Analysis: DT signals Flashcards
(11 cards)
What is the standard form of the transfer function in the Z-domain?
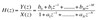
Finite Impulse Response (FIR)
The co-efficients of the denominator poles are zero
What is the trignometric form of z transform?

When is a DT system considered stable?
If all poles lie within the unit circle in the z-plane.
How do we find the magnitude of H(z)?
|H(z)| = (product of lengths of the zero vectors)/(product lengths of the pole vectors)
How can the Laplace Transform be mapped?
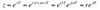
How do we find the phase of H(z)?
phase = (the sum of angles of zero vectors) - (the sum of the angles of the pole vectors)
What is the frequency content of an impulse signal?
Impulse signal contains all possible sinusoidal frequency components
What can we determine from by evaluating a system’s impulse reponse?
- By identifying the presence of increasing or decreasing oscillations in the impulse response we can determine whether a system is stable or unstable
- By identifiying the presence of sinusoids in the impulse reponse we can determine the frequency response
What is the primary use of the Z-transform?
Taking the Z-transform of a systems impulse response allows us to determine the stability and the frequency response
Describe how the Z-transform is carried out
- n = sample number
- x[n] = system response at sample n
- z = complex number = esT= e(σ + jω)T , where T is the sampling period
- multiply x[n] (train of impulses) by corresponing z-n
- perform a summation


