Analysis: CT Systems Flashcards
(21 cards)
What is a transfer function?
A transfer function H(s) is the relationship between output Y(s) and the input X(s), represented by:
Y(s) = H(s)X(s)
(A function that transfers the input X to the ouput Y)
What is the equation for the transfer function?
H(s) = Y(s)/X(s)
Transfer function = Output/Input
How do we find the impulse reponse of a system with transfer function H(s)?
By taking the inverse Laplace transform of H(s)
What is the transfer function of a series interconnection?
H = H1H2
What is the transfer function of a parallel interconnection?
H = H1 + H2
What is a zero?
The roots of the numerator of a transfer function
What is a pole?
The roots of the denominator of a transfer function
When considering poles-zero map when is a system considered stable?
A system is stable if all poles lie in the left-half of the s-plane where σ < 0
If we plot a zero-pole map of a transfer function, how can we evaluate the magnitude and phase at s=p?
Magnitude = (product of the distances of zeros to p) / (product of the distances of pole to p)
Phase = (sum of zero angles to p) - (sum of pole angles to p)
How do we form the transfer function for steady state analysis?
s = σ + jω for the Laplace transform, but growth factor σ = 0.
This means s = jω
Then we must subsitute s = jω into the transfer function for evaluation
How do we evaluate the steady state response from a pole-zero diagram?
By evaluating H(s) along the imaginary axis from complex poles/zeros to point s = jω.
How do we identify areas of attenuation (steady-state)?
Frequencies near zeros get amplified as the length of the vector from those points to the pole is small (small denominator)
How do we identify areas of amplification (steady-state)?
Frequencies near poles get attentuated as the length of the vector from those points to the zero is small (small numerator)
How can we represent a second order transfer function?
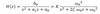
What is ω0, ζ and K?
ω0 = natural frequency
ζ = damping factor
K = gain
What equation do we evaluate to find the step response?
Multiply transfer function by 1/s = unit step
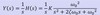
What is the method for finding the step response in the time domain from a transfer function?
Calculate the inverse Laplace Transform
- Find the roots of the denominator polynomial (poles) and factorise
- Use partial fraction expansion to express the sum of first order fractions
- Use the Laplace transform table to revert to the time domain
What is ζ = 1?
Critical damping
- roots (poles) will be a double real negative
- the step response takes the form of an exponential
- it has the fastest response without oscillations
What is ζ > 1?
Overdamped
- poles are two real and negative poles
- step response has still has the form of a growing exponential but is slower
What is ζ < 1?
Underdamped
- poles are complex
- the imaginary part of the poles indicates oscillation before coming to rest
What is ζ = 0?
Undamped
- roots are purely imaginary
- system oscillates and does not come to rest


