Anatomy Flashcards
the SCALP
- Skin
- Connective tissue
- Aponeurotic tissue
- Loose Connective Tissue
- Pericranium
- extends over the neurocranium
- Innervation to the scalp is from the trigeminal nerve and spinal cutaneous nerves
Bones of the skull
- the Neurocranium and the viscerocranium = 22 bones
- Neurcroniaum bones
- Occipital
- 2 x temporal
- 2x parietal
- Sphneoid
- ethmoid
- frontal
- Viscercranium
- 2x nasal conchae
- 2x nasal bones
- 2x maxilla
- 2x palatine bones
- 2x zygomatic bones
- 2x lacrimal bones
- vomer
- mandible
Foramina of the cranium
Cribiform: plate CN 1
Optic Canal: CN 2, Ophthalmic A
Superior Orbital Fissure: CN 3,4,6, 5 V1 (LFTSNIA)
Rotundum: CN5 V2
Ovale: CN 5 V3, AMMA
Spinosum: Middle Meningeal Artery
Lacerum: *Carotid Artery
Internal Acoustic Meatus: CN 7 and 8
Jugular foramen: CN 9, 10,11, IJV
Hypoglossal Canal: CN12
Magnum: Spinal Cord
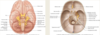
Dura Mater
- 2 layers of dura mater around the brain: create a sinus
- endosteal layer: outer layer stops at the foreman magnum, only lines the skull
- Meningeal layer around the brain and the skull
- falx cerebri: separates cerebral hemispheres
- tentorium cerebelli: separates the cerebellar hemisphere from the cerebral hemispheres
- falx cerebelli- separates cerebellar hemispheres
- supplied by CNX 5 (trigeminal), 10(vagus), C1-3 and sympathetic
- blood supply is the middle meningeal artery
Arachnoid Mater
- thin avascular layer between the pia and the dura
- loosely applied layer with projections
- all structures passing to/ from brain pass through the subarachnoid space
- Subarachnoid space contains cerebrospinal fluid produced by choroid plexus in brain ventricles
- the CSF provides buoyancy for the brains
- any excess CSG in the subarachnoid space goes to the arachnoid granulations which project into the superior sagittal sinus (the space between the two dura layers)
- these granulations affect the transfer of CFS into the venous system
Pia Mater
- very delicate vascular membrane: nourishes
- closely invests brain following gyri/sulci
- Cerebral arteries entering the brain carry a bit of the pia with it
Leptomengittis
- infection and inflammation in the arachnoid and the pia mater
- infection may enter the subarachnoid space and enter into the blood (septicemia)
Dural Sinuses
- Sinuses sit between the dural folds.
- Drained blood and CSF from the brain via cerebral veins.
- Communicate with the veins of the skull and scalp.
- Thick-walled endothelium. No Valves or smooth muscle.
- Drain into the internal jugular vein.
Blood supply to the brain

Stroke
Occurs when the supply of blood to the brain is reduced or blocked completely, which prevents brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients.
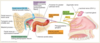
Describe the embryological stage of the face
- Development begins in week 4 and forms from 5 swellings.
- Frontonasal
- Maxillary X2
- Mandibular X2
- By week 5 two events;
- Maxillary prominences enlarge in medial direction
- Nasal placodes appear and form medial and lateral processes.
- The medial nasal processes merge towards each other and form intermaxillary segment
- The maxillary prominences fuse with the lateral and medial nasal processes to form the upper lip

What are the key muscles of the face and what are there roles
- Occipitofrontalis- elevates eyebrows
- Orbicularis oculi- closes eyelids
- Orbicularis oris- closes mouth
- Zygomaticus major- elevates labial commissure
- Buccinator- compresses cheek
- Platysma- depresses mandible against resistance, tenses

Innervation of the fascial muscles
- Cutaneous innervation by the Trigeminal nerve (Cranial nerve 5)
- All muscles of facial expression supplied by the Facial Nerve (Cranial nerve 7)
- Sensory, Taste and a general motor and visceral motor nerve
- Exits through:
- the internal acoustic meatus
- facial canal
- stylomastoid foramen
- Branches: Tempra facial and Vercofacial branch from the Posterior auricular nerve
- Motor-Posterior auricular, temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular, cervical
- Parasympathetic- branches: to pterygopalatine ganglion.
- Taste- via chorda tympani via lingual nerve from anterior two thirds of tongue.
- General sensory: skin over external auditory meatus.
`
The Parotid glands place in the face
- largest of the three salivary glands in the head and is superficial to the muscles in the face
- Parotid duct leaves gland at anterior edge and passes towards the corner of the mouth but turns deep through buccinator.
- The parotid duct opens into oral cavity at upper second molar tooth.
- The retromandibular vein and external carotid artery run through it.
- Facial nerve passes through the parotid gland.

Muscles responsible for mastication (chewing)
- Temporalis- elevation, retraction
- Masseter- elevation
- Medial Pterygoid- elevation, side to side
- Lateral Pterygoid- protrusion and depression
Innervation of the mastication muscles
- supplied by the motor nerve of V3
- the Mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve
Cranial NErve 5
- the Trigeminal Nerve
- it’s a somatic and somatic motor to derivatives of the 1st pharyngeal arch
- It has three main divisions
- Ophthalmic (V1): exits through the Superior orbital fissure
- Maxillary (V2): exits through the Foramen Rotundum
- Mandibular (V3): exits through the Foramen Ovale

Explain the Ophthalmic Nerve V1
- Type: Sensory fibres skin, mucous membranes, conjunctiva, front of head and nose
- Path: Branches into lacrimal, nasociliary, frontal
- Exit: Superior Orbital Fissure

Explain the Maxillary Nerve V2
- Type: Sensory fibres dura, nasal, upper cheek, lip, teeth
- Path: Enters pterygopalatine fossa, gives off branches to the pterygopalatine ganglion, through the inferior orbital fissure.
- Exit: Foramen rotundum
- Branches: Infraorbital, zygomatic, superior alveolar.

Explain the Mandibular Nerve V3
- Type: Mixed, sensory, lower face, lip, teeth. Motor to muscles of mastication
- Exit: Foramen Ovale
- Branches:
- Sensory-auriculotemporal, buccal, lingual, inferior alveolar, mental
- Motor- temporalis, masseter, medial and lateral pterygoids, nerve to mylohyoid
- Parasympathetic (hitchhiking)- to salivary glands

The Temporal and infratemporal fossa
- The temporal fossa is a fan-shaped space that is located on the lateral surface of the skull.
- The temporal fossa contains: temporalis muscle, branches of V2
- The infratemporal fossa is inferior to the temporal fossa.
- The infratemporal fossa contains: medial and lateral pterygoids, maxillary artery, V3, branches of the facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve and pterygoid plexus of veins.

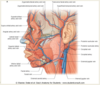
Describe the arterial supply to the face
arterial supply from the external carotid artery
- Lingual
- Facial
- Maxiallry
- Superficial temporal
in this order

Venous drainage of the face
- the facial vein drains the majority of the face, starting near the eye
- the facial vein passes inferiorly and drains into the internal jugular vein
- the superficial temporal vein drains into the external jugular vein

Draw out this image