Anatomy Flashcards
Differences between male and female bony pelvis
Female:
- Wider pelvic outlet
- Wide subpubic angle
- Wide and short sacrum
- Round/oval shaped pelvic inlet
Male
- Heart shaped pelvic inlet
- Long and narrow sacrum
- Bony structures are thick and heavy

Which muscle of the pelvic floor is more likely to be injured during normal childbirth?
Pubococcygeus

Lymphatic drainage of the uterus, ovary and vagina
Ovaries - aortic/caval lymph nodes
Uterus:
- lumbar
- superficial inguinal
- external iliac
- internal iliac
- sacral
Vagina:
- Superior – drains to external iliac nodes
- Middle – drains to internal iliac nodes
- Inferior – drains to superficial inguinal lymph nodes.

Describe the nerve supply to the uterus
The uterus is supplied by the uterovaginal nerve plexus which derives from the inferior hypogastric plexus
- Uterovaginal nerve plexus contains sympathetic, parasympathetic + visceral sensory fibers
- Viceral sensory fibers from intraperitoneal fundus and body of uterus passes back with sympathetic fibers to lower thoracic and upper lumber spinal ganglia
What is the position of the ureter in relation to the uterine artery at the lateral wall of the uterus?
The ureter lies posterior to the uterine artery

What does the R ovarian vein drain into?
The Inferior vena cava
The medialumbilical ligament is the remnant of which embryological structure?
The remnant of the embyronic umbilical artery
Which artery supplies the area above the pectinate line? (divides the upper two thirds and lower third of the anal canal)
inferior mesenteric artery
Which artery supplies the area below the pectinate line? (divides the upper two thirds and lower third of the anal canal)
The inferior rectal artery
Which nerve supplies the external anal sphincter?
Pudendal nerve
Where is the pouch of douglas situated?
The pouch of douglas is known as the rectouterine pouch in females and it lies between the rectum and the uterus
The epithelium changes from _____ to _____ across the pectinate line in the rectum?
From columnar epithelium to stratified squamous non-keratinised epithelium.
The fibres of which 2 muscles make up the Scrotal skin?
- Dartos muscle
- Cremasteric muscle
How do the dartos and cremaster muscles react to hot/cold water temperatures?
Temperature receptors are located in the scrotum.
When the temperature is too low:
- The dartos muscle contracts, causing the scrotal skin to wrinkle, and thus the scrotum has a smaller surface area for heat loss.
- The cremaster muscle also contracts and raises the testes to bring them closer to the warmer groin region.
When the scrotal temperature rises:
- Both muscles relax and the scrotum descends.
Cremaster muscle
- Location?
- Nerve supply?
Location: The cremaster muscle is found in the inguinal canal and scrotum between the external and internal layers of spermatic fascia, surrounding the testis and spermatic cord
Nerve supply: genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve
Apart from the dartos and cremaster muscles what else is involved in thermoregulation of the testes?
Pampiniform plexus - a loose network of small veins found within the male spermatic cord
How come the testes and ovaries are supplied by L1-2?
- The testes and ovaries develop in the posterior abdominal wall at levels L1-2
- When they descend they drag their arterial and nerve supply down with them
Look
All pelvic organs are autonomic (involuntary responses) meaning they are parasympathetic or sympathetic

Innervation of the pelvic organs
All autonomic so…
Sympathetic supply:
- Comes from Lumbar splanchnic nerve L1-2 => the superior hypogastric plexus lies on the sacral prominence and it carries the lumbar nerves down from the aortic plexus
- From the sacral prominence the superior hypogastric plexus divided into 2 hypogastric nerves which run down either side of the rectum and bladder
Parasympathetic supply:
- The Pelvic splanchnic nerves arise from levels S2,3 and 4
- They join the sympathetic nerves to form the inferior hypogastric plexus/ ‘pelvic plexus’
- From there the nerves go to the various organs and supply them with both

What muscle lies on the posterior wall of the true pelvis?
The piriformis muscle
also the coccygeus muscle but it lies further down

Which main lumbar plexus nerve lies on the side-wall of the true pelvis?
The obturator nerve plexus
What is meant by the true/false pelvis?

What muscle forms the floor of the true pelvis?
The levator ani
Branches of the internal iliac artery
The Internal iliac arteries supply most of the pelvic organs (everything except the ovaries). The internal iliac then splits into:
- Anterior division – supplies midline and side wall pelvic organs. The anterior division can be further split into:
- Uterine artery
- Superior and inferior vesical arteries – bladder
- Posterior division – goes back into gluteal area
What does the inferior vesical/vaginal artery supply in males/females?
- In males the inferior vesical artery supplies the prostate
- In females it is different and is called the inferior vaginal artery - supplies the vagina
Superficial perineal pouch
Anatomical space, not an actual open pouch

Pudendal nerve
- The pudendal nerve originates from S2-S4 of the lumbosacral plexus.
- It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen
- It then crosses over the ischial spine and reenters the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen, inferior to the pelvic floor.
The ischial spine is a useful anatomical landmark to target these nerves for obstetric anaesthesia
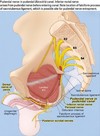
Pudendal nerve block
This transvaginal approach allows a bilateral pudendal nerve block to anaesthetise the inferior vulva, which is helpful when an episiotomy or related procedure is necessary.

What is the significance of the 2 pouches created by peritoneal folds in females?
This is where fluids (blood, pus etc) can accumulate clinically i.e infection or rupture
What is the broad ligament?
It’s the fold of peritoneum which covers the anterior and posterior surfaces of the uterus and Fallopian tubes.
It is often divided into 3 regions but these are continuous peritoneum:
- covering the ovaries (mesovarium)
- covering the Fallopian tubes (mesosalpinx)
- covering the uterus (mesometrium)

Which pouch exists in males?
Rectrovesical (between rectum and bladder)


