200/201/220/221 - Anatomy of Abdominal Wall, Pelvis, Perineum I, II, III Flashcards
How do the upper rectus sheath and the lower rectus sheath differ?
-
Upper sheath:
- All 3 aponeuroses envelop each rectus muscle
-
Lower sheath
- All 3 aponeuroses pass anterior to all the muscles
- The posterior sheath terminates abruptly at the arcuate line

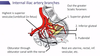
The transversus abdominis contributes to the [layer of covering of the spermatic cord]
The transversus abdominis contributes to NONE of the layers covering the spermatic cord

The splanchnopleure gives rise to the [superficial/deep] body wall
The somatopleure gives rise to the [superficial/deep] body wall
The splanchnopleure gives rise to the deep body wall
The somatopleure gives rise to the superficial body wall
The [layer of the body wall] contributes to the internal spermatic fascia and deep inguinal ring
The Transversalis Fascia contributes to the internal spermatic fascia and deep inguinal ring

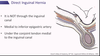
In females, the gubernaculum persists as which two structure?
Ovarian ligamnet
Round ligament of the uterus

What is contained in the superficial pouch?
(In general, not specific structures)
External genital organs
- Penis
- Clitoris (body and crura)

The [layer of the body wall] contributes to the cremaster muscle
The internal oblique muscle contributes to the cremaster muscle
Which muscle maintains constant muscle tone to bend the rectum and relaxes to allow defecation?
Puborectalis (aka pubo-rectal sling)
- Skeletal muscle => under somatic control*
- Most medial part of levator ani (=> most medial part of the pelvic diaphragm)*

Which structure marks the transition from internal to external anal sphincter?
Pectinate line
Where splanchnopleure meets somatopleure
This is the site of the cloacal membrane (vestigial)

What are the boundaries of the inguinal triangle?
- Lateral edge of the rectus
- Inferior epigastric artery
- Inguinal ligament

List the muscle sof the pelvic diaphragm (2 but kind of 3)
- Levator ani [without puborectalis?]
- Pubococcygeous
- Iliococcygeus
- Ischiococcygeus

As the testes descends, each layer of the body wall except the _____ contributes to the covering of the spermatic cord
As the testes descends, each layer of the body wall except the transversus abdominus contributes to the covering of the spermatic cord

Between which landmarks is the largest diameter of the birth canal?
Transverse dimension of the pelvic brim
Above the pectinate line:
- Type of muscle:
- Innervation:
- Venous drainage:
- Lymph drainage:
Below the pectinate line:
- Type of muscle:
- Innervation:
- Venous drainage:
- Lymph drainage:
Above the pectinate line: endoderm
- Type of muscle: Smooth
- Innervation: Visceral, autonomic
- Pelvic splanchnics
- Venous drainage: Portal system
- Lymph drainage: With internal iliac vessels
Below the pectinate line: ectoderm
- Type of muscle: Skeletal (striated)
- Innervation: General sensory, somatomotor
- Pudendal nerve
- Venous drainage: Iliac/caval system
- Lymph drainage: Superficial inguinal nodes
A women with chronic, severe cramping of the uterus can get relief from severing or anesthetizing which of the following?
A. Pudendal nerve
B. Nerve roots in the sacral canal
C. Superior hypogastric plexus
D. Pelvic splanchnic nerves
C. Superior hypogastric plexus (aka Lumbar Splanchnics)
Lumbar splanchnics provide sensory innervation to the uterine body and fundus and internal sphincter

The transversalis fasciacontributes to the[layer of covering of the spermatic cord]
The transversalis fasciacontributes to theinternal spermatic fascia (and deep inguinal ring)

[direct/indirect] hernias are lateral to the inferior epigastric artery
Indirect hernias are lateral to the inferior epigastric artery

Which part of the pelvis marks the course of the pudendal nerve?
Ischial spine
Which part of the urethra constitutes the membranous urethra?
The part that passes through the UG diaphragm

A needle through the vagina can most easily sample peritoneal fluid from which location?
Rectouterine pouch

Which of the following is NOT part of the pelvic diaphragm?
- Iliococcygeus
- Pubococcygeus
- Coccygeus
- Obturator internus
- Puborectalis
d. Obturator internus
All others are part of the pelvic diaphragm
Where in the anal canal does the epithelium change from GI to skin?
Which type of epithelium is found in each place?
White line
GI = simple columnar
Skin = stratified squamous

Infection in which of the following locations might impair function of the external anal sphincter by interrupting its nerve supply?
A. Superficial perineal pouch
B. Ischioanal fossa
C. Deep perineal pouch
D. Rectouterine pouch
E. Pelvic peritoneal cavity
B. Ischioanal fossa
Inferior rectal branches of the pudendal nerve must traverse the ischioanal fosa to reach the external anal sphincter
- Rectouterine pouch and pelvic cavity have nothing to do with rectal innervation*
- Perineal pouch relates to the UG diaphragm*
How does fluid in the superficial perineal pouch drain?
Must flow in between superficial (scarpa’s) and deep investing fascia