3: Blood supply of the brain Flashcards
For which percent of the body weight and cardiac output does the brain makes up?
Only 2% of body weight but
10- 20% of cardiac output
Which two major arteries supply the brain with blood?
- Internal carotid artery
- Vertebral arteries
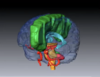
What is the circle of Willis?
Anastomosis of arteries supplying the brain
–> allows collater circulation in the cerebral circulation















Summarise the overall venous drainage of the brain
Cerebral veins
–> Venous sinuses (in subarachidonic space) –>
–> Dura mater
Internal jugular vein
What is a Cerebrovascular accident (CVA)?
A Stroke
rapidly developing focal disturbance of brain function of presumed vascular origin and of >24 hours duration
–> 85% infarction, 15% hemmorage
What is a Transient Ischaemic Attack (TIA)?
rapidly developing focal disturbance of brain function of presumed vascular origin that resolves completely within 24 hours
–> warning sign: patients are at hight risk of getting a stroke!
What is an infarction?
Degenerative changes which occur in tissue following occlusion of an artery
What is cerebral ischemia?
Lack of sufficient blood supply to nervous tissue resulting in permanent damage if blood flow is not restored quickly
hypoxia/anoxia
What are posiible causes for an occlusion
- Thrombus (blood cloth at site of formation)
- Embolus (any other substance or other blood cloth formed in another place)
What are the main risk factors for stroke?
- Age
- Hypertension
- Cardiac disease
- Smoking
- Diabetes mellitus
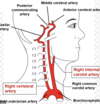
Which part of the brain is supplied by the anterior cerebral artery?
Medial two thirds of the Cortex
- Medial prtions of frontal lobes
- Superior medial parietal lobes

Which part of the brain is supplied by the middle cerebral artery?
Lateral 2/3 of cortex + forebrain

Which part of the brain is supplied by the posterior cerebral artery?
The occipital lobe (posterior part)

Which symptoms might occur when ther is a blockage to the anterior cerebral artery?
Paralysis of
- contralateral leg (more than arm)
- face
Disturbance of intelect, executive function and judgement (–>abulia)
Loss of appropirate social behaviour

Which symptoms might occur when there is a occlusion of the middle cerebral artery?
“Classic stroke”
- Contralateral hemiplegia (=hemiparesis): arm rather than leg
- Contralateral hemisensory (=altered sensation) deficits
- Hemianopia (optical disturbance (blurred/blindness)
- Aphasia (L sided lesion) (loss of speach)

What is hemiplegia?
Hemiparesis
(half sided paralysis)
What is hemianopia?
Visual field loss in a vertical line