17. Microvascular Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Flashcards
Site of diabetes microvascular complications
- Retinal arteries (Diabetic retinopathy)
- Glomerular arterioles (nephropathy)
- Vasa vasorum (blood vessels that supply the nerves, causes neuropathy)
Factors effecting the risk of microvascular complications
- Severity of hyperglycaemia
- Hypertension
- Genetic- Some people are predisposed to worsening microvascular problems
- Hyperglycaemic memory- Poor diabetes control, even for a short period of time, will increase risk of complications compared to an individual who has been well controlled throughout
- Tissue damage
Mechanisms of Glucose Damage


Main cause of visual loss in people with diabetes and blindness in people of working age
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
Features of a normal retina
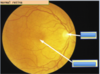
You look at an eye through a fundoscope:
- The optic disc is at the nasal part of the eye and the macula is more lateral
- The vessles come out into the back of the eye and have a very regular arrangement

FOUR different types of diabetic retinopathy
- Background diabetic retinopathy
- Pro-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- proliferative retinopathy
- Maculopathy
Features of background diabetic retinopathy
- Hard exudates begin to appear as cheesy yellow spaces in the retina
- These are caused by the leakage of lipid contents
- Microaneurysms begin to appear- can rupture causing blot haemorrhages

Features of pre-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy

- Cotton wool spots called SOFT EXUDATES- these are caused by retinal ischaemia
- Shows several pre-retinal haemorrhages

Features of proliferative retinopathy
- This involves the formation of new vessels- can be on the optic disc or elsewhere in the retina
- The new vessles form as a result of retinal ischaemia
- If vessels form in the region of the macula, there can be colour vision problems
- New vessels are more fragile

Features of maculopathy
- You get hard exudates near the MACULA (same as background but near the macula)
- This can threaten direct vision

Treatment of background DR
- Improve control of blood glucose
- Inform patient of warning signs
Treatment of Pre-Proliferative DR
- Cotton wool spots indicate ischaemia- If left untreated will lead to proliferative retinopathy
- Treatment via pan-retinal photocoagulation- laser the retina and prevent the vessels from bleeding
Treatment of Proliferative DR
- Also need pan-retinal photocoagulation
Treatment of maculopathy
- The effected area is concentrated around the macula
- This means that you only need a GRID of photocoagulation in the affected area
- NOT pan-retinal photocoagulation
Key features of diabetic nephropathy
- Hypertension
- Progressively increasing proteinurea
- Progressively deteriorating kidney function
- Histological changes
- Increased prevalence of cardiovascular events
Glomerular changes resulting from nephropathy
- Mesangial expansion
- Basement membrane thickening
-
Glomerulosclerosis
- The glomerulus becomes less flexible and harder
- Absorption of nutrients can change so you get more pressure through the kidneys
- Leads to alteration of blood pressure control
- There is overproduction of matrix
- These effects contribute to sclerosis and secondary effects on the tubointerstitium
Cause of hitological change in nephropathy
There are several stimuli including the effect of prolonged exposure to high glucose/glycosylated proteins
The increased pressure within the glomerular capillaries associated with DM can also stimulate matrix expansion
Angiotensin (which is produced in spite of systemic supression) stimulates constriction of the efferent arterioles, increasing transglomerular capillary pressure and contributing to sclerosis
Epidemiology of diabetic nephropathy
- T1DM= 20-40% after 30-40 years
- T2DM= equivalent
Key clinical features of diabetic nephropathy
- Progressive proteinurea
- Increased blood pressure
- Deranged renal function
Normal, Microalbuminuric, Assymptomatic and Nephrotic ranges of proteinurea
Measured using urine dipsticks:
Normal: <30mg/24hrs
Microalbuminuric: 30-300mg/24hrs
Assymptomatic: 300-3000mg/24hrs
Nephrotic: >3000mg/24hrs
As urinary albumin increases, serum becomes less osmotic= oedematus
Strategies for diabetic nephropathy intervention
- Diabetic control- lower the HbA1c, lower the risk of microvascular complications
- Blood pressure control- will slow deteriorating kidney function
- Inhibition of renin-angiotensin system- ACE inhibitors
- Stopping smoking
Types of diabetic neuropathy
- Peripheral polyneuropathy
- Mononeuropathy
- Mononeuritis multiplex
- Radiculopathy
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Diabetic amyotrophy
At Parties, Marilyn Manson Regularly Abuses Drugs
All result from blockade of the VASA VASORUM
Features of peripheral neuropathy
Loss of sensation in the hands and feet
Most likely to occur in:
- Tall patients
- Patients with poor glucose control
testes using monofilament examination
Also leads to loss of ankle jerks and loss of vibration sense


