Anatomy Flashcards
Of the External Intercostal muscle describe: Orientation of fibres? Membranous in what part of intercostal space? Involved in what type of respiration? Relation to intercostal NV bundle? Supplied by what nerve?
- Antero-interior direction - Anterior portion is membranous. - Involved in inhalation - Superficial to Nerve Bundle - Supplied by intercostal nerve and artery.

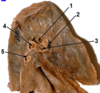
- Vertebral Body
- Pedicle
- Articular facet of Transverse process
- Inferior vertebral notch
- Spinous Process

- Intercostal vein
- Intercostal artery
- Intercostal nerve
- External intercostal muscle (note antero-inferior direction of fibres)
- Collateral branch of intercostal nerve
The manubriosternal junction is at the level of the intervertebral disc below?
T4
horizontal plane taken backwards from manubriosternal junction bisects the interertebral disc between T4 and T5.
The intercostal neurovascular bundle runs between?
Betwen the internal and innnermost intercostal muscles.
Where do the intercostal nerves “branch from”?
Each thoracic spinal nerve emerges from the intervertebal foramen and divides into a dorsal and a ventral ramus. The ventral ramus continues as the intercostal nerve of the space.
Where do the intercostal arteries branch from?
Posterior –> come from aorta
anterior –> come from internal thoracic arterW
What vessels arise from the pulmonary trunk?
Right and Left pulmonary arteries
What are the anterior and inferior structures at the hilum of each lung?
The Pulmonary veins.
Return oxygenated blood from the blood-gas interface ot the left arium via the hilum of each lung where they are situated naterir and inferior tothe othe rhilar stuctures.
What system to the Bronchial viens run into?
Drain into the azygous vein.
RIght side directly drain.
Left side typically drian into the hemiazygos or accessry hemiazygos vein.
Where do the Bronchial arteries come from? What do they supply?
The left bronchial arteries arise from the descending thoracic aorta.
Righ bronchial artery normally do as well.
Sometimes they arise from righ posterior intercostal branch of descending thoracic aorta.
Supply the hilar structures, supporting tissues and visceral pleura, but there is overlap with branches of pulmonary artery.
The thoracic duct pierces the diaphragm at what level and with what other structure?
Pierces at the level of T12 with the aorta.
It originates in the abdomen and passes through the aortic hiatus in the diaphragm into the posterior mediastinum where it ascends between the oesophagus anteriorly and vertebral column posteriorly.
Name the four structures that the phrenic nerve supplies?
Diaphragm, diaphragmatic pleura, mediastinal pleura and pericardium.

- Trachea
- Arch of azygous vein
- Sympathetic trunk
- Posterior intercostal vein
- Superior vena cava

- Left Phrenic nerve
- Left vagus nerve
- Left pulmonary artery
- Left main bronchus
- Anterior interventricular artery (LAD)
It is the Base of the Heart

- Right subclavian artery
- Right common carotid artery
- Brachiocephalic trunk
- Right Brachiochepalic vein
- Right Phrenic Nerve
Left Ventricle

- Aortic valve, semilunar cusp
- Chordae Tendinae
- papillary muscle
- Trabeculae carnae
- Aortic Sinus, origin of coronary artery

- Arch of the Aorta
- Ligamentum arteriosum
- Ascending Aorta
- Pulmonary Trunk
- Anterior Interventricular artery (LAD)

- Superior Vena Cava
- Right Coronary Artery
- Left Subclavian Artery
- Left Common Carotid
- Left Brachiocephalic Trunk

- Opening of Superiov vena cava
- Fossa Ovalis
- Opening of Coronary sinus
- Cusp of tricuspid valve
- Papillary muscle
What forms the right border of the heart?
Right Atrium
What lies either side of the anterior atrioventricular sulcus?
Right Side = Right Atrium
Left Side = Right Ventricle
What forms the left border of the heart?
Left ventricle
What chamber receives the coronary sinus?
Right Atrium
Which ventricle has two papillary muscles? which has three papillayr muscles?
2 = Left venticle
3 = Right venticle
Which chamber receives the pulmonary veins?
Left atrium
What coronary artery runs in the anterior atrioventricula sulcus?
The right coronary artery
Emerges on to the front of the heart and runs down in the anterior atrioventicular sulcus supplying right atrium and ventricle
What artery runs in the posterior atrioventricular sulcus?
The circumflex artery
branch of the left coronary artery which turns onto the back of the heart and into the posterior atrioventricular groove.
Which vessel entering the right atrium has a rudimentary valve?
THe IVC
THe SVC does NOT
What coronary artery commonly gives rise to the anterior interventricular artery?
The Left coronary artery
What artery most commonly gives rise to the posterior interventricular artery?
Right coronary artery
What artery most commonly supplies the atrio-ventricular node?
Right Coronary Artery
What major vessels recieves the azygous vein?
Superior vena cava

- Impression of descending thoracic aorta
- Oblique fissure
- Impression of aortic arch
- Pulmonary ligament
- Cardiac notch
- Left Pulmonary Artery
- Hilar lymph node
- Anterior pulmonary vein
- Left Main bronchus
- Inferior pulmonary Vein

- Pulmonary Artery
- Anterior Pulmonary vein
- Left main bronchus
- Hilar Lymph Node
- Inferior pulmonary vein

- Oblique fissure
- Impression of arch of azygos vein
- Hilar lymph Node
- Right upper lobe bronchus
- Bronchus intermedius
- Inferior pulmonary vein
- Pulmonary artery branch to right upper lobe
- Right pulmonary artery
- Anterior pulmonary vein
- Oblique Fissure
Identify the features on the chest X-ray?

- Arch of the Aorta
- Right Pulmonary Artery
- Right Atrium
- Gastric air bubble
- Left Costrophrenic angle

- Left Ventricle
- Descending Aorta
- Left first rib, anterior part
- Right Hemi-diaphragm
- Trachea

- Manubriosternal joint
- RIght hemi-diaphragm (higher than left)
- Left atrium
- Left main bronchus (narrower and more horizontal than R main bronchus)
- Thoracic Vertebral body

- Retrosternal airspace
- Arch of aorta
- RIght Ventricle
- Left Hemi-diaphragm
- Breast shadow
Which brances of the aorta supply the liver?
The common hepatic branch of the coeliac trunk supplies the liver.
Which branch of the aorta supplies the descending colon?
The descending colon is a hindgut derivative supplied by the inferior mesenteric artery.
What branch of the aorta supplies the Jejunum?
The jejunum is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery which runs along the root of the mesentery.
What branch of the aorta supplies the appendix?
The appendix is a midgut derivative supplied by the superior mesenteric artery.
What arteries supply the pancreas?
Body and tail?
Head?
The body and tail of the pancreas are supplied by the splenic artery. The head is supplied by the superior pancreaticoduodenal branch of the hepatic artery; (plus some supply from the inferior pancreaticoduodenal branch of the SMA). All branhces from the coeliac trunk.
What arteries supply the kidney? At what level do the arise from?
The renal arteries arise directly from the sides of the abdominal aorta at the level of L1.
Where do the arties that supply the external oblique muscles arise from?
The anterior and posterior abdominal wall structures are supplied by the paired lumbar arteries which arise from the posterior aspect of the abdominal aorta.
What branches of the aorta lead to the supply of the gall bladder?
The cystic artery typically arises from the right hepatic branch of the common hepatic artery, from the coeliac trunk.
Venous drainage from the spleen?
The splenic vein joins the superior mesenteric vein behind the neck of the pancreas to form the portal vein.
Venous drainage of the kidney?
The renal veins drain directly into the IVC at the level of L1.
Venous drainage of the pancreas?
The pancreas drains via the splenic vein into the portal system.
Venous drainage of the descending colon?
The inferior mesenteric vein joins the splenic vein in the portal system.
Venous drainage of the posterior abdominal wall structures such as the quadratus lomborum?
Posterior abdominal wall structures drain via the lumbar veins directly into the IVC.
Venous drainage of the adrenal gland?
The adrenal veins drain into the IVC.
Venous drainage of the appendix
The appendix drains via the superior mesenteric vein into the portal system.
Venous blood drainage from the liver?
The hepatic veins open into the IVC just below the diaphragm.

- Right psoas shadow
- Gas in fundus of stomach
- 12th rib (floating rib), left
- L1 transverse process, right
- Gas in small intestine

- Linea Alba
- Spermatic chord
- Rectus Abdominis
- Transversus Abdominis
- Tendinous Intersection

- Gall Bladder
- Spleen
- Inferior Mesenteric Artery
- Right Ureter
- IVC

- Left Kidney
- Quadratus Lumborum
- Iliacus
- Transverus Abdominis
- Inginual Ligament

16, Spleen
- Splenic Artery
- Splenic Flecture of Colon
- Pancreas
- Second Part of Duodenum

- Falciform Ligament
- Right lobe of Liver
- Gall Bladder
- Mesentary
- Small intestine.

- Spleen
- Splenic Vein
- Left Kidney
- Portal Vein
- Superior Mesenteric Vein

- Coracoid Process
- Glenoid Fossa
- Greater Tuberosity of the humerus
- AC joint (acromio-clavicular)
- Surgical Neck of humerus
- Acromion process

- Olecranon fossa of humerus
- Coronoid process of ulna
- Radial Tuberosity
- Capitulum
- Superior radioulnar joint
- Olecranon Process of ulna
- Neck of Radius
- Medial epicondyle of humerus

- Scaphoid
- Hook of the Harnate
- Styloid process of ulna
- Proximal interphalangeal joint
- Head of 4th metacarpal

- Biceps Brachii
- Pronator teres
- Brachioradials
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Palmaris longus

- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
- Deltoid
- Teres Minor
- Teres Major

- Flexor digitorum superficialis tendon
- Hypothenor eminence
- Flexor Retinaculum
- Thenar eminence
- Flexor carpi ulnaris tendon

- First carpometacarpal joint
- Scaphoid
- Lunate
- Lateral collateral ligament
- Articular disc
- Fibrous capsule of wrist joint
- Radius
- Ulna

- Medial Epicondyle
- Trochlea of humerus
- Coronoid Process
- Trochlear notch of ulna
- Olecranon Process

- Coronoid Fossa
- Radial fossa
- Annular ligament
- Coronoid process
- Medial Co-lateral ligament
- Medial Epicondyle
- Lateral Co-lateral ligament

- Hamate
- Pisiform
- Scaphoid
- First carpometacarpal joint
- Metacarpophalangeal joint

- Axillary artery
- Musculocutaneous nerve
- Lateral root of median nerve
- Median nerve
- Musculocutaneous nerve

- Radial nerve
- Median Nerve
- Ulnar nerve
The brachial artery begins at the lower border of which muscle?
Teres Major
The brachial artery begins at the lower border of teres major as a direct continuation of the axillary artery.
At the level of the distal end of the humerus the brachial artery lies?
Medial?
Anterior?
Lateral?
Posterior?
Anterior
The common interosseous artery is a branch of which artery?
The Ulnar Artery.
Common interosseous artery which in turn divides into anterior and posterior interosseous arteries. The anterior interosseous artery runs directly on the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane supplying the deep structures of the anterior compartment. The posterior interosseous artery is the principal artery of the posterior compartment of the forearm.

- Axillary Artery
- Brachial Artery

- Brachial Artery
- Radial Artery
- Common interosseous artery
- Ulnar Artery
Which Nerve is involved?
Non-trauma reason for presentation?

Cutaneous distribution of the Median Nerve.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome = compression of median n. at wrist.
What are the contents of the Carpul Tunnel?
Median Nerve,
Tendons: Flexor digitorum superficials (four tendons), Flexor digitorum profundus (four tendons) , Flexor pollicis Longus (one tendon).
Symptoms of severe carpal tunnel syndrome?
- weakness in intrinsic hand muscles
- weakness and wasting in abductor pollicics brevis and opponens pollicis
- Lateral 2 lumbricals impaired.
- altered thumb posture
Key myotomes for elbow flexion and supination?
C5- elbow flexion
C6 - supination
Damage to the C5 myotome leads to weakness in which movements of the limb?
Loss of shoulder abduction and elbow flexion, so the limb hangs down
Damge in the C6 myotome causes weakness of which particular movements of limb?
Loss of elbow flexion (biceps, brachioradialis), and supination so the forearm is pronated.
Where would you sensory test for C5 and C6 dermatomes?

C5 - B (biceps)
C6 - C (thenar eminence)
Observe a medial border of the hand that is convave instead of convex. Which muslce is wasting? Innervated by which nerve?
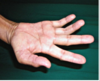
hypothenar eminence. (including: Abductor digiti minimi muscle, Flexor digiti minimi brevis, Opponens digitis minimi)
Ulnar Nerve
What muscles in the forearm are supplied by the ulnar nerve?
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris (FCU) - flexes and adducts the hand at wrist
and medial half of Flexor Digitorum progundus (FDP) - Flexes fingers
- all others in the anterior forearm are innervated by median nerve
What action reliably tests the fucntion of the ulnar nerve in the hand?
Finger abduction
Where is the ulnar nerve vunerable to damage?
Superficialy at the wrist, medial to the pisiform and superficial to flexor retinaculum
Or a fracture at the medial epicondyle (posterior) or in cubital tunnel between 2 heads of flexor cari ulnaris.
Where should you check cutaneous senory function of the ulnar nerve?

B
Which major nerve is responsbile for sensations in lateral forearm skin?
Musculocutaneous nerve?
Which nerves only have a cutaneous sensory distribution in the hand?
Ulnar and median.
What are the cutaneous sensory distributions of the radial nerve?
Posterior arm, posterior forearm and dorsal lateral hand.
What nerve is the only one with no distribution to the elbow and with cutaneous senosry distribution at the “miltary badge” pattern?
Axillary nerve
Course of the Axillary Nerve? What muscles does it innervate? When is it clincial at risk?
Course: Runs from the axilla through the quadrangular space beneath the glenohumeral joint, turns around the neck of the humerus to extend beneath deltoid.
Innervation: Deltoid, Teres minor and shoulder joint.
At risk: shoulder dislocation or fracture of surgical neck of humerus.
Motor signs that indicate damage to the axillary nerve?
Weakness of ABDuction at the shoulder.
Deltoid responsible after starting of motion by supraspinatus.
What is this sydnrome?
Where is the lesion location?

Ulnar nerve palsy.
Claw is caused by the long flexors and extensor digitorum being unopposed by the paralysied lumbricals. Lesion is at the wrist as only effecting medial 2 fingers and not FDP is intact.
Which nerve is responsible for the flexion of lateral three digits?
Median Nerve.
In what upper limb locations is the median nerve more vulnerable to injury?
- Compression in carpal tunnel
- proximal to flexor retinaculum superficial and injured by lacerations
- proximal forearm - between 2 heads of pronator teres or under arch of flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS).
Which region is best for testing the cutaneous sensory function of the median nerve?

A
What is this syndrome called where is the problem in the nerves? Which muscles aren’t working?

Klumpke’s paralysis. Lower brachial plexus. Paralysis of the lumbricals is a key factor.
What nerve does thumb ABDuction test? What does thumb ADDuction test? If both are weak which myotome is suspected to be damaged?
ABDuction tests median nerve
ADDuction tests Ulnar nerve
Suspect T1 myotome.
For Sensory testing: which locations best represent C8 and T1 dermatome?

C8: E
T1: G
What nerve supplies the triceps?
Radial nerve
Which chord does the ulnar nerve arise from?
The medial chord
What nerve supplies the deltoid and teres minor muscle?
Axillary nerve
Action of Pectoralis major at the glenohumeral joint?
Helps to extend the muscle from flexed- postion
ADDucts and medially rotates the arm at the shoulder
Is the radial nerve responible for flexion or extension at wrist?
Extension of the wrist.
Does the postior chord of the brachial plexus supply the extensor or flexor muscles of the wrist?
extensor
What kind of movement is the deltoid muscle responsible for at the glenohumeral joint? Supplied by what nerve?
Major:
Abduction - initiated by supraspinatus
Flexion
Medial and lateral rotation
Axillary nerve (C5 and C6)
Which nerve contins fibres from all Brachial plexus all roots? And what are these roots?
Median nerve:
C5,6,7,8, and T1
Flexor digitorum superficialis?
Attachments? Insertion?
Innervation?
Action?
Attachments: Common flexor orgin and the radias
Insertion: Bodies of the middle phalanges (medial four digits)
Innervation: Median nerve C7, 8 and T1)
Action: Flexor of the proximal interphalangeal joints, elbow and wrist
What muscle moves the scapular forward on chest wall?
Serratus anterior.
Along the upper limb what are the boundaries that note the transition of the Axillary artery to:
Brachial Artery:
Radial and Ulna Arteries:
Brachial Artery: Inferior border of teres major muscle
Radial and Ulna Arteries: After passing through cubital fossa
What is the communication between cephalic and basilic vein called? Which side of the forearm do each of teh veins run on?
Median cubital vein.
Cephalic runs on lateral side
Basilic vein runs on the medial side.
Muscles responsible for the ABduction of the shoulder?
Supraspinatus and deltoid.
Contents of the carpal tunnel?
Flexor digitorum superficialis (four tendons)
Flexor digitorum progundus (four tendons)
Flexor pollicis longus (one tendon)
Median nerve
FLexor carpi radials (one tendon) runs in th eflexor retinaculum.
Which direction does the shoulder joint usually dislocate in?
Antero-inferior direction


