1st week 3 (second topic, third lecture) Flashcards
The zebrafish: Danio rerio advantages
- similarity with humans, more precisly?
- another charachteristics that is more than in flies or worms?
It’s vertebrate!
Behaviour
Name advantages:

Orger & de Polavieja (2017)

When is it possible to see zebrafish gene circuity developing, even gene expression? Why
Transparent embryo
Zebrafish takes X hours to develop from egg to an adult.
Lives X months.
72h
3 months
Is live brain imaging possible with zebrafish?
yes
mutation in cntnap2a is related to what disease?
Causes what in zebrafish?
Autism
Hyperactivity (night time activity)
Hoffman et al. 2016
Biran & Levkowitz (2016) tested psychoactive compunds and found a suppressor for hyperactivism (vaused by cntnap2a).
What is the suppressor?
Estrogenic phenotypic suppressors were able to suppress hyperactivity.
Mus musculus?
Is a … with social ….
x% of it’s genes are homologus to human
Mouse
Is a mammal with social behaviour.
90%
loss of xxxxx pathway
degenerative loss of xxxx neurons in the SNpc
(xxx xxxx xxx compacta)
loss of nigrostriatal pathway
degenerative loss of dopaminergic neurons in the SNpc
(substantia nigra pars compacta)
What condition typically follows:
What is the effect of dopamine not reaching striatum?
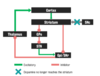
D1 and D2 affected, Gpi/SNr not inhibited, messages don’t get to thalamus
Kravitz et al 2010
Studied voluntary movement what did they do to adenovirus?
What does that do?
Modified with channelrhopsin ChR2-YFP
Channelropsin is a protein that can be activated by light pulse –> over activation of a neuron.
What is optogenic activation?
Switching neurons on/off by light (for example D1 or D2 neurons in striatum)
What does tyrosine hydrolaxe do?
Enzyme leading to dopamine production
What does 6-OHDA do?
What can it be used for?
It is antagonist of dopamine.
Used to create Parkinson’s model in mice.
What happens in the basal ganglia of mice that are given 6-OHDA and ChR2 affecting either D1 or D2 pathway (with light cables into the brain)
What can be shown about D1 and D2 pathways
6-OHDA (dopamin antagonist) blocked the effect of dopamin –> PD model
ChR2 possible to activate with laser (light pulse). When D1 activated mice ran.
When D2 activated mice stopped.
Shows that D1 activation can overcome Parkinsonian phenotype.
Friend&Kravits 2014


