Anatomy Flashcards
What are modalities are used to image the pelvis?
- MRI
- U/S
What are the advantages and disadvantages of MRI?
- No Ionising radiation
- Better soft-tissue contrast
- useful for staging cancers/tumours
- Longer examination time (45 mins)
- More expensive
When would a CT be used to image the pelvis?
- In an emergency or acute settings
- produces a lot of artefact due to the pelvic girdle
- also has poor soft-tissue contrast
What key structures are in the male pelvis at this level?

- Prostate
- Rectum
- Ischio-rectal fossae
- cancers of the rectum erode into this area - looking for a clean line of fat (not present in this image)
- Obturator internus
- provides lateral rotation and the abduction of the hip
What key structures are in the male pelvis at this level?

- rectus sheath at the front
- the bladder
- the seminal vesicles (bowtie)
What key structures are in the female pelvis at this level?

- Uterus
- Endometrium (looks bright white in T2)
- Myometrium (same density as skeletal muscle)
- Junctional zone
- if this is narrowed or thickened –> suggest endometrial cancer
- Ovary- fluid-filled and bright on the T2 weighted image
- Bladder
- Cervix
What can be seen in this Sagittal MRI of the female pelvis?

- Bladder
- Uterus (OM)
- (anteverted uterus in this image- no functional difference)
- Cervix
- Rectum
- the sacral space should have a clear line fo fat - sigmoid colon cancer can infiltrate into this space
How are the ovaries imaged?
- HSG: Hysterosalpingogram
- very similar to a smear test
- you want to see a blurring from the contrast - shows the infundibulum is clear
- HSG: Hysterosalpingogram

The Peritoneum in the female pelvis - sagittal MRI -

- The peritoneal reflections in the pelvis consist of the peritoneum wrapping around
- the bladder
- the uterus
- the rectum
- this creates two pouches/spaces
- vesicouterine pouch
- rectouterine pouch (pouch of Douglas)
- the pouches are a common site of infection/ abscess
The peritoneum in the male pelvis - sagittal MRI -

- there is only the vesicorectal pouch - as the perineum wraps around the bladder and down the front of the rectum
- common site of abcist formation
What types of Ultrasound imaging can be down to image the pelvis?
- Transabdominal
- Transvaginal
- Transrectal
What is measured in an Ante-natal ultrasound?
- 12 week scan (dating scan)
- 20-week scan (looking for congenital abnormalities)
- growth rate: crown-rump length, head measurements etc.
How is the vascular anatomy of the pelvis?
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (using contrast (e.g gadolinium), similar to MRI)
- Duplex U/S (doppler effect)
- plots the wave form blood flow of the artery
- CT angiogram
- iodinated intra-venous contrast through the peripheral cannula with imaging
- Angiography (direct catheter angio)
What type of imaging is this?
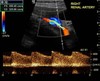
Duplex ultrasound of the right renal artery

What type of imaging is this?

CT Angiogram

What type of imaging is this?

Catheter angiogram

At what level does the aorta and vena cava bifurcate?
- aorta is L4
- vena cava is L5:
- the right CIA crosses the origin of the Left CIV –> left iliac DVT
- May-Thurner syndrome
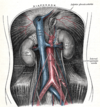
Anatomy of the Internal Iliac artery

- Divides into the Anterior and posterior division
- the posterior division is iliolumbar
- lumbosacral and superior gluteal

What pathology is this?

Unifying Pseudoaneurysm of the Right Common Femoral Artery
- the blood vessel isn’t dilating there is just a hole in it
Labelled anatomy of the sagittal female pelvis


What is the blood supply and nerve supply of the ovaries?
- supplied by the ovarian artery and the vein within the suspensory ligament
- Nerve supply of the ovarian plexus
Describe the structure of the uterine tube
- VAN
- Infandibulum
- Ampulla
- often the site of fertilization
- Isthmus
- Uterine
- VAN
- V: ovarian arteries pass laterally and drain into the left renal vein (on the left side), drain into the inferior vena cava (on right side)
- A: ovarian artery
- N: sympathetic supply from the ovarian nerve and parasympathetic from the pelvic splanchnic nerve

Where is pain from the ovaries felt in which dermatome region?
- ischaemia and pain which is referred to the dermatome region of T10
Describe the structure of the uterus
- made up of the fundus, body of the uterus and cervix
- Formed of 3 layered walls
- Perimetrium – outer serous wall covering the uterus
- Myometrium – thick muscular layer, responsible for the process of parturition
- Endometrium – inner mucous layer; site of implantation; thickness changes through menstrual cycle













