Abdominal Pain (Complete) Flashcards
Most abdominal diseases present usually with which symptom alone?
Pain
Most abdominal diseases present with pain alone. However there is likelihood of making a correct diagnosis based on focusing on which 2 things in the history?
Site of pain
Character of pain
What acronym is useful in determing cause of abdominal pain in history taking?
SOCRATES
Site
Onset
Character
Radiation
Associating
Time course
Exacerbating or relieving factors
Severity
Label the abdominopelvic regions


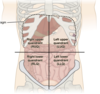
Label the 4 abdominopelvic quadrants

Label the horizontal planes of surface anatomy


The transpyloric plane is at which vertebral level?
L1
List 6 anatomical structures that lie within the transpyloric plane (L1)

Pylorus of stomach
Neck of pancreas
Fundus if gallblader
Dueodenojejunal flexure
Hillum of kidney
End of spinal cord (Adult)

What vertebral level is subcostal plane located?

L3
What important anatomical structure lies within the subcostal plane (L3)?

Origin of inferior mesenteric artery

What vertebral level does the supracristal plane lie on?
L4
What important anatomical structure lies at the level of the supracristal plane (L4)?

Bifurcation of aorta (Common iliac arteries)

Pain in the right hypochondriac region is mostly a result of which anatomical structure?
Gallbladder
Pain in the left hypochondriac region is mostly a result of which anatomical structure?
Pancreas
Pain in the epigastrum is mostly a result of which 3 anatomical structure?
Stomach
Duodenum
Pancreas
Pain in the right and left lumbar region is mostly a result of which anatomical structure?
Kidneys
Pain in the right iliac region is mostly a result of which 2 anatomical structures?
Appenidx
Cecum
Pain in the left iliac region is mostly a result of which anatomical structure?
Sigmoid colon
Pain in the hypogastric region is mostly a result of which anatomical structure?
Colon (Transverse)
Bladder
Uterus
Adnexae (Skin)
Useful pain site diagram

What are the 3 main divisions of the gut?
Foregut
Midgut
Hindgut
What 3 GI structures are a part of the foregut?
Distal oesophagus
Stomach
Proximal half of 2nd part (desecending) duodenum

Which important vessel of the abdominal aorta supplies the foregut?
Celiac trunk
What 3 GI structures form the midgut?
Distal half of 2nd part of duodenum
Small intestine
Proximal 2/3rds of transverse colon













