4/18 Infections of the Bones/Joints - Corbett Flashcards
suppurative arthritis
septic joint!
- only 20% of arthritis, BUT can lead to rapid joint destruction/be life-threatening
- need to aspirate the joint quick and rule it out
etiology: microorganisms of any type can lodge in joint → acute infl process
- often hematogenous spread (via vasculature of synovium - lacks a bm!)
- could be direct/traumatic innoculation, contiguous spread from osteomyelitis or soft tissue abscess
at risk?
who?
1. age/gender
- generally hits old and young
- neonates: contiguous spread from epiphyseal osteomyelitis (H. influenza/Kingella)
- late adolescence/YA: Gonococcus; F > M
- older kids/adults: S. aureus
- what about sickle cell disease? Salmonella at any age!
- joint trauma
3. previous joint patho (RA, OA, crystal, SC disease)
- impaired host defense
* which joints?*
-
85% monoarticular
- knee 50, hip 20, shoulder, ankle wrists
- 10-15% polyarticular
- prior damage, RA, gout, systemic conn tissue disorders, DGI
what pathogens?
in old/young, mostly Staphylococcus
in 16-40 age range…Gonococcus

Kingella

suppurative joint pathophys
- microbes get into joint space
-
neutrophils infiltrate synovium → edema, purulent effusion
- proteolytic enzymes released → damage to articular cartilage, subchondral bone, joint capsule
suppurative joint
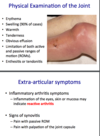
phys exam & extra-articular sx
erythema/swelling/ tenderness etc - v obvious
sx of infl arthritis, synovitis - usually no real extra-articular sx!
dx of infectious arthritis
JOINT ASPIRATION, looking for:
- crystals (polarizing microscopy) - should be none
- bacteria (Gram stain)
- WBC count (50k or over? septic joint likely)

treatment
drainage + antibiotics

types of infection
Gram positive
Gram positive
- majority of infections (S. aureus)
- most monoarthritic, large joints (knee)

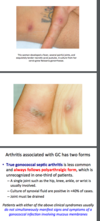
gonoccocal inf
Gonococcal
two forms:
- disseminated infection
- fever, chills, malaise
- asymmetric polyarthralgia (migratory arth)
- tenosynovitis
- synovial fluid cultures often negative
- true gonoccocal septic arthritis
- less common; always follows polyarthralgic form
Gram negative
rapid onset
more common with impaired immunity (DM 65+)
- E. coli and Pseudomonas!
- sickle cell → Salmonella
- IVDA → Pseudomonas
spirochete-assoc arthritis
Lyme disease
Borrelia burgdorferi → arthritis in up to 70% of pt
two patterns:
- early polyarthritis: wax/wane over 1mo
-
chronic infl synovitis: gradual
- monoarticular, large joints
- less infl but large effusions
- cultures neg, PCR maybe pos
Mycobacteria-assoc
tuberculous
- disseminated primary inf or late reactivation (often with HIV inf)
- common: chronic granulomatous monoarthritis (large wt bearing jts - hips, knees, ankles)
- progressive monarticular swelling/pain over months and years
viral assoc
Rubella
Mumps
Parvovirus B19

osteomyelitis
inflammation of bone caused by infecting organism
- bone is normally resistant to bacterial colonization BUT trauma/surgery/foreign bodies/prostheses can disrupt integrity
types:
- post traumatic 50
- vascular insufficiency 35
- direct trauma
- DM
- hematogenous seeding 15
pathophys
- osseous vascular affects location of bone inf
-
neonate: metaphyseal vessels penetrate growth plate → infl of metaphysis, epiphysis, both
- epiphyseal inf can spread to jt
- kids/adults: metaphysis is typical site
-
neonate: metaphyseal vessels penetrate growth plate → infl of metaphysis, epiphysis, both
- inf impairs blood supply → bone necrosis in the SEQUESTRUM
- deposition of reactive bone at periphery → shell of living tissue around necrotic infected bone (INVOLUCRUM)

hematogenous osteomyelitis
adults, common site: vertebrae (then long bones, pelvis, clavicle)
- Staph aureus, then Psuedomonas and Enterobacteriaceae
clnical findings
- acute systemic illness: malaise, fever, chills, leukocytosis
- joint: throbbing pain/erythema + decr motion + inability to bear weight
-
radiographic
- lytic focus of bone destruction surrounded by zone of sclerosis
osteomyelitis bacteria study guide

unusual osteomyelitis
- anaerobic bacteria
- bartonella henselae
- brucella
- salmonella
- fungi
- myco TB
- viruses



