3. Developmental Disorders Flashcards
(18 cards)
how do limb malformations arise
some are genetically determined - AuD
some due to insult to the developing bud usually between 4th and 5h week gestation
what is the most common congenital malformation
syndactyly
syndactyly
2 digits are fused together
surgical separation required (around age of 3 or 4)

polydactyly
extra digit formed
treated by amputating the extra one

fibular hemimelia
partial or complete absence of the fibula
leads to a shortened limb, bowing of the tibia and ankle deformity

how can fibular hemimelia be treated
mild cases - circular frame external fixator
severe cases - ankle amputation and use of a below knee prosthetic limb

what does absence or hypoplasia of radius lead to
underdevelopment of the hand (usually absence of thumb) with marked deformity (radial club hand)

how is radial hypoplasia treated
surgical reconstruction with thumb reconstruction from the index finger (pollicisation) and correction of the deformity
pollicisation
surgical technique in which a thumb is created from an existing finger

tarsal coalition
fusion between two tarsal bones of the foot
may cause painful flat feet later in life
abnormal connection may need surgically divided

who does Obstetric Brachial Plexus Palsy most commonly arise in
the incidence during vaginal delivery is around 2 in 1000
large babies (macrosomia in diabetes), twin deliveries and shoulder dystocia (difficult delivery of shoulder)
erb’s palsy
injury to C5 and 6 nerve roots results in loss of motor innervation to deltoid, supra and infra spinatus, biceps and brachialis muscles
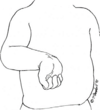
internal rotation of the humerus
leads to classic waiter’s tip posture

how is erb’s palsy treated
physio required to prevent contractures early
good outcome in 60-90% cases
surigcal release of contractures and tendon transfers may be required if no recovery
Klumpke’s palsy
rarer than Erb’s
lower brachial plexus injury (C8 and T1 roots) caused by forceful abduction of the arm
damage of C8 and T1 leads to combination of radial and ulnar injury which may produce claw hand due to loss of lumbrical function
arm is held in adduction
eg trying to break a fall by grabbing on to something above
what may Klumpke’s palsy result in
- Horner’s syndrome due to disruption of first sympathetic ganglion from T1
- remember sympathetic thoracolumbar outflow
- ptosis, miosis and anhydrosis
miosis
excessive constriction of pupil of one eye
ptosis
drooping of one eyelid
prognosis in Erbs compared to Klumpkes
better in Erb’s - good outcome 80-90% cases
Klumpke - 50% recovery and no specific treatment


