4 - Workplace: Risk Management Flashcards
Risk
- The effect of uncertainty on objectives” (from ISO 31000)
- Could take the form of threats or opportunities
Risk Management
- “Coordinated activities to direct and control an organization with regard to risk”
- Change probabilities or magnitude of impact on objectives
Benefits of Risk Management
- Strategic alignment of risk levels and management
- •More effective response to risk
- More consistent response across the organization
- Fewer resources wasted
- More integrated vision of risk in the organization
Barriers to Risk Management
- Structural—silo organizational structures
- Cognitive—mindset lacking imagination, or one of unreasonable optimism, resistance to change
- Cultural—poor alignment of the organization’s culture; inadequate communication of the culture’s risk approach
ISO 31000
11 principles—for example:
- Focused on value and continual improvement
- Integrated into all processes and decision making
- Transparency
- Responsive to change
Framework
- Management commitment
- Policies, processes, ethics, values, leaders’ examples, culture
Risk management process
Step 1: Establish the context of risk.
Risk Management
- Know internal and external sources of risk.
- Define risk criteria:
- Risk position (acceptable gain or loss)
- Risk appetite and risk tolerance (acceptable amount of uncertainty)

Strength of Organization’s Governance

Common Misaligned Risks
Moral hazard
- One party engages in risky behavior knowing that another party will incur any resulting loss.
Principal-agent problem
- An agent (ER) makes decisions on behalf of a principal (EE) but has personal incentives not aligned with those of the principal (EE).
Conflict of interest
- A person or organization has the potential to be influenced by two opposing sets of incentives.
Step 2: Identify and analyze risks.
Risk Management
Methods:
- Experts and information sources
- Focus groups and interviews
- Surveys
- Process analysis
- Direct observation
Duty of Care
Employer’s responsibility to take all reasonable steps to ensure the health, safety, and well-being of employees and protect them from foreseeable injury
Risk Formula
Risk level = Probability of occurrence ´ Magnitude of impact
Risk Scorecard

Risk Matrix

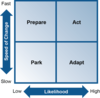
Prepare, Act, Park, Adapt (PAPA) model
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)
Early signals of increasing risk exposure; critical part of preparedness.
- Strategically aligned.
- Developed by identifying root causes of risks and intermediate events.
- Monitor for changes
Risk Register
- Risk category
- Risk event
- Risk classification
- KRIs
- Risk management controls
- Risk owner(s)
- Reporting requirements
Step 3: Manage risk.

Eliminate Uncertainty

Redefine Ownership

Increase/Decrease Effect

Take No Action

Residual Risk
The amount of risk that remains after all management efforts have been exhausted
Implementing Risk Management Plan
- Define objectives.
- Be strategically focused.
- Combine activities and results.
- Combine lagging and leading metrics.
- Modify risks related to noncompliance.
- Instill risk management principles in organization’s members and processes.
- Integrate actions across organization.
- Communicate needs, expectations, and new policies and processes
Emergency Preparedness
- Emergency response planning and training
- Securing employee health and safety