21 - Vertical Themes (Uni Days) Flashcards
(86 cards)
What is a standard LFT panel?
Look at clinical picture, often LFTs are isolated on their own and this is common and normal

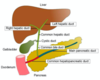
What are the different ducts in the HPB system?
What LFTs are raised in hepatocellular injury and cholestasis?
Hepatocellular Injury: infection, malignancy, autoimmune, alcohol, drugs, NAFLD
Cholestasis: pregancy, drugs, biliary atresia, primary biliary cholangitis, gallstones

What are some extender liver screening tests?

What are the different types of jaundice and the causes?

How does haemostasis occur?
Primary clot: see image
Secondary clot:
- Initiation
- Amplification
- Propagation
- Termination

How does post hepatic obstructive jaundice present?
Pale stools and dark urine
What is included in a basic clotting screen?
PT/INR: extrinsic clotting. FVII, V, X, prothrombin and fibrinogen
APTT: FVIII, IX, XI, XII, V, X, prothrombin and fibrinogen
Bleeding Time: platelets
Thrombin time: how long for fibrinogen to fibrin
ALWAYS TAKE FBC TO LOOK AT PLATELETS WITH CLOTTING SCREEN

What are some causes of abnormalities on clotting screens?
- Inherited deficiency of a clotting factor
- Inherited deficiency of or defective von Willibrand factor
- Consumption – clotting factors used up by DIC
- Dilution – massive blood loss when replacement is with IV fluids and red cells only
- Vitamin K deficiency or antagonism (affects factors II, VII, IX and X)
- Liver disease
- Anticoagulants

All clotting factors apart from two are made by the liver, which are these?
vWF
Factor 8
How will clotting screens (PT, APTT, fibrinogen, platelets) be affected in the following:
- Haemophillia A or B
- DIC
- End stage liver disease due to cirrhosis
Platelets adhere to vWF

How will clotting screens (PT, APTT, fibrinogen, platelets) be affected in the following:
- Over anticoagulation with warfarin
- Patient on therapeutic dose LMWH for DVT

What are the different types of followers in the Kelley leadership study?

What empirical antibiotic should you sue for meningitis?
- IV Ceftriaxone
- If over 60 use Ceftriaxone and Amoxicillin for listeria cover
- If allergy use Meropenem
Once cultures have come back can switch to narrower spectrum antibiotic

Why is vancomycin not used for meningitis?
Poor penetration through the BBB
What are some risk factors for a C.Diff infection?
- Recent broad spectrum abx use
- Prolonged hospital stay
- >65
- PPI therapy
- Immunosuppressed
- Chemotherapy

What antibiotics are used for cholecystitis?
- Co-amoxiclav or Metronidazole+Ciprofloxacin or Meropenem
- Also give IV fluids, analgesia and arrange for cholecystectomy

Is meropenem safe in penicillin allergy?
Has a beta lactam ring so can still cause some reactions
Check if patient has true penicillin allergy
How long doe patients need to take antibiotics for acute cholecystitis?
- If no surgery due to being too frail then 4-6 weeks
- If cholecystectomy and no perforation none needed after surgery
- If perforation then 5 days post operatively
IV fluids, analgesia, antibiotics
What is evidence based medicine?
Incorporates value based medicine

What are the benefits of value based medicine?
Never assume you and the patient hold the same values!!!

What is the difference between a sign and symptom?
Sign: objective that can be viewed by another person
Subjective: subjective that is only felt by the patient
If asked in an exam what symptoms by the examiner use jargon, if asked to ask the patients about their symptoms DO NOT use jargon

What investigations would you order for this patient?

- Bloods: FBC, U+Es, LFTs, CXR, eGFR, HbA1c, Lipid profile, NT-proBNP
- ECG
- Echocardiogram
- CXR
What signs will you see on a CXR for a heart failure patient?
- Cardiomegaly
- Pulmonary oedema (bilateral infiltrates/Batwing)
- Fluid in right fissure
- Pleural effusion
















