6. Visceral Manipulation Technique Integration Flashcards
(30 cards)
Origin and Insertion for:
- Anterior scalene
- Middle scalene
- Posterior scalene
- Serratus posterior superior
- 1st rib anterior = 3-6 anterior TP
- Middle of 1st rib = 2-7 anterior TP
- Posterior part of 2nd rib => C4-5 TP
- Lateral portion of C7-T3 SP => angle of ribs 2-5

trauma to neck: other structures involves
- •Sternocleidomastoid
- •Omohyoid/ Stylohyoid
- •Splenius capitus
- •Levator Scapulae
Neck trauma: what is <3 attached to and what suspends it?
- Attached to: diapgragm
- Suspended by: ribs, sternum and spine

what nerves pass through mediastinum?
- Phrenic
- Vagus
what visceral structures cause the following SD?
- Diaphragm strains =
- Sternal SD
- Rib SD
- Pull of vasculature into neck
- Trachea to the neck
- Diaphragm strains => heart
- Sternal SD => fascial attachments of heart
- Rib SD => displacement of sternum, strains to diaphragm
- Pull of vasculature into neck => from <3 through aortic arch => carotid a. and v.
- Trachea to the neck => mediastinal stress through trachea to neck m attachments.
If patient has [acute trauma 2 weeks ago], what are treatment considerations?
- Gentle direct MFR
- Indirect MFR
- Guide for joint release
- DO NOT let structres heal in asymmetric strained positions
If patient has [acute trauma 2 weeks ago], when do we treat next?
wait 1-2 weeks to treat
Direct and indirect treatments for trauma patients
- Direct: ME and ART
- Indirect: Stills, FPR, BLT
If neck trauma, what regions do we treat first (neck, thoracic vs ribs)?
- Treat thoracic bc muscular connections to neck and ribs = least painful
- Neck
- Ribs last, bc may have already resolved.
What indirect treatments can be used to treat trauma?
Stills
FPR
BLT
BLT Technique
Basic Steps:
- Position the structure in neutral position in all planes
- Hold and use an activating force
- Respiration: enhances ease until “air hunger”
- Inherent Motion: just by holding in position there is a motion that motivates improved function
- Release may be palpable: tissue may soften, inherent motion may improve
- Recheck motion in all planes, and repeat until desired results achieved
What is the purpose of BLT?
Balance the ST around the re-aligned straightened structural/bone components and restore EQUAL tension/motion.
PT has pyelonephritis. What somatic structures are involved?
- T10-11 => causes vertebral rotation and rib dysfunctions at that level
- Interconnections of muscles above and below cause vertebral dysfunction at multiple levels above and below
What somatic structures are involved in a case of pyelonephritis (T10-11)
what causes tension and pain
Adjacent tissue irritation from local inflammatory hormone release causes tension and pain
- •Psoas
- •Quadratus lumborum
- •Transversus abdominus
- •Diaphragm
What does a tight psoas cause?
- Lumbar Lordosis (anterior pull on lumbar)
- Ipsilateral SB (lateral pull on lumbar)
- Anterior innominate rotation
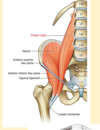
What does a tight quadratus lumborum cause?
- Inferior pull on and SD of Rib 12 (effects rib 11 too)
- Anterior innominate rotation => superior pull on ilium
- Lumbar side bending
why treat spine before ribs?
Because the vertebra and rib may move together as a unit => fixing vertebral dysfunction bring ribs back into relative alignment with other ribs negating the need for separate treatment.
how can we Balance the tissues and reduce tension when there is a disease (pyelonephritis)?
- Direct: stretching, MFR, inhibition
- Indirect: MFR, CS
when we have lower abdominal and sacral pain, how do we treat?
- Treat lumbar 1st!
- Treat pelvis and sacrum 2nd because lumbar treatment pressure through the pelvis may cause pelvic / sacral SD
UPL5 TP
LPL5 TP
-
UPL5 TP =
- Superior medial surface of the PSIS
-
LPL5 TP=
- Inferior to PSIS, on the ileum

PL3 gluteus TP
PL4 gluteus TP
- PL3 gluteus TP = 2/3 lateral from PSOS - TFL
- PL4 gluteus TP = posterior margin of TFL
PS1 TP
- Bilateral: medial to PSIS and in the mid-portion of the sacral sulci
- Treatment: pt prone/seated = apply anterior pressure DIAGONALLY OPPOSITE of TP

P2-4 TP
Location: midline of sacrum, between the sacral spines
Treatment: pt prone/seated = apply anterior pressure DIAGONALLY OPPOSITE of TP to cause transverse axis rotation.
- PS2 = inferior apex
- PS3= varies to ask pt
- PS4= base

PS5 TP
Treat L OR R: superomedial to ILA
Treatment: pt prone/seated = apply anterior pressure DIAGONALLY OPPOSITE of TP


