Anatomy of the Neurocranium (bones) Flashcards
How many bones make up the Neurocranium?
The Neurocranium is made up of 8 bones in total:
- Frontal
- Parietal (2)
- Temporal (2)
- Occipital
- Sphenoid
- Ethmoid
The cranial base/floor is made up of what bones?
All except the Parietal:
Frontal, Ethmoid, Sphenoid, Occipital and Temporal bones
What is a process?
Any prominence on a bony surface.
What is a condyle?
a relatively large, convex prominence, usually involving a joint.
What is a tuberosity?
a large, rough
prominence of bone.
what is an arch?
a bridge-like structure witha bowlike outline
what is a cornu?
hornlike prominence of bone.
what is a tubercle/eminence?
a rounded elevation of bone.
what is a crest?
prominent roughened border/ridge.
what is a “Line”?
a straight, small ridge
what is a spine?
abrupt, blunt/sharp pointed projection of bone.
what is a foramen?
short windowlike opening in bone
what is a canal?
long, narrow tubelike opening in bone.
what is a meatus?
type of canal
what is a fissure?
narrow cleftlike opening in bone
what is an ostium?
an entrance into a hollow organ or canal.
what is an aperature?
another type of opening or orifice
Skeletal Articulatiions
What is an Articulation?
What is a suture?
- An Articulation is an area of the skeleton where the
bones are joined to each other and can be movable or an immovable type of joint.
-A suture is the union of bones joined by fibrous tissue. fissures are often immovable, but can provide
mechanical protection from the force of a
blow.
Name the bones in the picture.
blue
green
purple

blue- Frontal bone
green- Parietal Bone
purple- Occipital bone
Name/Identify the sutures.

Where is the Supraorbital foramen/notch?
What structures can be found there
the supraorbital nerve and vessels are located here.
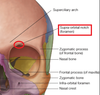
Where is the infraorbital foramen/notch?
What structures are found here?
the infraoribal nerve and vessels are found here.

Where are the infra and supratrochlear foramen located?
What structures are found here?
supratrochlear nerve and vessels, as well as infratrochlear nerve and vessels.
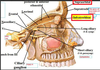
Where is the zygomaticofacial foramen?
what is located here?
zygomaticofacial nerves and vessels.

where is the zygomaticotemporal foramen?
what is located here?
the zygomaticotemporal nerve and vessels are located here.

where is the mental foramen?
what is located here?
the mental nerve branches and vessels are located here.

The frontal bone forms what two parts of the face?
What is found within the frontal bone?
what other bones does it articulate with.
the frontal bone makes up the forhead and superior orbits.
It contains the frontal sinuses.
it articulates with the parietal, sphenoid, lacrimal, nasal,ethmoid, and zygomatic bones as well as the maxilla.

where are the parietal bones located and what part of the head to they make up?
what suture is formed by their union?
They make the top of the head.
they come together to form the sagittal suture.
they articulate with the occipital temporal frontal and sphenoid bones.

where is the occipital bone located.
where are the pharyngeal tubercle, occipital condyle, jugular notch, basilar portion, hypoglossal canal and foramen magnum located?

Where is the temporal bone located, what are the three portions of the temporal bone?
The temporal bones form the lateral aspect of the cranium.
the three portions of the temporal bone are the:
squamous
tympanic
petrous

In the squamous portion identify the:
zygomatic process
atricular eminence
articular fossa
postglenoid process
In the petrous portion identify the:
Carotid canal
jugular notch
stylomastoid foramen
mastoid notch
mastoid process
external acoustic meatus
In the tympanic portion identify the:
external acoustic meatus
articular fossa
petrotympanic fissure


What does the squamoud portion form?
what does the tympanic portion form?
the squamous portion forms: the lateral aspect of the cranium, and the zygomatic process which contributes to the zygomatic arch, it also form the cranial portion of the TMJ.
The tympanic portion forms: most of the external auditory meatus. Seperated posteriorly from the petrous portion by the Petrotympanic fissure.
What is significant about the Petrotympanic fissure?
What emerges from this location, and what does it do?
This is the site of emergence for the Chorda Tympani Nerve
this nerve is branch of the facial nerve responsible for the special sensory taste from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue.

Describe the imporant parts of the Petrous portion of the temporal bone.
Mastoid process
Styloid process
Stylomastoid foramen
Carotid canal
- *Mastoid process-**
- Large roughened projection on the inferior aspect of the petrous portion
- Composed of air cells
- communicates with middle ear activity, site of attachment for sternocleidomastoid muscle
Styloid process
- located medial and inferior to EAM
- site of attachment for tongue and pharyngeal muscles and ligaments.
Carotid Canal
-Transmits the internal carotid artery
Stylomastoid foramen
-site of emergence of CNVII (facial nerve)

Often called the “keystone” of the neuro and visceral cranium
Identify the parts of the Sphenoid Bone
- pterygoid process (lateral and medial pterygoid plates and pterygoid fossa)
- greater wing
- foramen ovale
- foramen spinosum
- spine of sphenoid bone.

also recognize within the sphenoid bone are the sphenoid sinuses as well.
the sphenoid bone also forms the superior and inferior orbital fissures posterior to the eye.
The sphenoid bone is also the site of Irigin for many muscles of mastication as well as palatal and pharyngeal muscles.

what are the 5 margins of the infratemporal region (sits behind the zygomatic arch close to the cranium) and what bones make them up.
the 5 margins are:

- superior margin- greater wing of sphenoid and inferior of temporal bone
- anterior margin- convex posterior aspect of maxilla
- medial margin- lateral pterygoid plate of sphenoid
- lateral margin- medial surface of mandibular ramus
- inferior margin- trick question there isn’t one.
What two main branches of the trigeminal nerve originate from the infra temporal region?
the Maxillary nerve and Mandibular nerve.
the Maxillary then branches to form the zygomatic, infraorbital, anterior superior alveolar, and posterior superior alveolar nerves.

What are the two important venous structures in the infratemporal region?
Cavernous sinus (intracranially), and Pterygoid plexus (extracranially)

Where is the Ethmoid bone located? Describe its features.

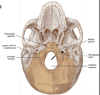
name the main bones of the basal/inferior portion of the skull.

Name the following structures at the inferior aspect of the skull.

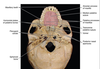
Name the following structures located at the interior portion of the skull.


Name the missing foramen and the nerves and vessels associated with each.

Incisive foramina -Nasopalatine nerve; Sphenopalatine vessels
Greater palatine foramen -Greater palatine nerve and vessels
Lesser palatine foramina - Lesser palatine nerves and vessels
Pterygoid canal - Pterygoid nerve and vessels
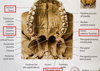
Name the foramen at the base of the skull.


What nerve is associated with the Foramen Ovale?
Mandibular Nerve (CNV3)
What blood vessel is associated with the Foramen Spinosum?
Middle Meningeal Artery
what is unique about the Foramen Lacerum?
It is filled with cartilage and isnt a true foramen
What structures are associated with the Carotid Canal?
The Internal Carotid Artery and nerve plexus
What structures are associated with the Jugular Foramen?
Internal jugular vein and inferior petrosal sinus.
what structures are associated with the styloid process?
muscles and ligaments associated with the tongue and pharynx
what nerve exits the stylomastoid foramen?
the Facial nerve CN(VII)
what structures are associated with the foramen magnum?
Continuation of brain and spinal cord; Vertebral arteries; Spinal artery; Accessory nerve (CNXI); Meningies
Identify these structures of the anterior cranial fossa.


what are the orbital plates?
Orbital plates: roof of bony orbit
what are the Cribriform Plates?
Cribriform plates: roof of nasal cavity, CN I (Olfactory nerve) has extensions through plate into nasal cavity
What is the Crista Galli?
Acts as the bony attachment for the Falx Cerebri of the brain.
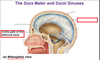
What structures pass through the Optic Canal?
CN II (optic), ophthalmic arteries
Where is the Superior Orbital Fissure located?
What structures pass through/ are associated with the Superior Orbital Fissure?
The superior orbital fissure is located between the greater and lesser wing of Sphenoid bone,
CN III (oculomotor n), CNIV (trochlear n), CNVI (abducens n), CNV1 (ophthalmic div. of trigeminal n) and ophthalmic veins
What structure passes throught he foramen rotundum?
CN V2 (Trigeminal – maxillary div.)
what nerves are associated with the internal auditory meatus?
CN VII (facial n), CN VIII (vestibulocochlear n)
what nerve runs through the hypoglossal canal?
CN XII (hypoglossal n)


