7.02 Pituitary Function Flashcards
What are the two parts of the pituitary gland? Give their alternate names too
- Posterior Pituitary (neurohypophysis)
- Anterior Pituitary (adenohypophysis)

Despite being structurally linked to each other as the pituitary gland, how are the anterior and posterior pituitary different to one another?
The anterior and posterior pituitary glands can be considered two completely different structures.
- Embryologically
- Structurally
- Functionally different
Describe the posterior pituitary in terms of tissue and the link to the hypothalamus
It is a neural tissue
- Outgrowth of brain, nervous tissue
- Neural link to hypothalamus
Describe the anterior pituitary in terms of tissue and the link to the hypothalamus
Glandular
- Origin from glandular epithelial tissue, ectodermal cells
- Vascular link to hypothalamus
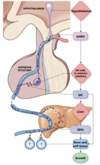
Draw the relationship of the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland and the anatomy surrounding it
- The pituitary gland hangs off the hypothalamus
- The infundibulum is a stalk that connects the pituitary to the hypothalamus
- The pituitary gland sits in the sella turcica of the body of the sphenoid bone (a well protected gland)

Describe the general flow of information (neural and hormonal) through the pituitary
- From the hypothalamus (trophic hormones)
- To the anterior/posterior pituitary gland (trophic hormones)
- To endocrine glands (hormones)
- To the target organ
- To the target cell

What are the two major hormones produced in the posterior pituitary gland?
What does each of them do?
Vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone ADH)
- increases collecting duct permeability
- decreases urine volume (water retention)
Oxytocin
- Causes milk ejection from the breast (contraction of the myoepithelium)
- Contraction of the myometrium in the uterus for birthing
Describe the synthesis, storage, and release of posterior pituitary hormones
- The hormone is made and packaged in cell body of neuron in specific cells of the hypothalamus
- These travel down the axon of the neurons into the posterior pituitary
- The hormone is stored in vesicles in the posterior pituitary
- A signal for release is recieved from the neuron causing release of the hormone into the blood stream to act on distant target organs/cells

Higher centres impact on the neuroendocrine and endocrine relationsips.
What are the main neurons of the hypothalamus synthesising and influencing the posterior pituitary gland?
Supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei are responsible for regulating the posterior pituitary hormones
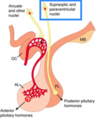
What are the main neurons of the hypothalamus synthesising and influencing the anterior pituitary gland?
Arcuate nuclei and other nuclei

How does information from the hypothalamus reach the anterior pituitary gland?
Through the hypothalamic‐hypophyseal portal system
= a vascular system
What are the major hormones being produced by the anterior pituitary gland?
Briefly describe each one [7]
-
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH/corticotropin)
- Stimulates the adrenal gland to produce a hormone called cortisol. ACTH is also known as corticotrophin.
-
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete its own hormone, which is called thyroxine. TSH is also known as thyrotrophin
-
Luteinising hormone (LH)
- Controls reproductive functioning and sexual characteristics. Stimulates the ovaries to produce oestrogen and progesterone and the testes to produce testosterone and sperm.
-
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Same as LH
-
Prolactin (PRL)
- Stimulates the breasts to produce milk. This hormone is secreted in large amounts during pregnancy and breast feeding, but is present at all times in both men and women.
-
Growth hormone (GH)
- Stimulates growth and repair in all cells of the body.
-
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
- Exact role in humans is unknown.
Describe the signaling of hormones through the hypothalamic-pituitary portal system
- Neurons in the hypothalamus (arcuate and others) synthesis trophic hormones and release them into the capillaries of the portal system
- Trophic hormones travel through the portal system to the anterior pituitary gland
- The different trophic hormones target specific cells in the anterior pituitary gland
- Endocrine cells of the pituitary respond and release their hormones into the second set of capillaries for distribution to the rest of the body.

What kind of disturbance will happen if there is disruption at the level of the hypothalamus or pituitary
Disturbance has potential to cause a wide impact because there are so many trophic and endocrine hormones that are produced and regulated in this region

Fill out the following table