19 - Hand and Wrist Flashcards
Label the following diagram

Some Lovers Try Positions That They Cannot Handle

Label the following diagram of the posterior forearm.


Label the following diagram of the wrist.


Label the following diagram of the muscles of the hand.


What are the muscles of the posterior forearm, how are they organised and what are they innervated by?
- Split into superficial and deep separated by fascia
- Innervated by radial nerve
- Rules of 3
- Superficial: brachioradialis, ECRL, ECRB, ED, EDM, ECU, Anconeus
- Deep: Supinator, APL, EPB, EPL, EI

What muscles originate from the common extensor origin?
- ECRB
- ED
- ECU
- EDM
- Supinator
At lateral epicondyle

What is the origin, insertion, action and innervation of the superficial muscles of the posterior forearm?
- All innervated by the radial nerve
- ECRB and Supinator: innervated by deep brranch of radial nerve as origin distal to the branching of radial nerve into superficial and deep
- ED, EDM and ECU: posterior interosseous branch of radial nerve

How do you test the function of the extensor digitorun?
Forearm pronated and extend fingers against resistance
Why can’t the middle or ring finger be fully extended if the other fingers are flexed? Why can the IP joints still fully flex but the MCP joints can’t?
- Juncturae Tendinum: fibrous bands on the dorsum of the hand linking the extensor digitorum tendons
- Index and little finger can fully extend as they have a second extensor each
- Extension of IP achieved by lumbricals not ED

When does the radial nerve become the posterior interosseous branch of the radial nerve?
When the deep branch of the radial nerve passes between two heads of supinator and enters posterior forearm

What are the origins, insertions, innervations and actions of the deep muscles of the posterior forearm?
All innervated by radial nerve
- Deep branch of radial nerve: supinator
- Posterior interosseous: APL, EPL, EPB, EI

What are the sensory and motor functions of the radial nerve?
Sensory: skin of posterior arm, lower lateral arm, posterior forearm, dorsal surface of radial hand, dorsal surface of lateral three and a half digits
Motor: triceps brachii and extensors of forearm

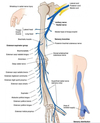
What is the anatomical course of the radial nerve?
- Arises in axilla posterior to the axillary artery
- In base of triangular interval it gives off branch to long and lateral head of triceps and posterior cutaneous nerve of arm
- Enters radial spiral groove and passes laterally across humerus to give off branch to medial triceps and two more cutaneous branches (inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm and posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm)
- Emerges laterally from radial groove and gives branch to brachioradialis, ECRL and sometimes brachialis
- Pierces lateral fascia and travels anterior to lateral epicondyle of humerus through cubital fossa where it divides into deep (motor) and superficial (sensory) branch
- Deep branch innervates ECRB and exits cubital fossa posterior to two heads of supinator which it innervates
- Becomes posterior interosseous nerve after supinator and innervates rest of the posterior muscles
What does the wrist joint consist of, what type of joint is it and what movements are possible?
- Distal radius, triangular fibrocartilage complex, scaphoid and lunatte NOT ulnar
- Ellipsoid
- Flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, circumduction

What ligaments stabilise the wrist joint?
- Dorsal and palmar radiocarpal ligaments (ensure hand follows radius during pronation and supination)
- Ulnar and radial collateral ligaements

What muscles cause each movement at the wrist and what is the innervation of the wrist?
Flexion: FCU, FCR, PL (long flexors like FDS assist)
Extension: ECU, ECRB, ECRL (long extensors assist)
Adduction: FCU, ECU
Abduction: ECRB, ECRL, FCR
Using hilton’s law the wrist nerve supply is median, ulnar and radial

How are the carpal bones arranged?
Into proximal and distal rows, SLTP in proximal

What is the significance of the hook of Hamate?
- On palmar surface
- Forms ulnar border of carpal tunnel
- Forms radial border of Guyon’s canal
- Flexor retinaculum and FCU attach here

Label the carpals on the x-ray.


What is the blood supply like to the scaphoid and why is this relevant?
- Dorsal carpal branch of radial artery that enters dorsal distal scaphoid and supplies scaphoid by retrograde
- High rate of non-union or AV necrosis if fractured

What carpal does each of the metacarpals articulate with?
1: trapezium
2: trapezoid
3: capitate
4 and 5: hamate

What movements can occur at the fingers and thumb?
- Circumduction
- Radial abduction in coronal plane
- Palmar abduction in sagittal plane

What are the movements of the fingers?

What are the different groups of muscles in the hand?
- Intrinsic: thenar, hypothenar, adductor and central compartment
- Extrinsic: ED, FDS, FDP