen by ALA dehydrogenase
(3) Porphobilinogen to protoporphyrin in many steps
(4) Protoporphyrin to heme by ferrochelatase within mitochondria
Why does lead poisoning cause sideroblastic anemia?
Lead inhibits ferrochelatase and ALAD, leading to build up of ALA
What characteristic cells are seen in sideroblastic anemia?
Ringed sideroblasts with iron-laden mitochondria surrounding the nucleus







