4. CVS Embryology Flashcards
(20 cards)
Describe the formation of the Primitive Heart Tube
- BEFORE the embryo folds, their are a pair of blood islands containing small blood vessels within the mesoderm on either side of the notocord
- These become two separate endocardial tubes
- As the embryo folds, tubes meet at midline forming the primitive heart tube

When does the formation of the primitive heart tube begin and end?
- Starts at 19 days
- Ends at 22 days
What are the 6 sectons of the primitive heart tube?
- Aortic roots
- Truncus Arteriosus
- Bulbus cordis
- Primitive ventricle
- primtive atrium
- Sinus venosus

Describe looping of primitive heart tube
- Pericardial sac drives size of looping
- Tube elongates, runs out of room
- Bulbus cordis folds down, Primitive atrium folds up
Note: ventricle enlarges more than atrium

Describe, in brief, the development of the great vessels
- Early arterial system = bilaterally symmetrical system of arched vessels
- degeneration of some of the vessels as we don’t need them
- RIGHT 4th arch remodels to give proximal part of subclavian artery. LEFT 4th arch = arch of aorta
- RIGHT 6th arch = R pulmonary artery, LEFT 6th arch = L pulmonary artery and ductus arteriosus (shunt that bypasses lungs)

What are important relations to the development of the great vessels?
- Left recurrent laryngeal nerve gets hooked around ductus arteriosus (shunt) which then after birth degenerates so is hooked around arch of aorta
- Right recurrent laryngeal nerve gets hooked around right subclavian artery
Describe fetal circulation
- Oxygenated blood from mother in placenta
- BY PASS LIVER (ductus venosus)
- IVC –> RA
- a little bit of blood goes from RA to RV to PT (so that RA forms) but then SHUNTED from PT to Aorta via ductus arteriosus
- most blood shunted from RA –> LA via foramen ovale to by pass RV
- Aorta
- Body
- deoxygenated blood back to placenta and exchange of nutrients with mother
Describe how the foramen ovale is built
- Septum primum forms = wedge of tissue from top down to endocardial tissue shelf. There is a hole in this tissue called the ‘ostium primum’
- Ostium primum obliterates and a hole forms above it within the septum primum called ‘ostium secundum’
- Once complete, a second wall built called ‘Septum secundum’. within it is a hole called the foramen ovale
- As pressure in right atrium > left atrium, leaves pushed apart so blood can move from right to left side of heart through foramen ovale and ostium secundum
Note: should not line up as after birth, pressure in LA > RA so want two leaves to push together obliterating shunt

How are the shunts obliterated?
- LA pressure > RA pressure as respiration begins so septum primum pushed against septum secundum obliterating it.
- Ductus arteriosus contracts due to pressure too
- Ductus venosus is obliterated as placental support removed
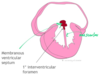
Describe how the interventricular septum is formed
- Muscular portion grow up from floor toward endocardial cushions
- Leaves a small gap (called the primary interventricular foramen)
- Membranous ventricular septum then forms in this foramen up to the endocardial cushions
Note: membranous portion can be underdeveloped = L –> R shunt
How are the outflow tracts separated?
- Endocardial cushions appear in truncus arteriosus (TA) forming a scaffold on which another septum can form
- Divides TA into two discrete channels which appear slightly ofset from each other
- Together they grow upward in a spiral manner into the lumen of the TA ‘spiral septum’.

Describe transposition of the great vessels
- Normally the aorta arises from the LV and PT from RV
- In this problem, it is switched
- Therefore baby = cyanotic as ox blood goes to lungs and deox around body
- Arterial switch surgery needs to be carried out

Describe tetralogy of fallot
- Large ventricular septal defect
- Overriding aorta (straddling two ventricles)
- Therefore Right ventricular outflow tract obstruction (pulmonary stenosis)
- Right ventricular hypertrophy
Could be due to abnormal septation of truncus arteriosus (skewed to one side?)
The neural crest cells control this - derived from neural ectoderm (v. sensitive to alcohol)

Describe patent ductus arteriosus
- Remains open after birth
- Blood will shunt from left to right (oxygenated blood will go into deox side)
- can be tied shut/plugged
Describe atrial septal defect
- ostium secundum and foramen ovale holes can align, septum primum resorbed, septum primum too short so stays open
- = L–>R shunt post birth
Describe ventricular septal defect
- oxygenated blood from LV to RV therefore
- LV volume overload
- pulmonary venous congestion
- eventual pulmonary hypertension
Describe atrio-ventricular septal defect
- Mixing of blood
Describe tricuspid atresia
- No blood inlet into RV
- RA pressure > LA pressure
- R to L atrial shunt
Describe pulmonary atresia
- no blood inlet into PT, no RV outflow
- Pressure in RA > LA
- Right to left shunt


