Amino Acids & Proteins Flashcards
Structure of proteins influences…
The binding of different molecules
All peptides, polypeptides and proteins in the mammals are polymers of…
Alpha-L-amino acids
How many alpha-amino acids are used to make up proteins
20
Give the general structure of an amino acid

Which functional groups are found on alpha-amino acids, peptides and proteins?
- Carboxylic (-COOH)
- Amino (-NH2)
Attached to the same carbon atom (alpha carbon)
All amino acids in proteins exhibit which configuration?
Why?
Absolute steric configuration
Based on: Proteinogenic L-amino acids, related to L-glyceraldehyde
What is a monoamino monocarboxylic acid?
Amino acids with aliphatic R-groups
List the monoamino monocarboxylic acids
- Glycine
- Alanine
- Valine
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
List the non-aromatic amino acids with Hydroxyl R-groups
- Serine
- Threonine
List the amino acids with sulphur-containing R-groups
- Cysteine
- Methionine
Give the amino acids with aromatic rings
- Phenylalanine
- Tyrosine
- Tryptophan
Give the interaction
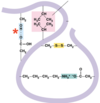
Hydrogen bond
Name the interaction
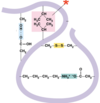
Van der Waals
Name the interaction

Disulphide bridge
Give the interaction
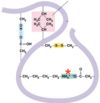
Ionic bond
What is happening in the figure?

- Condensation of two amino acids
- Forming a dipeptide with a peptide bond
What is shown?
What is shown in the red and blue circles?

Polypeptide chain
- Red circle: N-terminal
- Blue circle: C-terminal
Isoelectric point
pH value where the amino acid has no net charge
What classifies globular proteins?
They are water soluble
What classifies fibrous proteins?
They are water insoluble
What are intermediate proteins?
- Water soluble
- Rod-like
- Found in myosin and fibrinogen
List the protein classifications differing by shape or water solubility
- Globular proteins
- Fibrous proteins
- Intermediate proteins
List the proteins classifications by differing compositions
- Simple proteins
- Conjugated proteins
Simple proteins
During hydrolysis: Only amino acids/amino acid derivatives produced


