Anatomy semester two Flashcards
Describe the muscle innervation of the toungue ?

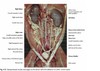
Muscles of the toungue

Extrinsic muscles
yellow = styloglossus
green = hyoglossus, attachment of the toungue
pink = genioglossus
Intrinsic muscles of the toungue
Proper lingual muscle
Describe the sensory and motor innervation of the toungue ?
Inervation
Sensory = lingual nerve and glassopharngeal nerve
Motor = hypoglossal nerve
Describe the structure and topography of the toungue ?
Toungue
- apex cranial part free and highly mobile
- body fixed thick
- caudal part fixed and attached to the hyoid bones, soft palate and the pharynx

Describe the topography of the heart ?

Heart
- lies between the 3rd and the 6th rib
- it is located between the two lobes of the mediastinum
- The base lies more dorsally, and the apex more ventrally
- The left face of the heart lies caudally
- the right side of the heart lies cranially
- the heart lies above the sternum just infront of the diaphragm
- in domesticated species its lies more to the left than the right

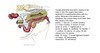
Describe the structure of the right face of the heart externally ?

Right face of the heart
The right side of the heart provides the small circulation of deoxygenated blood into the lungs.
Right atrium
- receives the cranial and caudal vena cava on the right side (large orifices without any valve)
- floor almost entirely occupied by the right atrioventricular orifice and tricupsid valve
Right ventricle
- two compartments pulmonary infundibulum and atrioventicular chamber
- right atrioventricular orrifice tricupsid valve
- pulmonary orifice semilunar valves
- blood exits through the pulmonary artery

Identify the structures numbered on the right side of the heart ?

- 1 right ventricle
- 9 cranial vena cava
- 14 caudal vena cava
- 7 aorta
- 10 and 11 left and right pulmonary arteries
- 13 left azygous vein

Describe the structure of the left external heart ?
Left side of the heart
Left atrium
- receives the orifices of five-six large pulmonary veins
- floor almost entirely occupied by the left atrioventricular orifice
Left ventricle
- two compartments the atriventricular chamber and the aortic infundibulum
- aortic orifice bicupsid valves

Identify the structures on the left side of the heart ?

- 10 left and right pulmonary arteries
- 11 left and right pulmonary veins
- 12 left azygous vein
- 7 aorta
- 8 ligamentum arteriosum

Describe the division of the ventricles ?
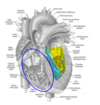
The medial and lateral division of the ventricles
Atrioventricular chamber
- veinous chamber yellow
Aortic infundibulum
- aortic chamber
- leads to the aortic orifice
- blue
Describe the structures within the heart ?

Heart inside
- yellow chordae tendinae
- green papillary muscle
- blue cusp of atrioventricular valve
- note right auricle above atrioventricular valve
- orange trabeculae carnae
- pink semilunar valve
craniolateral view of the internal right face of the heart.

Describe the location of the fossa ovalis ?

The fossa ovalis
It is a depression (Fossa ovalis) a remnant of the foramen ovale from. It is a communication between the right and left sides of the heart. In fetal life it allows the blood to bypass the pulmonary circulation as at this time the lungs are unfunctional.

Describe the three tissues which constitute the heart ?
- Fibrous structures (connective tissue
- myocardium
- nodal tissue (special nervous tissue)
Describe the layers of the pericardium ?

The layers of the pericardium
- 1 heart
- 2 great vessels
- 3 visceral pericardium
- pericardial cavity
- 5 parietal pericardium
- 6 connective tissue layer of the pericardium
- 7 mediastinal pleura
- 8 sternopericardial ligament

Describe the topography and structure of the nose ?

The nose
- The nostrils nares are the openings above the upper lip on each side of the surface called the nose
- nasal vestibule = entrance to each nasal cavity
- Horse = nasal diverticulum (cul de sac) false nostril
- cartiliginous skeleton strengthens openings, muscle and skin
- animal may increase and deacrease size of apetures
- nasal septum = median wall.

Describe the function, structure of the nasal cavity ?
Structure of the nasal cavity
- ensures the passage of air and is the site of olfaction
- the structure is bone and cartilage
- lined by the nasal mucosa (pituitary membrane)
Structure
- olfaction
- thermoregulation, filter, humidity (condition the air)
- respiration
- pheromone, behaviour
- Vomero nasal organ - detects pheromones

Identify the nasal cartilages in the nose ?

dorsal lateral nasal cartilage
alar plate of cartilage
ventral lateral nasal cartilage

Describe the topography of the nasal cavity ?
Topography of the nasal cavity
- There are two nasal cavities seperated by a median partition the nasal septum
- seperated from the oral cavity by the hard palate ( maxillary, incisive and palatine bone.
- corresponds with the nasopharynx through the corresponding choanae.
- contains anfractious annexes (which give attachment for the paranasal sinuses.)
- Nasal choncae define longitudinal gutters called meatus.

Identify the following structures within the nasal cavity ?

Identify the following structures of the nasal cavity ?
- dorsal meatus
- middle meatus
- ventral meatus
- ethmoid
- pharynx
- dorsal nasal chonae
- ventral nasal choncae

Describe chonchae ?

Nasal choncae
- thin coiled bone blades, supplemented by cartilage and lined by the nasal mucosa
- simple choncae delimit the narrow recess that communicates with the nasal cavity where air can circulate freely
- increases surface area
Bulla - if the coiled blade is joined to itself forming a cavity it is named bulla
There is a dorsal, ventral and middle choncae

Describe the nasal meatus ?

Nasal meatus
- Longitudinal gutters
- 1 dorsal, 1 ventral and one middle
- communicate along the medial side of the nasal septum by a vertical gap the common nasal meatus
- The middle nasal meatus is located between the dorsal and ventral nasal choncae, and ends caudally at the entrance of the ethmoid bone.

Name the paranasal sinuses of the dog, horse and Ox ?
Paranasal sinuses

Horse = 5 frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, rostral, maxillary and caudal maxillary
Ox = 4 frontal , sphenoid, ethmoid and maxillary sinus
Dog = 3 frontal, sphenoid and maxillary
What are the paranasal sinuses ?

Paranasal sinuses ?
The paranasal sinuses are anfractious cavities that are attached to the nasal cavities and communicate with them.
They are carved into the bones of the head and arranged around the ethmoid bones.
- lighten the bones of the head
- structural bony elements protect the brain and sensory organs
- allow for the conditioning of inspired air
- increase olfactory mucosa surface area in carnivores.

Describe the uniqueness of the equine choncae ?
Equine choncae

Dorsal nasal choncae not weel developed, but very long. Its caudal part forms the dorsal choncal sinus that communicates with the frontal sinus.
Middle nasal choncae not very well developed. Has a bulla conformation and dose not open into the middle meatus.
Ventral nasal choncae (maxillary choncae) developed but short. Its caudal part forms a ventral conchal sinus, that communicates with the rostral maxillary sinus forming its medial compartment.
Describe the uniqueness of the equine meatus ?

Equine meatus

Dorsal meatus = is very narrow
Middle meatus = caudally there is a narrow sinuso-nasal slot which caudal and rostral parts communicate with the caudal and rostral maxillary sinus.
Ventral equine meatus = height and width make it the preferred site for the naso gastric tube in the horse.