4. Development in Children Flashcards
what disorder of knee aligment do children often have at birth
varus knees - become neutrally aligned at around 14 months progressing to 10 to 15 valgus at age 3
and then gradually regress to physiological valgus of 6 around the age of 7-9
how many degrees of malalignment is considered pathological valgus/varus
alignment is considered outside the normal range when > 6 degrees
when do most cases of genu varus or valgum resolve by
age of ten
what does Blounts disease cause
genu varus
growth disorder of medial proximal tibial physis, causing lower leg to angle inward
what does Blount’s disease produce on X ray
beak like protrusion

name some pathological causes of genu varus/valgus
tumours: osteochondroma or enchondroma
rickets
neurofibromatosis (valgus)
skeletal dysplasia (varus)
how are excessive deformities of knee alignment corrected
osteotomy or growth plate manipulation surgery
what can persistent genu varus cause
early onset medial compartment OA
name 3 causes of in toeing
femoral neck anteversion
internal tibial torsion
forefoot adduction

femoral neck anteversion
child tends to sit in W position
in toeing and knock knees
can predispose to patellofemoral problems
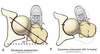
internal tibial torsion
bone rotated inwards about its vertical axis
often seen in toddlers and majority resolve by age 6

forefoot adduction

mobile flat feet
flattened medial arch forms wtih dorsiflexion of the great toe - Jack test
may be dynamic - present on weight bearing only
normal variant in children
what may mobile flat feet relate to
hypermobility
familial or idiopathic
rigid flat foot
arch remains flat regardless of great toe dorsiflexion
what does rigid flat foot imply
underlying abnormality - tarsal coalition where some tarsals are stuck together. may require surgery
may represent underlying inflammatory or neurological disorder
curly toes
minor overlapping of toes because flexor tendons are too tight - most common in 5th toe
in rarely persisting cases can consider flexor tenotomy
can cause discomfort

who is anterior knee pain common in
females and teens
take radiographs and check hips
refer to physio


