2. Neural Tissue Flashcards
(62 cards)
In the body superior means up and inferior means down, but in the brain what terms refer to up and down?
- dorsal = up or top like a dolphins fin on the top
- ventral = down

In the body ventral means up and dorsal means back, but in the brain what terms refer to front and back?
- front = rostral
- back = caudal

On the brain there are areas that sink in, similar to the crypts in the GI and then there are area that bulge out, as per the image below. What are the 2 terms used to describe these anatomical landmarks?

- gyrus = look like bumps
- sulcus** = brain **Sinks in (depressions) resembling the crypts

What is the the theory that describe the below:
- nervous system is made up of discrete individual cell
- All cells are individual BUT mutually rely on one another
neuronal doctrine theory
What is the cerebral cortex?
1 - outermost region of the cerebrum
2 - inner most layer of the cerebrum
3 - attached to the top of the brain stem
4 - located at the back of the brain, referred to as the mini brain
1 - outermost region of the cerebrum
- made up of neuronal cell bodies**, so appears **grey

What is a Brodmann area?
- boundaries of the brain
- determined by histological architecture and function, essentially the tissue and cell type
How many Brodmann areas are there in the brain?
- 52

Why are Brodmann areas of the brain important?
- they generally posses specific functions
Brodmann area 17 is located on either side of the calcarine sulcus, on the medial surface of the occipital lobe. What is this area also commonly referred to as and what is its function?
- primary somatosensory cortex
- primary visual cortex
- primary motor cortex
- primary auditory cortex
- primary visual cortex

Brodmann area 4 is located in the posterior portion of the frontal lobe. What is this more commonly known as and what is its function?
- primary somatosensory cortex
- primary visual cortex
- primary motor cortex
- primary auditory cortex
-
primary motor cortex
- heavily involved in motor function

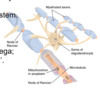
The head of a neuron is called the cell body. It has appendages that are designed to receive communications from other cells, what are these called?
- dendrites
- axon hillock
- axon terminal
- oligodendrocyte
- dendrites

The head of a neuron is called the cell body. What is the name where the cell body attaches to the axon and what is its role?
- dendrites
- axon hillock
- axon terminal
- oligodendrocyte
- axon hillock
- initiates an action potential

What is the end of the axon furthest away from the cell body called?
- dendrites
- axon hillock
- axon terminal
- oligodendrocyte
- axon terminals
- synapses with other neurons or tissues

Axon collaterals can be found along the axon, between the cell body and the axon terminals. What is the function of these?
- provide modulation of the cell firing
- wrap around the axon body ensuring good conduction
- connect the axon hillock the the axon
- provide modulation of the cell firing

How do we know if a neuronal cell is a white matter neuron?
- if it is encapsulated in myelin sheath
- myelin is a white protein
In the CNS which cell is responsible for myelinating neurons?
- microglia
- schwann cell
- oligodendrocytes
- astrocytes
- oligodendrocytes
- able to do this for multiple neurons

In the PNS which cell is responsible for myelinating neurons?
- microglia
- schwann cell
- oligodendrocytes
- astrocytes
- Schwann cells
- one neuronal cell per schwann cell
Each neuron is a separate entity with a limiting cell membrane, like all other cells in the body. Why is this important?
- confirms neuronal doctrine
- all cells are individual but dependent on one another
Morphology refers to the size and shape of neurons. How many different types of neuronal cells are there?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 4

Morphology refers to the size and shape of neurons. There are 4 different types of neuronal cells. What are they?
- unipolar, bipolar, pseudo-unipolar, facet-polar
- membrane polar, bipolar, pseudo-unipolar, multipolar
- synaptic polar, bipolar, pseudo-unipolar, multipolar
- unipolar, bipolar, pseudo-unipolar, multipolar
- unipolar, bipolar, pseudo-unipolar, multipolar

What are dendrites in neuronal cells?
- part of neuron responsible for immunity
- part of neuron that facilitates conduction
- protoplasmic appendages of cell membrane
- part of nucleus of neuronal cells
- protoplasmic appendages of cell membrane
- designed to facilitate communication between cells
In some cells, what proportion of the neurones can consist of dendrites?
- 10%
- 30%
- 60%
- 95%
- up to 95%
In a neuronal cell, what is the soma?
- neuronal cell body containing nucleus
- appendages of neuronal cell
- connection between neuronal cell and axon
- connection between post synapse and pre synapse
- neuronal cell body containing nucleus
- metabolic activity and protein synthesis occur here

Neuronal transmitters are produced where in the neuronal cell, before being stored in the synaptic vesicles?
- soma (cell body)
- nucleus
- axon hillock
- axon terminal (pre synapse)
- soma