Anatomy of the Viscerocranium Flashcards
What are the 3 functional regions of the Viscerocranium?
Orbits , Nasal Cavity, and the Oral Cavity
What bones are associated with the Viscerocranium?
Maxilla (2), Palatine (2), Lacrimal (2), Inferior conchae (2), Vomer, Mandible, Hyoid
What are the 4 surfaces of the maxilla?

- Facial – forms the upper face
- Infratemporal – anterior wall of the infratemporal region
- Orbital – floor of the orbit
- Nasal – lateral wall of the nasal cavity
What are the 4 PROCESSES of the Maxilla?
- Alveolar – sockets & bone for the maxillary teeth
- Zygomatic – apex of the pyramid, contributes to arch
- Frontal – projects upward to form lateral support of nose
- Palatal – horizontal shelf from medial aspect, roof of oral cavity, floor of nasal cavity
Identify the features of the Maxilla:
- Orbital margin
- Anterior lacrimal crest
- Infraorbital foramen
- Nasal margin
- Anterior nasal spine
- Incisive fossa
- Canine ridge
- Canine fossa
- Buttress
- Posterior superior alveolar foramina
- Maxillary tubercle
- Inferior orbital fissure
- Posterior superior alveolar foramina
- Maxillary tubercle
- Inferior orbital fissure

- Orbital margin – inf & medial margin of orbit
- Anterior lacrimal crest – depression for nasolacrimal duct with lacrimal bone
- Infraorbital foramen – infraorbital nerves & vessels
- Nasal margin – anterior nasal aperature
- Anterior nasal spine – nasal support
- Incisive fossa – overlying roots of incisor teeth
- Canine ridge – overlying canine tooth
- Canine fossa – concavity distal to canine ridge, upward extension to infraorbital foramen 9. Buttress – extension from 1st molar to zygoma
- Posterior superior alveolar foramina – PSA nerves & vessels
- Maxillary tubercle – convexity behind 2nd molar
- Inferior orbital fissure – superior aspect of the infratemporal surface, cleft b/w maxilla and sphenoid bone (sup), Infraorbital nerve & vessels, zygomatic n br of CN V2
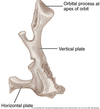
Where are the 3 processes of the palatal bone located?
- Orbital – articulates with sphenoid and ethmoid bones to form a portion of the posterior, medial orbital floor
- Vertical plate – forms a portion of the lateral walls of the nasal cavity
- Horizontal plate – forms posterior hard palate
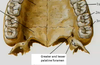
the palatal bones form 2 sutures and have 2 foramen , what are they?
The horizontal plates at the midline form the Median palatine suture
Articulation with the palatal portion of the maxilla forms the Transverse suture
Greater palatine foramen • Transmits the GP nerve and blood vessels to the hard palate • Landmark for a GP nerve block •
Lesser palatine foramen • Transmits the LP nerve and blood vessels to the soft palate
What are the 3 processes of the zygomatic bone?
- Frontal – superiorly w/ frontal bone
- Maxillary – inferiorly w/ maxilla
- Temporal – posteriorly with zygomatic process of temporal bone – “zygomatic arch”

Describe the Facial, Orbital and Temporal features of the Zygomatic bone.

- Facial – prominence of the cheek
- Orbital – lateral & inferior orbital margins, projection of lateral orbital wall and floor
- Temporal – curved medial aspect of temporal fossa
What are the names of the foramen located on the zygomatic bone?
What nerves are associated with these foramen?
Zygomaticofacial foramen – ZF nerve & artery (CN V2); facial aspect
Zygomaticotemporal foramen – ZT nerve & artery (CN V2); temporal aspect

Name the 5 features of the lacrimal bone.

- Orbital surface – medial orbital wall
- Nasal surface – lateral wall of nasal cavity
- Lacrimal sulcus – w/ frontal process of the Mx, lacrimal sac
- Posterior lacrimal crest – attachment of orbital septum
- Nasolacrimal duct formed at the junction of the lacrimal and maxillary bones

Describe the 4 main features of the nasal bone.

- Facial surface – nasal bridge
- Nasal (inner) surface – anterior ethmoidal nerve
- Superior border – w/ frontal bone – nasion
- Inferior border – upper lateral nasal cartilages

Describe the 3 processes of the inferior nasal concha.
- Maxillary process – over maxillary ostium, part of medial wall of Mx sinus
- Lacrimal process – medial wall of bony nasolacrimal canal
- Ethmoidal process – inferior border of hiatus semilunaris w/ ethmoid bone
Identify the location of the 3 borders of the Vomer as well as the location of the groove and its purpose.

- Anterior border – entire post. Nasal septum
- Posterior border – sup. 1/2 articulates with vertical plate of ethmoid bone, inf ½ articulates with cartilaginous septum
- Inferior border – articulates with nasal crest of maxilla (ant) & palatine bone (post)
- Groove for nasopalatine nerve & sphenopalatine artery – either side of vomer, towards incisive canal

Identify the 3 structures which make up the Nasal Septum.

- Septal cartilage • representing the movable portion
- Vertical plate of the ethmoid bone • contributes to the anterosuperior portion
- Vomer • contributes to the posteroinferior portion

On either side of the nasal septum are the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.
What sinus is located lateral to the upper half of the nasal cavity?
What sinus is located lateral to the lower half of the nasal cavity?

the Ethmoid sinuses lie lateral to the upper half of the nasal cavity.
The Maxillary sinuses lie lateral to the lower half of the nasal cavity.
What are the names of the bony projections which extend into the nasal cavity?
what are the air spaces between them called?
what is the name of the space above the most superior of these structures?

the bone projections which extend into the nasal cavity are called Turbinates (sup., middle, inf.)
Below each turbinate is a space termed the meatus
Above the Superior turbinate is the Sphenoethmoidal recess

the paranasal air sinuses drain into the nasal cavity through _________________
Ostia
the ____________ is a curved depression in the Middle meatus, the superior opening drains the _______, while the inferior opening drains the ______________.
the Hiatus semilunaris, is a curved depression in the Middle meatus, the superior opening drains the frontal sinus, while the inferior opening drains the maxillary sinus.

what is the Bulla ethmoidalis? what causes it? what does it drain?
Swelling on the superior border of the hiatus semilunaris caused by bulging of the ethmoidal air cells
Drains the anterior ethmoidal air cells
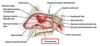
posterior ethmoidal air cells drain into the nasal cavity through what opening?

several openings in the lateral wall of the superior meatus

where is the sphenoethmoidal recess? what is its significance?
Sphenoidal air sinuses drain via the sphenoethmoidal recess

When you cry your nose gets runny, why?
This is because tears drain into the nasolacrimal duct which is connected to the inferior meatus.
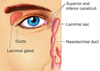
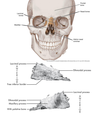
Name andIdentify the location of the paranasal sinuses.


Where do the frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal and maxillary sinuses drain into the nasal cavity?
Frontal- located in frontal bone, drain to the middle nasal meatus
Ethmoidal- Small, variable numbered sinuses located in the lateral mass of the Ethmoid bone • Anterior, Middle and Posterior • Posterior Sinus drains to the superior meatus • Anterior and Middle sinuses drain to the middle meatus
Sphenoidal- Located in the body of the Sphenoid bone • Paired sinuses which drain to the superior aspect of the superior nasal concha
Maxillary- Located in the right and left maxilla • Anterior extent is to the canine or 1st premolars • Inferior to the orbit • Lateral to the nasal cavity • Drain to the middle meatus
Label/ Identify the indicated parts of the mandible.
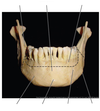

label the features of the mandible.

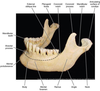
Label the lingual aspect of the mandible.

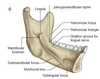
Where is the hyoid bone located?
describe its shape and features.
Located between the larynx and mandible
• Connects the oral cavity in front with the pharynx behind and the larynx below
U-shaped suspended bone •
• Composed of a body region, two lesser and two greater wings
-Supports the attachment of the Supra- and InfraHyoid musculature



