ADTs Flashcards
How do you implement the code for a function that counts the elements in a linkedlist?
- public driver - checks to make sure there are nodes
- private helper - if next isn’t null, add one and count the next

- Why use dummy nodes?
- How is it implemented?
- The first node, last node, only node or empty list lead to special coding cases:
- lots of ifs
- lots of potential bugs
- less readable
- less easily and reliable to modify
- Add a “dummy” or “header” or “trailer” node to one end or the other end or both ends of a linked list, to ensure that the nodes containing real data are never the first, last or only nodes, and that top is neve null.
- Dummy nodes may contain undefined data, but in ordered lists should have appropriate extreme data values
- with back linking you can tell if a node is a dummy node if one of its links is null.
For trailer and header Nodes, where do the variables exist?
How do you code the trailer and header?
Inside the constructor only

What is the code to insert an item into a header/footer ordered linkedlist?
How does it differ from a list without headers?
without a header we have to check if curr and prev are null etc..
With headers, that additional code is no longer necessary

How do you delete a value by key with a linkedlist with header files?
How does this differe for an ordered/unordered list?
For unordered-check if curr is not the dummy trailer as well
add to while loop: prev.next.next != null

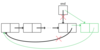
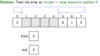
What is a circular linked list and why use it?
- The last node points to the first node (not top).
How it could be useful:
- This would allow you to search the list starting at any node
- An easy way to find both ends, have top pointer point to the last node
- Last node: last
- First node: last.next
Stack - where are new items added?
New elements are added at the top
LIFO - Last in first out
FILO - First in last out
Queue - where are new items added
Added to the back
FIFO - first in, first out
LILO - last in, last out
What are the stack main operations?
- push - add something to the top
- pop - remove something from the top
- top - only look at the top
- isEmpty
- constructor
- destructor - in languages without garbage collection
- isFull - if space is limited
What is the text representation of a stack?
[5 7 3 >,
[ represents the bottom
> represents the top

In general how do you implement a stack with an array?
- The bottom of the stack is always index-0
- The stack class needs an int variable called “top” that contains the index o the top of the stackin the array
- limitation - fixed size
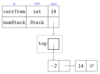
What is the code for the class implementation of a Stack using an array?

Draw the ?variable record? diagram for a stack using an array

In general, how would you implement a stack using a linkedlist
- each node contains an item in the stack
- the front of the list (the top pointer) is the top of the stack
What is the code for the class implementation of a stack using a linkedlist

Draw the ?variable record? for stack using a linkedlist
What is the pseudo code for implementing the bracket matching example

What is the text representation of a queue
< 7 3 4 <
the 7 would be at the front, the 4 would be at the end
angle brackets point in the direction that items move through the queue
What are queue basic operations?
- Enter (or enqueue) - add item
- Leave (or dequeue) - remove item
- Front - loop only at the front of the queue(without removing it)
- isEmpty
ADT Queue - LinkedList
Draw a general linkedlist style 1 using both a front and end pointer
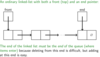
What is the class code for a queue linked list style 1 (front and end pointer)

Queue - Linkedlist style 1 - front and end pointer
Draw a ?varaible record? of what the implementation looks like
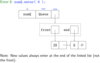
Queue - LinkedList Style 2 (circular)
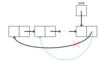
Draw the implementation of a queue using a circular linkedlist

Queue - LinkedList Style 2 (circular)
Draw the general implementation of a queue using a circular linkedlist to Enqueue(enter) an item.