Anatomy of the Cranial Nerves Flashcards
What are:
Efferent nerves-
Afferent nerves-
Ganglion-
Parasthesia-
Anesthesia-
Efferent nerve – motor nerve that carries information away from the brain or spinal cord to the periphery of the body
Afferent nerve – Sensory nerve that carries information from the periphery of the body to the brain or spinal cord
Ganglion/Ganglia – collection of neuron cell bodies outside the CNS
Parasthesia – partial loss of feeling or sensation
Anesthesia – loss of feeling or sensation
What is the difference between the Somatic and Autonomic nerve systems?
Somatic nervous system- part of the peripheral nervous system associated with voluntary control of skeletal muscles.
The autonomic nervous system- division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the involuntary function of internal organs
Describe the:
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Brainstem (Medulla, Midbrain, Pons)
- *Cerebrum**-
- Largest portion of the brain
- Coordinates sensory data and motor functions
- Governs many aspects of intelligence and reasoning, learning & memory
- *Cerebellum**-
- Produces muscle coordination
- Maintains normal muscle tone and posture
- Coordinate balance
Brainstem
Medulla-
•closest to the spinal cord
•Involved with regulation of heartbeat, breathing, vasoconstriction, vomiting, coughing, sneezing, swallowing & hiccupping
Pons-
-Connects the Medulla to the cerebellum and higher brain centers
•Houses cell bodies of CN V (Trigeminal) and VII (Facial)
Midbrain includes relay stations for hearing, vision and motor pathways

Where is the Diencephalon located?
It is located superior to the brainstem and contains the thalamus and hypothalamus.

what do the thalamus and hypothalamus do?
Thalamus-
Serves as a central relay point for incoming nerve impulse.
- *Hypothalamus-**
- Hypothalamus regulates homeostasis
- Thirst, hunger, body temperature, water balance, blood pressure
- Links the nervous system to the endocrine system
What is included in the Peripheral Nervous System?
•The PNS is composed of all of the nerves stretching along the CNS and the receptors, muscles and glands of the body.
What are the two divisions of the PNS?
The PNS is divided into the afferent (sensory) nervous system and the efferent (motor) nervous system.
The efferent is further divided into the
•Somatic nervous system
•Autonomic nervous system
What is included in the Somatic Nervous System?
and what is its function?
- Includes all nerves controlling the muscular system and external sensory receptors
- Sensory input from the PNS is processed by the CNS
- Responses are sent by the PNS from the CNS to the muscles and glands of the body
- Distinct set of motor neurons from the autonomic system
What is included in the Autonomic Nervous System?
What is its function?
- Fibers of efferent nerves, which always occur in two-nerve chains
- First nerve chain carries autonomic fibers to a ganglion; where they end near the cell bodies of the second nerve
•Operates without conscious control to regulate homeostatic body functions and organs.
the Peripheral Nervous System is broken up into two different Systems which work in opposition to one another called the ________ and __________ Nervous Systems.
The Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems.
What is the duty of the Sympathetic Nervous Systems?
Describe the unique features of the sympathetic nerves.
-“Fight or Flight” response

-Post-ganglionic fibers of the SCG travel as a plexus (meshwork) along arteries of the head and neck region to their destination.
•Sympathetic fibers to the head and neck region are associated with the Superior Cervical Ganglion
SHORT PRE, LONG POST ganglionic fibers
What is the role of the Parasympathetic Nervous System?
Describe the unique features of the parasympathetic nerves.
•“Rest or Digest” response
- Parasympathetic fibers associated with the glands of the head and neck region are carried by various cranial nerves
- There are four (4) parasympathetic ganglia located in the head region
- Ciliary ganglion – orbital region
- Pterygopalatine ganglion – Pterygopalatine fossa
- Otic ganglion – Infratemporal fossa
- Submandibualr ganglion – Floor of mouth/Sublingual region
LONG PRE SHORT POST ganglionic fibers

In order what are the names of the twelve cranial nerves?
Olfactory I
Optic II
Oculomotor III
Trochlear IV
Trigeminal V
Abducent VI
Facial VII
Vestibulocochlear VIII
Glossopharyngeal IX
Vagus X
Accessory XI
Hypoglossal XII

Describe the location of the Olfactory Nerve its function and its involvement with the nasal cavity.
- Arises from the Olfactory Trigone on the inferior surface of the forebrain
- extends forward on anterior cranial fossa floor, and ends as Olfactory bulbs
- Bulb sends rootlets through the pores of the cribriform plate and enter into the nasal cavity enabling us to smell.

Describe the origin of the optic nerve, its unique pathway to its destination and its function.
- Origin: Lateral geniculate bodies at base of the diencephalon
- Tracts travel forward, converge and cross over at the midline at the Optic Chiasma.
Not ALL fibres cross
- Travels through the Optic Canal and enters back of the eye.
- Function- Sight

Describe the location, pathway and function of the Oculomotor nerve.
- Emergence: Interpeduncular fossa of Midbrain
- Travels forward and through dura of Triangular fossa
- Passes through Cavernous sinus along the lateral wall
- Passes through the Superior Orbital Fissure and enters the orbit
Function:
Somatic motor to all extraocular muscles,
except Superior Oblique & Lateral Rectus (moves eyes up, down, medial, and up and out)
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) to sphincter
pupillae and ciliary muscles of the eye (change in shape of lens and pupillary constriction)
Describe the location, pathway and function of the Trochlear nerve.
- Only cranial nerve to arise from the dorsum of the brainstem
- enters the cavernous sinus
- Travels along lateral sinus wall and enters the orbit via the Superior Orbital Fissure
Function: Somatic motor control to superior oblique, (moves the eye down and out)

Describe the location, pathway and function of the Abducens Nerve.
Arises from between the pons and medulla
passes over petrous temporal ridge into the cavernous sinus below the Internal Carotid Artery.
Enters obit via superior orbital fissure
Function: somatic control of lateral rectus muscle (lateral eye movement)

What are the 3 branches of the Trigeminal nerve?
CNV1- Opthamic branch
CNV2- Maxillary branch
CNV3- Mandibular branch
All originate from the Trigeminal ganglion

Describe the Location, pathway and function of CNV1?
What are the three branches of CNV1 (Opthalmic branch of trigeminal) identify them.

Location: leaves trigeminal ganglion, enters Cavernous sinus, enters orbit at superior orbital fissure.
Function of CNV2 is ipsilateral sensation of the cornea, nare and forehead.
The Three branches of CNV1 are the Lacrimal, Nasocilliary and Frontal Nerves.

What are the two branches of the frontal nerve?

Supraorbital nerve
Supratrochlear nerve

Label/Identify the 5 branches of the Nasociliary nerve from CNVI

Infratrochlear
External nasal nerve
Internal nasal nerve
Ciliary nerves
Anterior ethmoidal nerve

Describe the location pathway and final site of emergence for CNV2 (Maxillary branch of Trigeminal).
what is its function?
- Leaves ganglion and passes through post. inf. of Cavernous Sinus
- Exits Cavernous sinus through Foramen Rotundum
- Enters the Pterygopalatine fossa
Function: ipsilateral sensation of the maxillary region of the face
What are the 5 main branches off of CNV2 (Maxillary branch of trigeminal)

Zygomatic Nerve
Infraorbital Nerve
Posterior Superior Alveolar Nerve
Palatine Nerves
Spheno/naso-palatine Nerve

Name the branches of the Zygomatic, Infraorbital, and Palatine nerves.
Zygomaticofacial n.,
Zygomaticotemporal n.
**Middle Superior Alveolar**
**Anterior Superior Alveolar**
Greater Palatine
Lesser Palatine
Describe the location, pathway and final site of emergence for CNV3.
What is its function?
CNV3 descends through the Foramen Ovale into the Infratemporal region.
Motor root of CNV travels ONLY with mandibular division.
Function:ipsilateral sensation of the mandibular region of the face, and ipsilateral motor control of muscle of mastication

Name the 5 branches from the anterior trunk of CNV3
Anterior deep temporal nerve
Posterior deep temporal nerve
Pterygoid nerve
Buccal nerve
Masseteric nerve

What are the 3 main branches from the Posterior trunk of CNV3.
Auriculotemporal nerve
Inferior Alveolar nerve ****
Lingual Nerve

Name the 3 branches of the Inferior alveolar nerve.
Incisive nerve
Mental nerve
Mylohoid nerve

Describe the location,pathway and site of emergence and function of the Facial Nerve CNVII
Exits brainstem laterally between pons and medulla
Exits through Internal Auditory Meatus
Enter Petrous portion of temporal bone
Branches near middle ear within the bone as it travels through Facial Canal
Exits onto the skull through the Stylomastoid foramen
Function: facial movement, lacrimation, salivation, taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue, sensation around ear
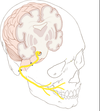
What are the 3 branches that extend from the facial nerve within the petrous portion of the temporal bone?
Stapedius nerve (innervates ossicles of ear)
Greater Petrosal nerve (carries parasympathetic preganglionic fibers from facial nerve to pterygopalatine ganglion, postganglionic fibers travel to the lacrimal gland and the mucosal glands of the nose, palate, and pharynx)
Chorda Tympani nerve (carries sensory fibers for taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.Presynaptic parasympathetic fibers to the submandibular ganglion, providing secretomotor innervation to two salivary glands:
Excluding the branches within the petrous portion of the temporal bone what are the 5 main branches off of the Facial Nerve CNVII

Temporal Branches – supply facial muscles above the zygomatic arch
Zygomatic Branches –supply facial muscles in the zygomatic, orbital, and infraorbital areas
Buccal Branches – supply muscles of the cheek and circumoral muscles
Mandibular Branches – supply muscles of the chin and lower lip
Cervical branches – descend to the neck to supply the platysma, posterior belly of the digastric and stylohyoid muscles

What are some of the Main functions of the Facial Nerve CNVII
- Special sensory taste anterior two thirds of tongue
- General sensory small part of external ear and external auditory meatus
- Motor control to muscles of facial expression, stylohyoid, posterior belly of digastric and stapedius muscles.
Visceral motor (parasympathetic) control to all major and minor glands of head except parotid gland
Describe the location, pathway and final site of emergence for CNVIII (Vestibulocochlear nerve)
From brainstem lateral to Facial Nerve
to Internal Auditory Meatus
Enters Petrous portion of temporal bone to supply inner ear
divides into Vestibular portion (to semilunar canals) and Cochlear portion (to Cochlea)

What is the main function of the Vestinulocochlear nerve?
Special sensory hearing
Balance
Describe the location, site of emergence from the skull and function of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CNIX)
Arises as multiple rootlets from the medulla
Fibers converge into bundle
Passes through Jugular Foramen
FUNCTION:
- Special sensory taste (posterior 1/3 of tongue)
- General sensory: posterior 1/3 of tongue, pharynx, middle ear
- Visceral sensory from carotid body and sinus
- motor to Stylopharyngeus muscle
- Visceral motor (Parasympathetic) to parotid gland

Describe the Location and site of emergence for the Vagus Nerve CNX
Arises as several rootlets from the medulla
converge and pass through Jugular Foramen
Travel to the NECK region
What are the main functions of the Vagus Nerve CNX?
•Special sensory taste from laryngeal inlet area
•General sensation from small area of external ear
•Visceral sensory from pharynx, larynx, gut to left colic flexure, bronchial tree and the heart
•Visceral motor (parasympathetic) to thoracic and abdominal viscera

Where does the Accessory nerve originate from?
What foramen does it exit through?
(Hint: two places)
The Accessory nerve originates from TWO sources:

Cranial portion arises as several converging rootlets below the vagus nerve
Spinal portion arises from motor spinal contributions of spinal cord segments C1 to C6
The filaments unite and pass through the Foramen Magnum
What are the functions of the Accessory Nerve CNXI?
- Cranial - voluntary motor to muscles of the larynx, pharynx and soft palate
- Cranial & Spinal – voluntary motor to Sternocleidomastoid &Trapezius muscles
What are the main functions of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve CNIX?
stimulates parotid gland,
sensation to:
pharynx,
soft palate,
posterior third of tongue,
auditory tube,
tympanic cavity
carotid sinus
What are the main functions of the Vagus nerve CNX?
muscles of soft palate and pharynx
parasympathetic control of heart and smooth muscles
What are the main functions of the Accessory Nerve CNXI?
muscles of the soft palate; movement of neck and shoulders
Describe the location and final site of emergence for the Hypoglossal Nerve CNXII?
What is its function?
Arises as several rootlets in celft of medulla between the Olive and Pyramid.
rootlets converge and exit through Hypoglossal canal.
- *Function:**
- •Somatic motor to extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue*

What are the 4 main Ganglion in the Head and Neck Region?*****
Ciliary Ganglion
Pterygopalatine Ganglion
Otic Ganglion
Submandibular Ganglion
Where is the Ciliary Ganglion Located?
What fibers are incoming?
What fibers are outgoing?
Tiny swelling associated with the nasocillary nerve in the orbit.
Incoming fibers:
•Occulomotor nerve (CN III)
Outgoing fibers:
•Short ciliary nerves (CN V1)
•supply the constrictor pupillae and ciliary muscles of the eye

Where is the Pterygopalatine Ganglion located?
Incoming Fibers?
Outgoing Fibers?
Small swelling on the Maxillary nerve as it crosses the Pterygopalatine Fossa.
Incoming:
-CNVII facial nerve within the facial canal of the petrous temporal bone as the Greater Petrosal nerve
Outgoing:
•CN V2 (occulomotor) to supply the minor salivary glands of the mucosa of the hard and soft palate, nasal mucosa, mucosa of the paranasal air sinuses, mucosa of the superior portion of the pharynx and the lacrimal gland.

Where is the Otic Ganglion located
Incoming Fibers?
Outgoing Fibers?
Small swelling on CNV3 Occulomotor nerve as it passes through the foramen ovale.
Incoming Fibers:
lesser petrosal nerve, from tympanic nerve which originates from Glossalpharyngeal nerve CNIX.
Outgoing Fibers:
hitch hike with Auriculotemporal nerve from CNV3 to continue the Parotid gland
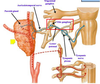
Where is the Submandibular Gangion located?
Incoming Fibers?
Outgoing Fibers?
•Flattened small swelling by ganglionic branches of the lingual nerve
Incoming Fibers:
•carried to the ganglion via the Chorda tympani nerve (Br of CN VII) traveling with the Lingual nerve
Outgoing Fibers:
•Travel with the Lingual nerve from CNV3 to supply the Sublingual, Submandibular glands and the Minor salivary glands of the floor of the mouth



