140 Antiarrhythmic Drug Therapy Flashcards
Mechanisms/Classifications of Bradyarrhythmias
- Diminished automaticity
- Block

Mechanisms of Tachyarrhythmias
- Enhanced automaticity
- Increased phase 4 depol
- Make threshold more negative
- Renentry
- Triggered activity
- Early after depols
- •During Phase 2, 3 of AP
- Early after depols
- Ca2+ current Dependent
- Occurs in setting of prolonged APD (prolonged QT interval)
- Delayed afterdepols
- During Phase 4 of AP
- Delayed afterdepols
Associated with high Ca2+ (eg digoxin toxicity)

Supraventricular tachyarrhythmias list
oSinus Tachycardia
oAtrial Premature Beats
oParoxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
(aka Supraventricular Tachycardia aka SVT)
oAtrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)
oAtrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia (AVRT)
oEctopic Atrial Tachycardia
oAtrial Flutter
oAtrial Fibrillation
oMultifocal Atrial Tachycardia

Ventricular tachyarrhythmias list

AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)

Atrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia (AVRT)

Atrial Flutter

Atrial Fibrillation

Ventricular Tachycardia

Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia

Ventricular Fibrillation

Treating Enhanced Automaticity (theory)
- •Make maximum diastolic potential more negative
- •Reduce slope of phase 4 depolarization
- •Make the threshold potential more positive
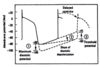
Treating Reentry (theory)
Disrupt the Balance
- e.g. slow the “slow conduction” even more so it blocks
- supress premature beats which often set up slow conduction

Treating Triggered Activity (theory)

Rate Control vs. Rhythm Control in Atrial Fibrillation

Vaughan-Williams Classification

Na+-Channel Blockers Mechanism

Na+-Channel Blockers: Effect on Phase 0
Na+-Channel Blockers: Effect on Action Potential Duration

Procainamide
Class 1A
•Drug-induced Lupus: arthralgia, pleuritis, pericarditis with PO (not clinically available)
•Torsades de Pointes:
N-acetylprocainamide a first pass
metabolite with strong K+ channel
activity
Quinidine
Class 1A
•Additional vagolytic effects
–eg urinary retention, constipation, blurred vision, dry mouth
•Cinchonism: CNS toxicity – tinnitus, psychosis
•Torsades de Pointes: K+ blocking activity
Disopyramide
Class 1A
- Additional stronger vagolytic effects
- Additional negative inotropic effects
•Antimuscarinic: urinary retention, constipation, blurred vision, dry mouth
•Torsades de Pointes: K+ blocking activity
Lidocaine
Class 1B

•CNS Toxicity:
confusion, delerium, grand mal seizures
good for post MI
Mexelitine
Class 1B
•CNS Toxicity:
confusion, delerium, grand mal seizures
Flecainide
Class 1C
- Potent negative inotropic effects
- Propafenone: beta-blocking effects
- Slows conduction (because of potent Na+ blocking)
•Contraindicated in LV systolic dysfunction and heart block
Propafenone
Class 1C
- Potent negative inotropic effects
- Propafenone: beta-blocking effects
- Slows conduction (because of potent Na+ blocking)
- Contraindicated in LV systolic dysfunction and heart block
β-Blockers Mechanism
Side effects
- Hypotension
- Bradycardia
- Depression, Bronchospasm, Cognitive Impairment, Sexual Dysfunction

Esmolol
Beta blocker, Class 2
- Hypotension
- Bradycardia
- Depression, Bronchospasm, Cognitive Impairment, Sexual Dysfunction
GIven IV
Metoprolol
Beta blocker, Class 2
- Hypotension
- Bradycardia
- Depression, Bronchospasm, Cognitive Impairment, Sexual Dysfunction
GIven PO
Side effect: oClass II (eg Metoprolol) – Depression, Bronchospasm, Cognitive Impairment, Sexual Dysfunction
K+-Channel Blockers Mechanism

Amiodarone

Sotalol
Class 3 antiarrhythmic, K+ blocker
- B-blocking effects
- PO
- •Prolong QT-interval à Torsades de Pointes
- should be avoided in renal failure.
Dofetilide
Class 3 Antiarrhthmic, K+ blocker
- PO
- requires renal dose adjustment
- •Prolong QT-interval à Torsades de Pointes
Ibutilide
Class 3 antiarrhtymic, K+ channel blocker
- IV
- •Prolong QT-interval à Torsades de Pointes
Ca2+-Channel Blockers Mechanism

Verapamil

Diltiazem
Side Effect: oClass IV (eg Diltiazem) – Constipation, Peripheral Edema

Adenosine
non classified antiarrythmic
- Transient Elective Heart Block
- Treatment of AVNRT, AVRT
- – reentrant rhythms that depend on the AV node
- Diagnosis of Supraventricular Tachyarrhythmias
- –gets rid of QRS complexes
- –see underlying Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter

Digoxin
Unclassified antiarrythmic drug

- Narrow Therapeutic Window
- Toxicity: nausea, diarrhea, yellow vision
- Proarrhythmic Effects:
–almost anything
•Treatment of severe toxicity:
anti-digoxin Fab fragments
Side effect: nausea, diarrhea, yellow vision
Tx Disrupting AVNRT, AVRT
- Acute: Adenosine – rapidly acting
- Chronic: Beta Blockers, Calcium Channel Blockers, perhaps Digoxin
Tx AFib, AFlutter: Rate Control
•Beta Blockers (Class II)
–slows conduction through AV node
•Calcium Channel Blockers (Class IV)
–slows conduction through AV node
•Digoxin
–slows conduction through the AV node
Tx AFib, AFlutter: Rhythm Control
•Class Ic Agents: Flecainide, Propafenone
–Probably Interferes with Reentry by slowing conduction
•Class III Agents: Amiodarone, Sotalol, Dofetilide, Ibutilide
–Probably Interferes with Reentry by prolonging repolarization
•Class Ia Agents
–obsolete for this indication
Tx Suppress VT and Symptomatic PVCs
•Class II Agents : beta-blockers
–Can slow conduction in sick tissue
•Class III Agents : Sotalol and Amiodarone
–Interferes with Reentry by prolonging repolarization
•Class Ib Agents
–Interferes with Reentry by slowing conduction
•Class Ia Agents
–almost obsolete for this indication
–Procainamide occasionally used in ischemic VT
–Disopyramide occasionally used in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (negative inotropic effects)
Tx
Suppress VT and Symptomatic PVCs
Special Case: In setting of Myocardial Infarction
•Class II Agents : beta-blockers
–Can slow conduction in sick tissue
- Class III Agent: Amiodarone
- Class Ib Agents
–Interferes with Reentry by slowing conduction
•Class Ia Agents
–almost obsolete for this indication
–Procainamide occasionally used in ischemic VT
–Disopyramide occasionally used in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (negative inotropic effects)
Tx
Suppress VT and Symptomatic PVCs
Special Case: Treatment of Torsades de Pointes
- Magnesium
- Phenytoin
- Isoproterenol
- Overdrive Pacing
- Shock
Pacemaker cells APs (vagus, b-adrenergic, SA node)

Wolff-Parkinson-White
- oWolff-Parkinson-White pattern
- oECG finding only of a delta wave
- oWolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
- oECG finding of a delta wave
- oECG evidence also of arrhythmia using accessory pathway
- oAVRT – orthodromic vs. antidromic
- oYou could also have Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, or even AVNRT
Tx AVRT



